Java(30)集合五Set
作者:季沐测试笔记
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/testero/p/15228440.html
博客主页:https://www.cnblogs.com/testero
1.Set集合
1.1Set集合概述和特点
- Set集合的特点
- 元素存取无序
- 没有索引、只能通过迭代器或增强for循环遍历
- 不能存储重复元素
- Set集合的基本使用
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
//添加元素
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("java");
//不包含重复元素的集合
set.add("world");
//遍历
for(String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
1.2哈希值
-
哈希值简介
是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数字算出来的int类型的数值
-
如何获取哈希值
Object类中的public int hashCode():返回对象的哈希码值
-
哈希值的特点
- 同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
- 默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不同的。而重写hashCode()方法,可以实现让不同对象的哈希值相同
-
获取哈希值的代码
- 学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } // @Override // public int hashCode() { // return 0; // } }- 测试类
public class HashDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("张三",30); //同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的 System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); //1510467688 System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); //1510467688 System.out.println("--------"); Student s2 = new Student("张三",30); //默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不相同的 //通过方法重写,可以实现不同对象的哈希值是相同的 System.out.println(s2.hashCode()); //1995265320 System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("hello".hashCode()); //99162322 System.out.println("world".hashCode()); //113318802 System.out.println("java".hashCode()); //3254818 System.out.println("world".hashCode()); //113318802 System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("重地".hashCode()); //1179395 System.out.println("通话".hashCode()); //1179395 } }
1.3HashSet集合概述和特点
-
HashSet集合的特点
- 底层数据结构是哈希表
- 对集合的迭代顺序不作任何保证,也就是说不保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
- 没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
- 由于是Set集合,所以是不包含重复元素的集合
-
HashSet集合的基本使用
public class HashSetDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>(); //添加元素 hs.add("hello"); hs.add("world"); hs.add("java"); hs.add("world"); //遍历 for(String s : hs) { System.out.println(s); } } }
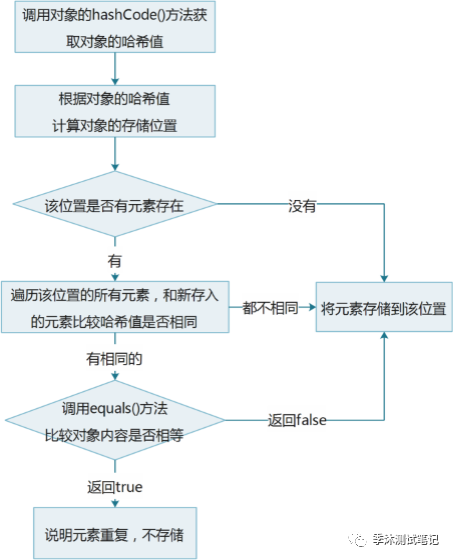
1.4HashSet集合保证元素唯一性源码分析
-
HashSet集合保证元素唯一性的原理
1.根据对象的哈希值计算存储位置
如果当前位置没有元素则直接存入
如果当前位置有元素存在,则进入第二步
2.当前元素的元素和已经存在的元素比较哈希值
如果哈希值不同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果哈希值相同,则进入第三步
3.通过equals()方法比较两个元素的内容
如果内容不相同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果内容相同,则不存储当前元素
-
HashSet集合保证元素唯一性的图解
1.5HashSet集合存储学生对象并遍历
-
案例需求
- 创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
- 要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
-
代码实现
-
学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student student = (Student) o; if (age != student.age) return false; return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null; } @Override public int hashCode() { int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0; result = 31 * result + age; return result; } } -
测试类
public class HashSetDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建HashSet集合对象 HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>(); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 30); Student s2 = new Student("李四", 35); Student s3 = new Student("王五", 33); Student s4 = new Student("王五", 33); //把学生添加到集合 hs.add(s1); hs.add(s2); hs.add(s3); hs.add(s4); //遍历集合(增强for) for (Student s : hs) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); } } }
-
1.6LinkedHashSet集合概述和特点
-
LinkedHashSet集合特点
- 哈希表和链表实现的Set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序
- 由链表保证元素有序,也就是说元素的存储和取出顺序是一致的
- 由哈希表保证元素唯一,也就是说没有重复的元素
-
LinkedHashSet集合基本使用
public class LinkedHashSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); //添加元素 linkedHashSet.add("hello"); linkedHashSet.add("world"); linkedHashSet.add("java"); linkedHashSet.add("world"); //遍历集合 for(String s : linkedHashSet) { System.out.println(s); } } }
2.Set集合排序
2.1TreeSet集合概述和特点
-
TreeSet集合概述
- 元素有序,可以按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
- TreeSet():根据其元素的自然排序进行排序
- TreeSet(Comparator comparator) :根据指定的比较器进行排序
- 没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
- 由于是Set集合,所以不包含重复元素的集合
- 元素有序,可以按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
-
TreeSet集合基本使用
public class TreeSetDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>(); //添加元素 ts.add(10); ts.add(40); ts.add(30); ts.add(50); ts.add(20); ts.add(30); //遍历集合 for(Integer i : ts) { System.out.println(i); } } }
2.2自然排序Comparable的使用
-
案例需求
- 存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用无参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
-
实现步骤
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,无参构造方法使用的是自然排序对元素进行排序的
- 自然排序,就是让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(T o)方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
-
代码实现
-
学生类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public int compareTo(Student s) { // return 0; // return 1; // return -1; //按照年龄从小到大排序 int num = this.age - s.age; // int num = s.age - this.age; //年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序 int num2 = num==0?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num; return num2; } } -
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29); Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28); Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30); Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33); Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33); Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33); //把学生添加到集合 ts.add(s1); ts.add(s2); ts.add(s3); ts.add(s4); ts.add(s5); ts.add(s6); //遍历集合 for (Student s : ts) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); } } }
-
2.3比较器排序Comparator的使用
-
案例需求
- 存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用带参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
-
实现步骤
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,带参构造方法使用的是比较器排序对元素进行排序的
- 比较器排序,就是让集合构造方法接收Comparator的实现类对象,重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
-
代码实现
-
学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } -
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) { //this.age - s.age //s1,s2 int num = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge(); int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num; return num2; } }); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29); Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28); Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30); Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33); Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33); Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33); //把学生添加到集合 ts.add(s1); ts.add(s2); ts.add(s3); ts.add(s4); ts.add(s5); ts.add(s6); //遍历集合 for (Student s : ts) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); } } }
-
2.4成绩排序案例
-
案例需求
- 用TreeSet集合存储多个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩),并遍历该集合
- 要求:按照总分从高到低出现
-
代码实现
-
学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int chinese; private int math; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int chinese, int math) { this.name = name; this.chinese = chinese; this.math = math; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getChinese() { return chinese; } public void setChinese(int chinese) { this.chinese = chinese; } public int getMath() { return math; } public void setMath(int math) { this.math = math; } public int getSum() { return this.chinese + this.math; } } -
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) { // int num = (s2.getChinese()+s2.getMath())-(s1.getChinese()+s1.getMath()); //主要条件 int num = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum(); //次要条件 int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese() : num; int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num2; return num3; } }); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 98, 100); Student s2 = new Student("张曼玉", 95, 95); Student s3 = new Student("王祖贤", 100, 93); Student s4 = new Student("柳岩", 100, 97); Student s5 = new Student("风清扬", 98, 98); Student s6 = new Student("左冷禅", 97, 99); Student s7 = new Student("赵云", 97, 99); //把学生对象添加到集合 ts.add(s1); ts.add(s2); ts.add(s3); ts.add(s4); ts.add(s5); ts.add(s6); ts.add(s7); //遍历集合 for (Student s : ts) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getChinese() + "," + s.getMath() + "," + s.getSum()); } } }
-
2.5不重复的随机数案例
-
案例需求
- 编写一个程序,获取10个1-20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复,并在控制台输出
-
代码实现
public class SetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建Set集合对象 // Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<Integer>(); //创建随机数对象 Random r = new Random(); //判断集合的长度是不是小于10 while (set.size()<10) { //产生一个随机数,添加到集合 int number = r.nextInt(20) + 1; set.add(number); } //遍历集合 for(Integer i : set) { System.out.println(i); } } }

