事务传播和隔离
第一次被问到这个问题是面试Oracle的时候. 第二次被问到是面试某云的时候.
复习一下:
这个问题的答案可以看Sping的annontation @Transactional.
有个配置节点:
Propagation: 传播
Isolation: 隔离
传播这种东西吧, 怎么说呢, 代码规范得好一点, 就不会频繁碰见. 耦合太多,A->B,B->C这种多了, 就不能不看.
做过EJB的人应该会很懂~~~
Spring中七种Propagation类的事务属性详解: 网上抄来, 翻译得渣渣....看原文吧NND.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 /** 2 * Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists. 3 * Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 4 * <p>This is the default setting of a transaction annotation. 5 */ 6 REQUIRED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED), 7 8 /** 9 * Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists. 10 * Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 11 * <p>Note: For transaction managers with transaction synchronization, 12 * PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS is slightly different from no transaction at all, 13 * as it defines a transaction scope that synchronization will apply for. 14 * As a consequence, the same resources (JDBC Connection, Hibernate Session, etc) 15 * will be shared for the entire specified scope. Note that this depends on 16 * the actual synchronization configuration of the transaction manager. 17 * @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization 18 */ 19 SUPPORTS(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS), 20 21 /** 22 * Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists. 23 * Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 24 */ 25 MANDATORY(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY), 26 27 /** 28 * Create a new transaction, and suspend the current transaction if one exists. 29 * Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 30 * <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box 31 * on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to 32 * {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager}, 33 * which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be 34 * made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE). 35 * @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager 36 */ 37 REQUIRES_NEW(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW), 38 39 /** 40 * Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists. 41 * Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 42 * <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box 43 * on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to 44 * {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager}, 45 * which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be 46 * made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE). 47 * @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager 48 */ 49 NOT_SUPPORTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED), 50 51 /** 52 * Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists. 53 * Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name. 54 */ 55 NEVER(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER), 56 57 /** 58 * Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists, 59 * behave like PROPAGATION_REQUIRED else. There is no analogous feature in EJB. 60 * <p>Note: Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on specific 61 * transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC 62 * DataSourceTransactionManager when working on a JDBC 3.0 driver. 63 * Some JTA providers might support nested transactions as well. 64 * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager 65 */ 66 NESTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED);
/** * Use the default isolation level of the underlying datastore. * All other levels correspond to the JDBC isolation levels. * @see java.sql.Connection */ DEFAULT(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT), /** * A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads * can occur. This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read by * another transaction before any changes in that row have been committed * (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back, the second * transaction will have retrieved an invalid row. * @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED */ READ_UNCOMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED), /** * A constant indicating that dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads * and phantom reads can occur. This level only prohibits a transaction * from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it. * @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED */ READ_COMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED), /** * A constant indicating that dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are * prevented; phantom reads can occur. This level prohibits a transaction * from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it, and it also prohibits * the situation where one transaction reads a row, a second transaction * alters the row, and the first transaction rereads the row, getting * different values the second time (a "non-repeatable read"). * @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ */ REPEATABLE_READ(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ), /** * A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom * reads are prevented. This level includes the prohibitions in * {@code ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ} and further prohibits the situation * where one transaction reads all rows that satisfy a {@code WHERE} * condition, a second transaction inserts a row that satisfies that * {@code WHERE} condition, and the first transaction rereads for the * same condition, retrieving the additional "phantom" row in the second read. * @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE */ SERIALIZABLE(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE);
事务隔离级别写得不清楚, 看Oracle的文档更好些
/** * A constant indicating that transactions are not supported. */ int TRANSACTION_NONE = 0; /** * A constant indicating that * dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur. * This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read * by another transaction before any changes in that row have been * committed (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back, * the second transaction will have retrieved an invalid row. */ int TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1; /** * A constant indicating that * dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads and phantom * reads can occur. This level only prohibits a transaction * from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it. */ int TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED = 2; /** * A constant indicating that * dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are prevented; phantom * reads can occur. This level prohibits a transaction from * reading a row with uncommitted changes in it, and it also * prohibits the situation where one transaction reads a row, * a second transaction alters the row, and the first transaction * rereads the row, getting different values the second time * (a "non-repeatable read"). */ int TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4; /** * A constant indicating that * dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads are prevented. * This level includes the prohibitions in * <code>TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ</code> and further prohibits the * situation where one transaction reads all rows that satisfy * a <code>WHERE</code> condition, a second transaction inserts a row that * satisfies that <code>WHERE</code> condition, and the first transaction * rereads for the same condition, retrieving the additional * "phantom" row in the second read. */ int TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;
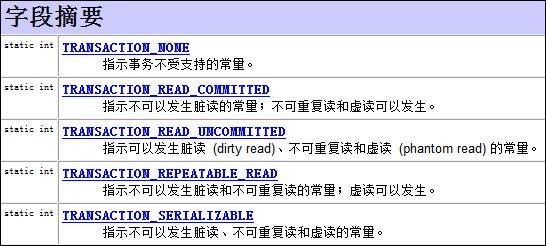
这个是java.sql.Connection里写的.
这个是抄别人的
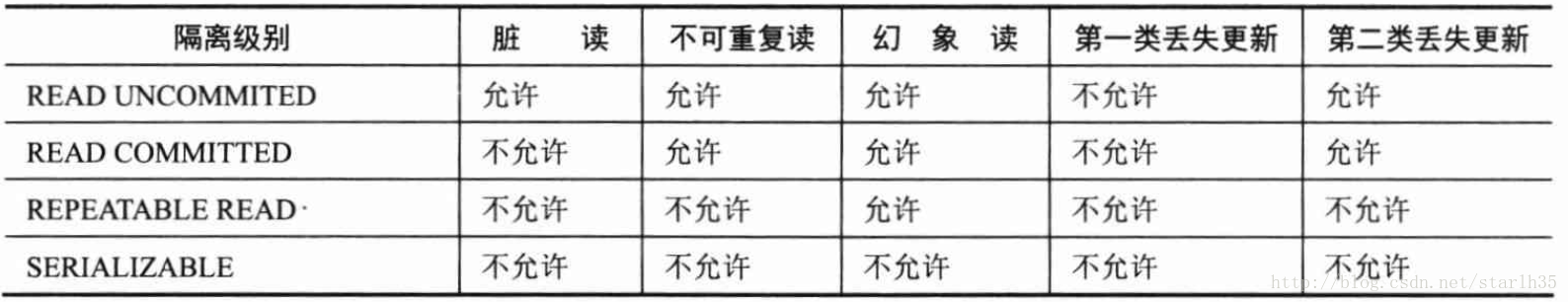
以前Oracle一本黄书上写得很好, 回家找找, 先抄一段网上的
1、脏读(dirty read):一个事务读取了被其他事务写入但还未提交的数据。
2、不重复读(nonrepeatable read):一个事务再次读取其之前曾经读取过的数据时,发现数据已被其他已提交的事务修改或删除。
3、幻象读(phantom read):事务按照之前的条件重新查询时,返回的结果集中包含其他已提交事务插入的满足条件的新数据。
默认read committed: 不允许脏读, 允许(不重复读), 允许(幻象读)
分类:
软考-数据库概论





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现