poj3764-The xor-longest Path
Description
In an edge-weighted tree, the xor-length of a path p is defined as the xor sum of the weights of edges on p:
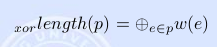 ⊕ is the xor operator.
⊕ is the xor operator.We say a path the xor-longest path if it has the largest xor-length. Given an edge-weighted tree with n nodes, can you find the xor-longest path?
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains an integer n(1<=n<=100000), The following n-1 lines each contains three integers u(0 <= u < n),v(0 <= v < n),w(0 <= w < 2^31), which means there is an edge between node u and v of length w.
Output
For each test case output the xor-length of the xor-longest path.
Sample Input
4 0 1 3 1 2 4 1 3 6
Sample Output
7
Hint
The xor-longest path is 0->1->2, which has length 7 (=3 ⊕ 4)
题意:求树上两点路径的异或和的最大值 用d[x]表示根到x路径上所有边权的异或和,由异或的性质,x到y路径上所有边权的异或和等于d[x] xor d[y],所以就是在d[0]-d[n-1]中找两个数,使得异或之后最大。 把每个整数看作长度为31的01串(数值较小的在前面补0),然后插入到一棵字典树中
每次查找一个数,先尝试沿着与当前位相反的字符指针向下访问,如果没有就访问相同的,这样构造出来的一定是与当前查找的数做xor运算结果最大的。

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> //#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std; const int N=2e5+100; int n,cnt,tot; int last[N],d[N]; struct tree{ int v,nex,w;}t[N*2]; int trie[N*32][2]; void add(int x,int y,int z) { cnt++; t[cnt].v=y; t[cnt].nex=last[x]; last[x]=cnt; t[cnt].w=z; } void dfs(int x,int fa,int dis) { d[x]=dis; for (int i=last[x];i;i=t[i].nex) { if (t[i].v==fa) continue; dfs(t[i].v,x,dis^t[i].w); } } void Insert(int x) { int p=0,now; for (int i=31;i>=0;i--) { now=(x>>i)&1; if (!trie[p][now]) trie[p][now]=++tot; p=trie[p][now]; } } int fund(int x) { int p=0,now,ret=0; for (int i=31;i>=0;i--) { now=!((x>>i)&1); ret<<=1; if (trie[p][now]) { p=trie[p][now]; ret++; } else p=trie[p][!now]; } return ret; } int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { memset(last,0,sizeof(last)); memset(trie,0,sizeof(trie)); cnt=0; tot=0; int x,y,z; for (int i=1;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); add(x,y,z); add(y,x,z); } d[0]=0; dfs(0,-1,0); int ans=0; for (int i=0;i<n;i++) Insert(d[i]); for (int i=0;i<n;i++) ans=max(ans,fund(d[i])); printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }



