HashMap中的遍历及Java中的排序
HashMap中的遍历
public class HashMapStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一般来说,最好初始化一下, 小于12的就不要初始化了
// 默认的就是16,因为加载因子是0.75,也就是到16*0.75=12的时候会扩容
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(3);
map.put("welcome","to");
map.put("java","study");
map.put("wechat","best396975802");
//遍历方法1: 先遍历key , 再取出value
System.out.println("遍历方法1: 先遍历key , 再取出value");
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key is "+key);
System.out.println("value is "+ map.get(key));
}
//遍历方法2: 直接遍历value
System.out.println("遍历方法2: 直接遍历value");
for (String value : map.values()) {
System.out.println("value is "+value);
}
//遍历方法3: 通过遍历entry来取Key和value,推荐的方法!!!
System.out.println("遍历方法3: 通过遍历entry来取Key和value,推荐的方法!!!");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key is "+entry.getKey());
System.out.println("value is "+ entry.getValue());
}
//遍历方法4: 通过forEach方法直接遍历key和value
System.out.println("遍历方法4: 通过forEach方法直接遍历");
map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println("key is "+ key);
System.out.println("value is "+ value);
});
}
}
Java中的排序
升序
使用 java.util.Arrays 类中的 sort() 方法对数组进行升序分为以下两步:
1.导入 java.util.Arrays 包。
2.使用 Arrays.sort(数组名) 语法对数组进行排序,排序规则是从小到大,即升序。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义含有5个元素的数组
double[] scores = new double[] { 78, 45, 85, 97, 87 };
System.out.println("排序前数组内容如下:");
// 对scores数组进行循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
System.out.print(scores[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println("\n排序后的数组内容如下:");
// 对数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(scores);
// 遍历排序后的数组
for (int j = 0; j < scores.length; j++) {
System.out.print(scores[j] + "\t");
}
}
降序
在 Java 语言中使用 sort 实现降序有两种方法:
1)利用 Collections.reverseOrder() 方法(Collections 是一个包装类。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = { 9, 8, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 6, 5 }; // 数组类型为Integer
Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int arr : a) {
System.out.print(arr + " ");
}
}
2)实现 Comparator 接口的复写 compare() 方法,代码如下:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 注意,要想改变默认的排列顺序,不能使用基本类型(int,double,char)而要使用它们对应的类
*/
Integer[] a = { 9, 8, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 6, 5 };
// 定义一个自定义类MyComparator的对象
Comparator cmp = new MyComparator();
Arrays.sort(a, cmp);
//转换为函数式接口
Arrays.sort(a, (first, second) -> first- second ); //这是升序
Arrays.sort(a, (first, second) -> second - first); //这是降序
for (int arr : a) {
System.out.print(arr + " ");
}
}
}
// 实现Comparator接口
class MyComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
/*
* 如果o1小于o2,我们就返回正值,如果o1大于o2我们就返回负值, 这样颠倒一下,就可以实现降序排序了,反之即可自定义升序排序了
*/
return o2 - o1;
}
}
注意:使用以上两种方法时,数组必须是包装类型,否则会编译不通过。
Comparator下的compare方法:
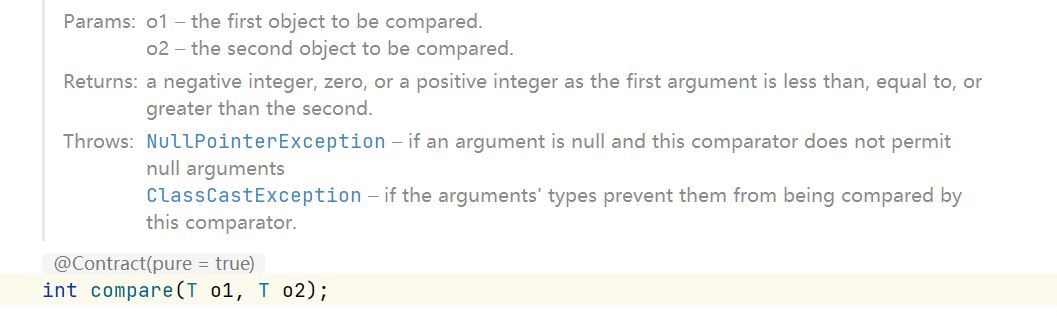
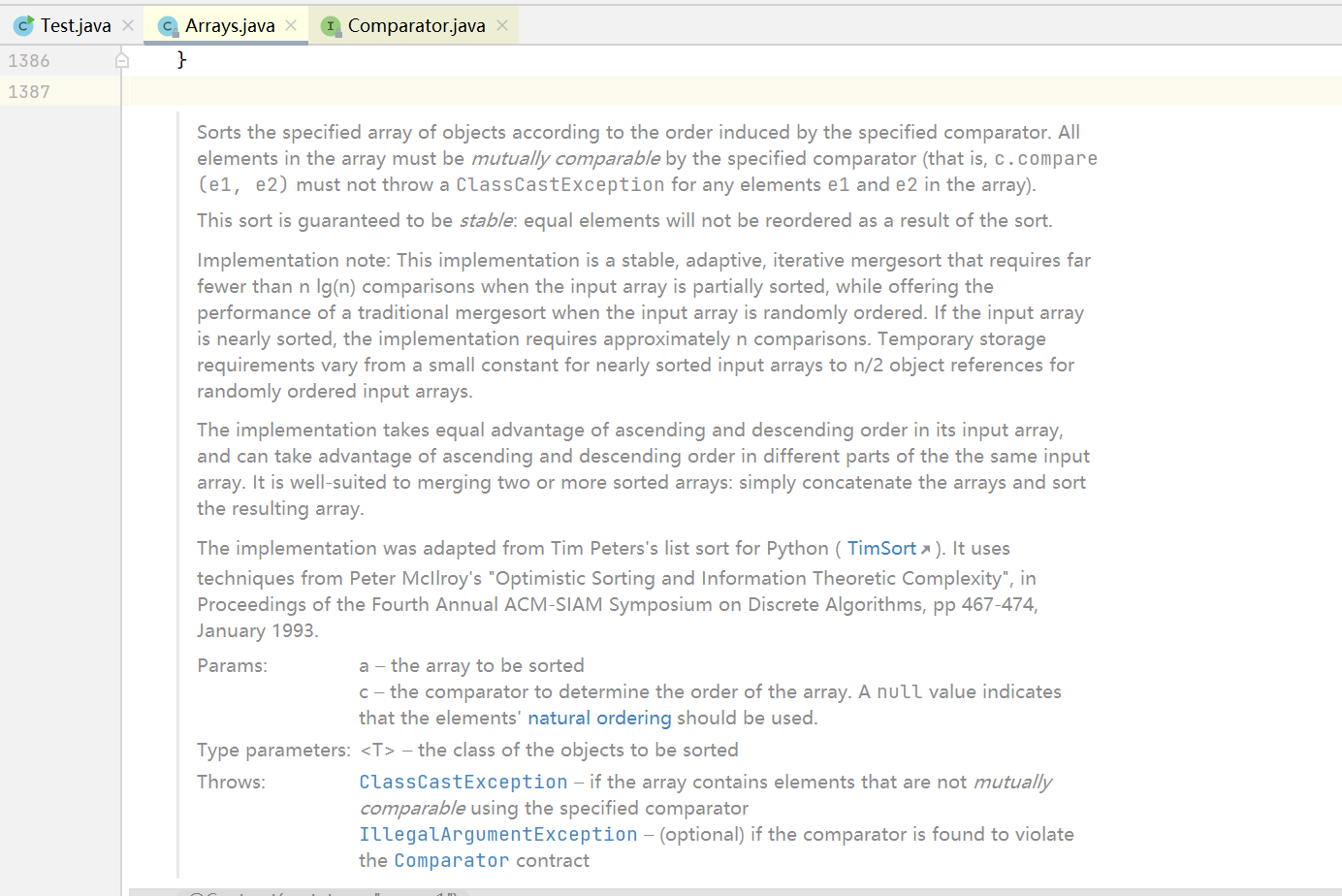
Arrays.sort()方法:
它是一个stable的排序方法,相等的元素位置不会交换。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号