【Implementing a Dispose method】
0、Dispose() and Dispose(Boolean)
The IDisposable interface requires the implementation of a single parameterless method, Dispose. However, the dispose pattern requires two Dispose methods to be implemented:
-
A public non-virtual (
NonInheritablein Visual Basic) IDisposable.Dispose implementation that has no parameters. -
A protected virtual (
Overridablein Visual Basic)Disposemethod whose signature is:
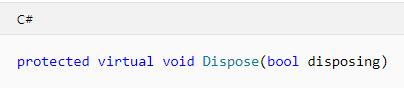
1、Dispose() has a standard implementation, The Dispose method performs all object cleanup, so the garbage collector no longer needs to call the objects' Object.Finalizeoverride.
实现System.IDsiposable.Dispose()方法。不能将此方法设置为virtual,子类不能override此方法。此方法的实现必须为如下代码。
// Implement IDisposable. // Do not make this method virtual. // A derived class should not be able to override this method. public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); // This object will be cleaned up by the Dispose method. // Therefore, you should call GC.SupressFinalize to // take this object off the finalization queue // and prevent finalization code for this object // from executing a second time. GC.SuppressFinalize(this); }
2、实现析构函数(Finalize)。析构函数必须实现为以下代码。
// Use C# destructor syntax for finalization code. // This destructor will run only if the Dispose method // does not get called. // It gives your base class the opportunity to finalize. // Do not provide destructors in types derived from this class. ~MyResource() { // Do not re-create Dispose clean-up code here. // Calling Dispose(false) is optimal in terms of // readability and maintainability. Dispose(false); }
3、实现virtual Dispose(bool disposing)方法,必须为protected。如果dispoing为true,说明从Dipose()方法调用而来;如果为false,说明从析构函数(Finalize)调用而来。在析构函数中,不能再使用引用类型(Ref)成员类型,所以只处理unmanaged resource的释放即可;而在Dipose()调用过程中,managed res & unmanaged res都要释放。
最后,添加一个成员变量disposed来标记是否已经释放过。
// Dispose(bool disposing) executes in two distinct scenarios. // If disposing equals true, the method has been called directly // or indirectly by a user's code. Managed and unmanaged resources // can be disposed. // If disposing equals false, the method has been called by the // runtime from inside the finalizer and you should not reference // other objects. Only unmanaged resources can be disposed. protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing) { // Check to see if Dispose has already been called. if(!this.disposed) { // If disposing equals true, dispose all managed // and unmanaged resources. if(disposing) { // Dispose managed resources. component.Dispose(); } // Call the appropriate methods to clean up // unmanaged resources here. // If disposing is false, // only the following code is executed. CloseHandle(handle); handle = IntPtr.Zero; // Note disposing has been done. disposed = true; } }
3.1、Here's the general pattern for implementing the dispose pattern for a derived class that overrides Object.Finalize:
A class derived from a class that implements the IDisposable interface shouldn't implement IDisposable, because the base class implementation of IDisposable.Dispose is inherited by its derived classes.
1 using System; 2 3 class DerivedClass : BaseClass 4 { 5 // Flag: Has Dispose already been called? 6 bool disposed = false; 7 8 // Protected implementation of Dispose pattern. 9 protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) 10 { 11 if (disposed) 12 return; 13 14 if (disposing) { 15 // Free any other managed objects here. 16 // 17 } 18 19 // Free any unmanaged objects here. 20 // 21 disposed = true; 22 23 // Call the base class implementation. 24 base.Dispose(disposing); 25 } 26 27 ~DerivedClass() 28 { 29 Dispose(false); 30 } 31 }
4、An object must also call the Dispose method of its base class if the base class implements IDisposable.
如果基类有Dispose()方法,子类必须的Dispose()必须调用基类的Dispose()。
5、什么时候需要Dispose()?
1)包含Disposable对象的容器类需要实现Dipose,而不需要实现Finalize()。因为清空一个容器,并不表明需要释放unmanged resource。
2)自身包含unmanged resource的类需实现Dispose、Finalize。
6、DO throw an ObjectDisposedException from any member that cannot be used after the object has been disposed of.
当调用一个已经Disposed对象时,抛出 ObjectDisposedException。
public class DisposableResourceHolder : IDisposable { bool disposed = false; SafeHandle resource; // handle to a resource public void DoSomething(){ if(disposed) throw new ObjectDisposedException(...); // now call some native methods using the resource ... } protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing){ if(disposed) return; // cleanup ... disposed = true; } }
7、一些C#自带类库的Close()语言与Dispose()语义是一样的。
public class Stream : IDisposable { IDisposable.Dispose(){ Close(); } public void Close(){ Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } }
参考:
1、https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.idisposable.dispose?view=netframework-4.7.1
2、https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/standard/design-guidelines/dispose-pattern



