[Java] SpringMVC工作原理之二:HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter
一、HandlerMapping
作用是根据当前请求的找到对应的 Handler,并将 Handler(执行程序)与一堆 HandlerInterceptor(拦截器)封装到 HandlerExecutionChain 对象中。在 HandlerMapping 接口的内部只有一个方法,如下:
- HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request);
HandlerMapping 是由 DispatcherServlet 调用,DispatcherServlet 会从容器中取出所有 HandlerMapping 实例并遍历,让 HandlerMapping 实例根据自己实现类的方式去尝试查找 Handler,而 HandlerMapping 具体有哪些实现类下面就会详细分析。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 这些 HandlerMapping 在容器初始化时创建,在 initHandlerMappings 时放入集合中 for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
另外上面说到的 Handler 有可能是一个 HandlerMethod(封装了 Controller 中的方法)对象,也有可能是一个 Controller 对象、 HttpRequestHandler 对象或 Servlet 对象,而这个 Handler 具体是什么对象,也是与所使用的 HandlerMapping 实现类有关。如下图所示,可以看到 HandlerMapping 实现类有两个分支,分别继承自 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping(得到 HandlerMethod)和 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping(得到 HttpRequestHandler、Controller 或 Servlet),它们又统一继承于 AbstractHandlerMapping。

先来看一下 AbstractHandlerMapping,它实现了 HandlerMapping 接口中的 getHandler() 方法,源码如下所示
@Override public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据请求获取执行程序,具体的获取方式由子类决定,getHandlerInternal() 是抽象方法 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } // 将 Handler 与一堆拦截器包装到 HandlerExecutionChain 对象中 return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); }
可以看到在这个方法中又调用了 getHandlerInternal() 方法获取到了 Handler 对象,而 Handler 对象具体内容是由它的子类去定义的。下面就来一看下 AbstractHandlerMapping 的两个分支子类
1 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型实际就是一个 Controller 类,所以一个 Controller 只能对应一个请求(或者像 Struts2 那样定位到方法,使同一个业务的方法放在同一个类里),源码如下所示
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据当前请求获取“查找路径” String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 根据路径获取 Handler(即Controller),先尝试直接匹配,再尝试模式匹配 Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request); if (handler == null) { // We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to // expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well. Object rawHandler = null; if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) { rawHandler = getRootHandler(); } if (rawHandler == null) { rawHandler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (rawHandler != null) { // Bean name or resolved handler? if (rawHandler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) rawHandler; rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(rawHandler, request); handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null); } } return handler; }
1.1 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 实现类及使用

1) ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping:根据类名访问 Controller。
<!-- 注册 HandlerMapping --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping" /> <!-- 注册 Handler --> <bean class="com.controller.TestController" />
2) ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping:根据 Bean 名访问 Controller,与 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping 类似,但是bean名称不用遵循URL公约。
<!-- 注册 HandlerMapping --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping" /> <!-- 注册 Handler --> <bean id="test" class="com.controller.TestController" />
3) BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:利用 BeanName 来作为 URL 使用。
<!-- 注册 HandlerMapping --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping" /> <!-- 注册 Handler --> <bean id="/test.do" class="com.controller.TestController" />
4) SimpleUrlHandlerMapping:可以将 URL 与处理器的定义分离,还可以对 URL 进行统一的映射管理。
<!-- 注册 HandlerMapping --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <props> <prop key="/test.do">testController</prop> <prop key="/hello.do">testController</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- 注册 Handler --> <bean id="testController" class="com.controller.TestController" />
1.2 Controller 类
使用 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 的实现类时,需要让控制层的类实现 Controller 接口(一般继承 AbstractController 即可),另外还有一些已经实现了的 Controller 类,如下图所示。但是不论是自己实现 Controller 接口还是使用系统已经实现的类,都只能处理一个请求(除了 MultiActionController 可以通过参数的方式让一个类可以处理多个请求)。
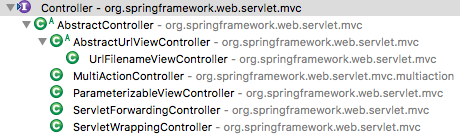
另外下面所有的 Controller 均采用 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 方式的。
1) UrlFilenameViewController:用于跳转界面,控制器根据请求的URL直接解析出视图名,省去了自己实现 Ccntroller 跳转页面。
<bean id="indexController" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.UrlFilenameViewController" />
2) ParameterizableViewController:同样用于界面跳转,控制器根据配置的参数来跳转界面,使用方式如下
<bean id="indexController" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.ParameterizableViewController"> <property name="viewName" value="/index.jsp" /> </bean>
3) ServletForwardingController:将请求转发到 Servlet,使用方式如下
<bean id="indexController" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.ServletForwardingController"> <property name="servletName" value="indexServlet" /> </bean>
另外还要在 web.xml 中配置要转发到的 Servlet
<servlet> <servlet-name>indexServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.servlet.ServletForwarding</servlet-class> </servlet>
4) ServletWrappingController:将某个 Servlet 包装为 Controller,所有到 ServletWrappingController 的请求实际上是由它内部所包装的这个 Servlet 实例来处理的,这样可以将这个 Servlet 隐藏起来
5) MultiActionController:一个 Controller 可以写多个方法,分别对应不同的请求,使同一业务的方法可以放在一起了。在使用时让自己的 Controller 类继承 MultiActionController 类,使用方式如下
public class IndexController extends MultiActionController { public ModelAndView add(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) { ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); mv.addObject("message","add"); mv.setViewName("add"); return mv; } public ModelAndView delete(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) { ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); mv.addObject("message","delete"); mv.setViewName("delete"); return mv; } }
配置自己的 Controller 时要配置一个方法名解析器(默认是 InternalPathMethodNameResolver )
<bean id="indexController" class="com.controller.IndexController"> <property name="methodNameResolver"> <!-- InternalPathMethodNameResolver 根据请求路径解析执行方法名 ParameterMethodNameResolver 根据参数解析执行方法名 PropertiesMethodNameResolver 根据 key/value 列表解析执行方法名 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.multiaction.ParameterMethodNameResolver"> <!-- 指定参数名为action --> <property name="paramName" value="action" /> </bean> </property> </bean>
当我们访问 http://localhost:8080/***/indexAction.do?action=add 时,进入 add() 方法;
当我们访问 http://localhost:8080/***/indexAction.do?action=delete 时,进入 delete() 方法。
2 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型是 HandlerMethod,即这个 Handler 是一个方法,它保存了方法的信息(如Method),这样一个 Controller 就可以处理多个请求了,源码如下所示
@Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据当前请求获取“查找路径” String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 获取当前请求最佳匹配的处理方法(即Controller类的方法中) HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); }
上述代码中 lookupHandlerMethod() 方法主要工作是在 Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods 中找到 HandlerMethod,这里的 T 是 HandlerMappingInfo,它封装了 @RequestMapping 注解中的信息。那 HandlerMethod 是怎么创建的(即怎么把 Controller 的方法变成了它),继续看一下源码找到 initHandlerMethods() 方法,这个方法是在这个类创建后调用的,如下所示是它的源码
protected void initHandlerMethods() { // 从容器中获取所有 Bean 的名称,detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 默认false,不从父容器中查找 //即默认只查找 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器,不查找它的父容器 Spring 的 IOC 容器 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); for (String beanName : beanNames) { // 这里的 isHandler()方法由子类实现,判断是否拥有 @Controller 注解或 @RequestMapping 注解 if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX) && isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ // 利用反射得到 Bean 中的 Method 并包装成 HandlerMethod,然后放入 Map 中 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
看完上述代码后,可以知道是在 detectHandlerMethods() 方法中将 Bean 的方法转换为 HandlerMethod 对象,具体实现如下
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { // 获取这个 Bean 的 Class 对象 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); // 避免重复调用 getMappingForMethod(),getMappingForMethod() 将重新构建 RequestMappingInfo 实例 final Map<Method, T> mappings = new IdentityHashMap<Method, T>(); // 获取被代理前的原始类型 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); // 获取 Method Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { @Override public boolean matches(Method method) { // 根据 Method 和它的 @RequestMapping 注解,创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象。 // 这里的 T 就是 RequestMappingInfo,它封装了 @RequestMapping 信息 T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType); if (mapping != null) { mappings.put(method, mapping); return true; } else { return false; } } }); for (Method method : methods) { // 注册 Method 和它的映射,RequestMappingInfo 储存着映射信息 registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mappings.get(method)); } }
最后在 registerHandlerMethod() 方法中,将 RequestMappingInfo 作为 key,把 Method 包装成 HandlerMethod 作为 value 添加到了 Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods 中。
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = this.handlerMethods.get(mapping); if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) { throw new IllegalStateException(""); } this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod); Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); for (String pattern : patterns) { if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping); } } }
1.1 AbstractHandlerMapping 实现类及使用

AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> 只有一个实现类 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
二、HandlerAdapter
根据 Handler 来找到支持它的 HandlerAdapter,通过 HandlerAdapter 执行这个 Handler 得到 ModelAndView 对象。HandlerAdapter 接口中的方法如下:
- boolean supports(Object handler); // 当前 HandlerAdapter 是否支持这个 Handler
- ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, Object handler); // 利用 Handler 处理请求
- long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler);

1 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
从上面的文章中可以知道,利用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 获取的 Handler 是 HadnlerMethod 类型,它代表 Controller 里要执行的方法,而 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 可以执行 HadnlerMethod 对象。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 的 handle() 方法是在它的父类 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 类中实现的,源码如下所示
@Override public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler); }
handleInternal() 方法是由 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 自己来实现的,源码如下所示
@Override protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { // 是否通过 @SessionAttributes 注释声明了 session 属性。 if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true); } else { checkAndPrepare(request, response, true); } // 是否需要在 synchronize 块中执行 if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { // 执行 HandlerMethod return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } } // 执行 HandlerMethod,得到 ModelAndView return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); }
继续再来看一下如何得到 ModelAndView,invokeHandlerMethod() 方法如下
private ModelAndView invokeHandleMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { // ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); // 数据绑定 WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); // 绑定参数,执行方法 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod requestMappingMethod = createRequestMappingMethod(handlerMethod, binderFactory); // 创建模型和视图容器 ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); // 设置FlasgMap中的值 mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); // 初始化模型 modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, requestMappingMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); final WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); requestMappingMethod = requestMappingMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } requestMappingMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); }
2 HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 可以执行 HttpRequestHandler 类型的 Handler,源码如下
@Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response); return null; }
3 SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 可以执行 Controller 类型的 Handler,源码如下
@Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); }
4 SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
SimpleServletHandlerAdapter 可以执行 Servlet 类型的 Handler,源码如下
@Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((Servlet) handler).service(request, response); return null; }
三、HandlerExceptionResolver
负责处理异常的类,负责根据异常来设置 ModelAndView,然后交由 render 渲染界面。HandlerExecptionResolver 接口中只有一个方法,如下:
- ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, Object handler, Exception ex);





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步