盘点总结
一、盘点列表逻辑梳理
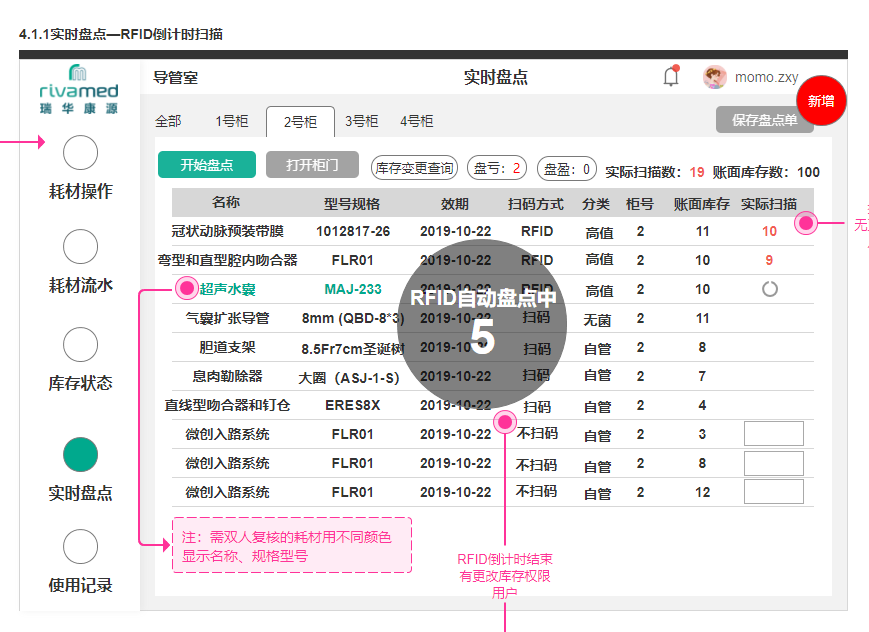
1、RFID耗材逻辑处理
private List<FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo> judgeRfidConsumables(FhvcInventoryDto dto) { // 耗材柜组在柜耗材的列表,根据cstId和deviceId区分 List<FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo> inventoryConsumablesVos = fhvcInventoryService.inventoryCurrentConsumables( dto.getDeviceId(), FhvcInventory.STATUS_TWOIN, dto.getThingId(), Cst.SCAN_RFID); // 扫描到的epc List<String> epcs = dto.getScanEpcDetails().stream().map(s -> s.getEpc()).collect(Collectors.toList()); dto.setEpcs(epcs); List<String> noralEpcs = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> addEpcs = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> reduceEpcs = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> errorEpcs = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> rightEpcs = new ArrayList<>(); differentEpcs(dto, epcs, addEpcs, reduceEpcs, errorEpcs, rightEpcs); if (rightEpcs != null && !rightEpcs.isEmpty()) { List<FhvcInventory> fhvcInventories = corresDevice(rightEpcs, dto); inventoryConsumablesVos = judgeNormalEpc(inventoryConsumablesVos, fhvcInventories, noralEpcs); } setMoreAndLittileEpcs(dto, addEpcs, rightEpcs, noralEpcs, reduceEpcs); return inventoryConsumablesVos; }
1)先根据deviceId和thingId查询出在柜的耗材基础信息:
List<FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo> inventoryConsumablesVos = fhvcInventoryService.inventoryCurrentConsumables(
dto.getDeviceId(),FhvcInventory.STATUS_TWOIN, dto.getThingId(), Cst.SCAN_RFID);
2)根据传进来RFID扫描到的EPC求出正确的(库存里有的)和错误的(库存里不存在)EPC
List<String> allEpcs=fhvcInventoryService.allEpcs(); //扫描到的epc和全部epc求差集就是错误的epc errorEpcs.addAll((List<String>) CollectionUtils.subtract(epcs, allEpcs)); //扫描到epc与库里有的epc求交集就是正常的epc rightEpcs.addAll((List<String>) CollectionUtils.intersection(epcs, allEpcs)); dto.setErrorEpcs(errorEpcs);
3)根据正确的EPC查询出库存信息。并求出盘盈的EPC和正常在柜子的EPC
//查询出柜子本应所在柜子和司机所在柜子,用isSameDevice,如果一致为true否则为false
private List<FhvcInventory> corresDevice(List<String> rightEpcs, FhvcInventoryDto dto) { List<FhvcInventory> fhvcInventories=fhvcInventoryService.findFhvcInventoryByEpcs(rightEpcs); // 把扫描的epc的deviceId和详情对应上 for (FhvcInventory fhvcInventory : fhvcInventories) { for (ScanEpcDetail scanEpcDetail : dto.getScanEpcDetails()) { if (scanEpcDetail.getEpc().equals(fhvcInventory.getEpc())) { if (scanEpcDetail.getDeviceId().equals(fhvcInventory.getDeviceId())) { fhvcInventory.setIsSameDevice(true); }else { fhvcInventory.setIsSameDevice(false); } fhvcInventory.setDeviceId(scanEpcDetail.getDeviceId()); } } } return fhvcInventories; }
/** * 方法名: judgeNormalEpc * 方法功能描述: 比对出正常epc有多少,每个列表中盘盈的epc,set到对应的列表后 * @param: * @return: */ private List<FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo> judgeNormalEpc(List<FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo> inventoryConsumablesVos, List<FhvcInventory> fhvcInventories, List<String> noralEpcs) { // 对比出正常的epc for (FhvcInventoryConsumablesVo inventoryConsumablesVo : inventoryConsumablesVos) { List<String> addEpcs1=new ArrayList<String>(); Integer num=0; for (FhvcInventory fhvcInventory : fhvcInventories) { if (inventoryConsumablesVo.getCstId().equals(fhvcInventory.getCstId()) && inventoryConsumablesVo.getDeviceId().equals(fhvcInventory.getDeviceId()) && fhvcInventory.getStatus().equals(FhvcInventory.STATUS_TWOIN) && fhvcInventory.getIsSameDevice()) { // 如果扫描到的cstId,和扫描的柜子并且为在库状态即为正常耗材,否则为盘盈耗材 num=num+1; inventoryConsumablesVo.setScanCount(num); noralEpcs.add(fhvcInventory.getEpc()); }else if (inventoryConsumablesVo.getCstId().equals(fhvcInventory.getCstId()) && inventoryConsumablesVo.getDeviceId().equals(fhvcInventory.getDeviceId())) { num=num+1; inventoryConsumablesVo.setScanCount(num); addEpcs1.add(fhvcInventory.getEpc()); } } // 每个列表的实际扫描数量 inventoryConsumablesVo.setScanCount(num); // 每个列表对应的盘盈的epcs inventoryConsumablesVo.setAddEpcs(addEpcs1); } return inventoryConsumablesVos; }
4)计算出总体盘盈盘亏的EPC
/** * 方法名: setMoreAndLittileEpcs * 方法功能描述: 计算出总体盘盈盘亏的epc推送到安卓端 * @param: * @return: */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void setMoreAndLittileEpcs(FhvcInventoryDto dto, List<String> addEpcs, List<String> rightEpcs, List<String> noralEpcs, List<String> reduceEpcs) { // 找出盘盈的epc addEpcs = (List<String>) CollectionUtils.subtract(rightEpcs, noralEpcs); // 找出盘亏的epc List<String> inEpcs = fhvcInventoryService.findEpcs(dto.getDeviceId(), FhvcInventory.STATUS_TWOIN, dto.getThingId(), Cst.SCAN_RFID); // 扫描到的正常耗材与全部在库耗材做差集即为未扫描到的即为盘亏 reduceEpcs = (List<String>) CollectionUtils.subtract(inEpcs, noralEpcs); // 即盘盈又盘亏的epc,不进行显示 List<String> commonEpcs = (List<String>) CollectionUtils.intersection(addEpcs, reduceEpcs); addEpcs.removeAll(commonEpcs); reduceEpcs.removeAll(commonEpcs); dto.setAddEpcs(addEpcs); dto.setReduceEpcs(reduceEpcs); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号