树-二叉树存储及遍历
一、二叉树的概述

二、树和二叉树的区别
1、普通树中节点的最大度数没有限制,而二叉树节点的最大度数是2。
2、无序树的节点无左右之分,而二叉树的节点有左右之分,也就是二叉树的是有序树
三、满二叉树
如果它包含了2的整指数节点,就是满二叉树,满二叉树的特点是每一层上的节点数都是最大节点数,即各层节点数分别为1、2、4、8、16...2的k-1次方
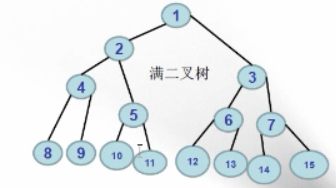
四、完全二叉树
如果一棵二叉树除最后一层外,就其余层的所有节点都是满的,并且最后一层或者是满的,或者仅仅在右边缺少若干连续的节点,这就是完全二叉树。

五、二叉树的性质
1、二叉树第i层上的节点数目至多为2的i-1次方。
2、深度为k的二叉树总共的节点数为:至多有2的k次方-1个节点
3、在任何一棵二叉树中,如果其叶子节点的数量为n0,度(节点拥有子树的个数)为2的子节点数量为n2
4、具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为deep=log2 n +1;

六、二叉树-顺序存储
顺序存储指的是充分利用满二叉树的特性,每层的节点数分别是1、2、4、8.......2的i-1次方
缺陷:如果右节点过多时会产生空间浪费,数组中会产生好多空余数组元素。
package com.zxc.TreeLearning.BinaryTreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/19 0019. * 二叉树顺序存储 */ public class BinaryTreeA { private Object[] datas;//使用数组来记录该树的所有节点 private int DEFAULT_DEEP=8;//保存该树的深度 private int arraySize;//二叉树中总节点的个数 private int deep; public void init(String data){ this.deep=DEFAULT_DEEP; this.arraySize=(int)Math.pow(2,deep)-1;//按照满二叉树开的节点个数 datas=new Object[arraySize]; datas[0]=data; } public void add(int index,String data,boolean left){ if(datas[index]==null){ throw new RuntimeException(index+"处节点为空,无法添加子节点"); } if(2*index+1>=arraySize){//右越界左肯定越界,所以判断左节点 throw new RuntimeException("树底层的数组已满,树越界异常"); } if(left){//左节点 datas[2*index+1]=data; }else{//右节点 datas[2*index+2]=data; } } /** * * @param index:父节点索引 * @return 返回左子节点的数据 */ public String left(int index){ return datas[2*index+1].toString(); } /** * * @param index:父节点索引 * @return 返回右子节点的数据 */ public String right(int index){ return datas[2*index+2].toString(); } @Test public void test(){ this.init("A"); this.add(0,"B",true); this.add(0,"C",false); System.out.println(this.left(0)); System.out.println(this.right(0)); } }
七、二叉链式存储
利用链表特性,每个节点都有左节点和右节点
package com.zxc.TreeLearning.BinaryTreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; import sun.reflect.generics.tree.Tree; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/20 0020. * 二叉链表存储 */ public class BinaryTreeB { public static class TreeNode{ String data; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode() { } public TreeNode(String data) { this.data = data; } public TreeNode(String data, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this.data = data; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } //根节点 private TreeNode root; /** * * @param parent 父节点对象 * @param data 新增节点数据 * @param isLeft 是否为新增左子节点 * @return 返回新增的节点 */ public TreeNode addNode(TreeNode parent,String data,boolean isLeft){ if(parent==null){ System.out.println("不能增加子节点,父节点为空"); return null; } if(isLeft&&parent.left!=null){ System.out.println("左子节点已经存在,不能增加子节点"); return null; } if(!isLeft&&parent.right!=null){ System.out.println("右子节点已经存在,不能添加"); return null; } TreeNode node=new TreeNode(data); if(isLeft){ parent.left=node; }else{ parent.right=node; } return node; } /** * * @param parent 父节点对象 * @return 返回左子节点数据 */ public String leftChild(TreeNode parent){ if(parent==null){ throw new RuntimeException(parent+"节点为null,无法添加子节点"); } return parent.left==null?null:(String)parent.left.data; } /** * * @param parent 需要查询的父节点对象 * @return 返回右子节点数据 */ public String rightChild(TreeNode parent){ if(parent==null){ throw new RuntimeException(parent+"节点为null,无法添加子节点"); } return parent.left==null?null:(String)parent.right.data; } /** * * @param node:判断的当前节点 * @return :当前节点的深度 */ public int deep(TreeNode node){ if(node==null){ return 0; } if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){ return 1; } int leftdeep=deep(node.left); int rightdeep=deep(node.right); int max=0; max=leftdeep>rightdeep?leftdeep:rightdeep; return ++max; } public void init(String data){ this.root=new TreeNode(data); TreeNode a=this.addNode(this.root,"A",true); TreeNode b=this.addNode(this.root,"B",false); TreeNode c=this.addNode(a,"C",true); TreeNode d=this.addNode(a,"D",false); System.out.println(this.leftChild(a)); System.out.println(this.rightChild(a)); System.out.println(this.deep(a)); } @Test public void test(){ init("Root"); } }
缺陷:遍历树的时候效率不高,指定节点访问其父节点时也比较困难。
八、二叉树遍历
1、二叉树的先序遍历(DLR)
若二叉树为空,则不进行任何操作,否则
1、访问根节点
2、先序方式遍历左子树
3、先序遍历右子树
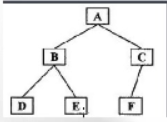
ABDECF
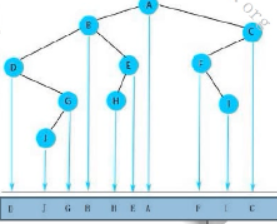
2、二叉树的中序遍历(LDR) 投影法遍历
若二叉树为空,则不进行任何操作,否则
1、中序遍历左子树
2、访问根节点
3、中序遍历右子树
3、二叉树的后序遍历(LRD)
若二叉树为空,则不进行任何操作,否则
1、后序遍历左子树
2、后序遍历右子树
3、访问根节点
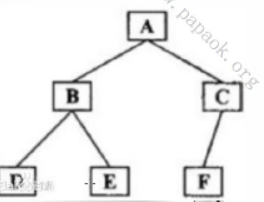
结果为 DEBFCA
package com.zxc.TreeLearning.BinaryTreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/20 0020. * 遍历二叉树,先序(DLR),中序(LDR),后序(LRD) */ public class BinaryTreeSearch { class TreeNode{ private String data; private TreeNode leftNode; private TreeNode rightNode; public TreeNode(String data,TreeNode leftNode,TreeNode rightNode){ this.data=data; this.leftNode=leftNode; this.rightNode=rightNode; } public String getData(){ return data; } public TreeNode getLeftNode(){ return leftNode; } public TreeNode getRightNode(){ return rightNode; } } public void printNode(TreeNode node){ System.out.println(node.getData()); } //初始化二叉树 /* * A * / \ * B C * / \ / \ * D E F G * / \ \ / * H I J P * */ @Test public void init(){ TreeNode D=new TreeNode("D",null,null); TreeNode H=new TreeNode("H",null,null); TreeNode I=new TreeNode("I",null,null); TreeNode E=new TreeNode("E",H,I); TreeNode B=new TreeNode("B",D,E); TreeNode J=new TreeNode("J",null,null); TreeNode P=new TreeNode("P",null,null); TreeNode F=new TreeNode("F",null,J); TreeNode G=new TreeNode("G",P,null); TreeNode C=new TreeNode("C",F,G); TreeNode A=new TreeNode("A",B,C); pre(A); System.out.println(); middle(A); System.out.println(); last(A); System.out.println(); } /** * 先序遍历 * @param node 从node处先序遍历 */ public void pre(TreeNode node){ System.out.print(node.data); if(node.leftNode!=null){ this.pre(node.leftNode); } if(node.rightNode!=null){ this.pre(node.rightNode); } } /** * 中序排序 * @param node 从node处开始中序遍历 */ public void middle(TreeNode node){ if(node.leftNode!=null){ this.middle(node.leftNode); } System.out.print(node.data); if(node.rightNode!=null){ this.middle(node.rightNode); } } /** * 后序排序 * @param node 从node处开始后序遍历 */ public void last(TreeNode node){ if(node.leftNode!=null){ this.last(node.leftNode); } if(node.rightNode!=null){ this.last(node.rightNode); } System.out.print(node.data); } }
九、二叉树的深度、广度优先搜索
深度优先搜索就是先序遍历
广度优先搜索就是按照层,从根开始依次从左向右,从上到下进行遍历输出。
package com.zxc.TreeLearning.BinaryTreeLearning; import org.junit.Test; import sun.reflect.generics.tree.Tree; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Stack; /** * Created by Administrator on 2018/2/20 0020. * 遍历二叉树,先序(DLR),中序(LDR),后序(LRD) */ public class BinaryTreeDW { class TreeNode{ private String data; private TreeNode leftNode; private TreeNode rightNode; public TreeNode(String data,TreeNode leftNode,TreeNode rightNode){ this.data=data; this.leftNode=leftNode; this.rightNode=rightNode; } public String getData(){ return data; } public TreeNode getLeftNode(){ return leftNode; } public TreeNode getRightNode(){ return rightNode; } } public void printNode(TreeNode node){ System.out.println(node.getData()); } //初始化二叉树 /* * A * / \ * B C * / \ / \ * D E F G * / \ \ / * H I J P * */ /** * 深度优先搜索,实际上就是一个DLR,即先序遍历 */ public void depthOrderTraversal(){ if(this.root==null){ System.out.println("不能深搜,因为没有根节点"); return ; } Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>(); stack.push(this.root); while(stack.isEmpty()!=true){ TreeNode node= stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.data); if(node.getRightNode()!=null){ stack.push(node.rightNode); } if(node.getLeftNode()!=null){ stack.push(node.leftNode); } } } /** * 广度优先搜索 */ public void levelOrderTraversal(){ if(this.root==null){ System.out.println("不能深度,因为没有根节点"); }//使用队列功能,先进先出 ArrayDeque<TreeNode> ad=new ArrayDeque(); ad.add(this.root); while(!ad.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node=ad.remove(); System.out.println(node.data); if(node.leftNode!=null){ ad.add(node.leftNode); } if(node.rightNode!=null){ ad.add(node.rightNode); } } } private TreeNode root; @Test public void init(){ TreeNode D=new TreeNode("D",null,null); TreeNode H=new TreeNode("H",null,null); TreeNode I=new TreeNode("I",null,null); TreeNode E=new TreeNode("E",H,I); TreeNode B=new TreeNode("B",D,E); TreeNode J=new TreeNode("J",null,null); TreeNode P=new TreeNode("P",null,null); TreeNode F=new TreeNode("F",null,J); TreeNode G=new TreeNode("G",P,null); TreeNode C=new TreeNode("C",F,G); TreeNode A=new TreeNode("A",B,C); root=A; depthOrderTraversal(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号