MIT 6.5840 MapReduce Lab
MapReduce
MapReduce 是一种编程模型,其思想是让程序员通过编写简单的 Map 和 Reduce 程序就能完成分布式系统的任务,而不需要关注分布式的具体细节。
用户自定义的Map函数接受一个 key/value pair 的输入值,然后产生一个中间 key/value pair 值的集合。MapReduce 库把所有具有相同中间 key 值 I 的中间 value 值集合在一起后传递给 Reduce 函数。
用户自定义的 Reduce 函数接受一个中间 key 的值 I 和相关的一个 value 值的集合。Reduce 函数合并这些 value 值,形成一个较小的 value 值的集合。通常来说,每次 Reduce 函数调用只产生 0 或 1 个输出 value 值。通常我们通过一个迭代器把中间 value 值提供给 Reduce 函数,这样我们就可以处理无法全部放入内存中的大量的 value 值的集合(迭代器可看为一个容器,所以数据放入一个容器中,Reduce 函数就从这个容器中取数据即可)。
例如:计算一个大的文档集合中每个单词出现的次数,Map 和 Reduce 伪代码如下:
map(String key, String value) {
// key: document name
// value: document contents
for each word w in value:
EmitIntermediate(w, "1");
}
reduce(String key, Iterator values) {
// key: a word
// values: a list of counts
int result = 0;
for each v in values:
result += ParseInt(v);
Emit(AsString(result));
}
MapReduce 框架原理
论文中描述的 MapReduce 框架的具体原理如下:
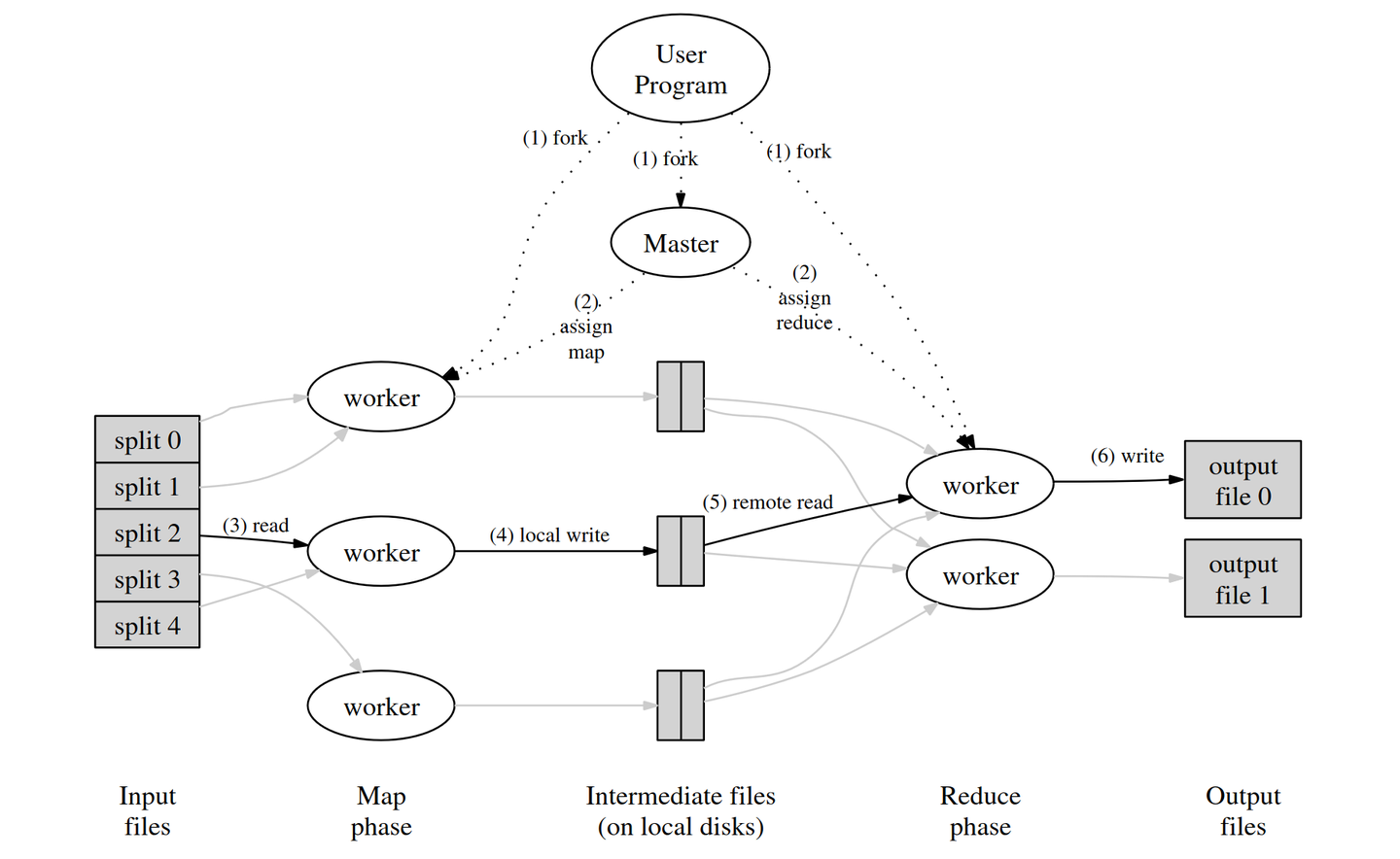
当用户程序调用 MapReduce 时,会发生下面一系列动作:
-
用户程序首先调用的 MapReduce 库将输入文件分成M个数据片度,每个数据片段的大小一般从 16MB 到 64MB (可以通过可选的参数来控制每个数据片段的大小)。然后用户程序在机群中创建大量的程序副本。
-
这些程序副本中的有一个特殊的程序 master。副本中其它的程序都是 worker 程序,由 master 分配任务。有 M 个 Map 任务和 R 个 Reduce 任务将被分配,master 将一个 Map 任务或 Reduce 任务分配给一个空闲的 worker。
-
被分配了 map 任务的 worker 程序读取相关的输入数据片段,从输入的数据片段中解析出 key/value pair,然后把 key/value pair 传递给用户自定义的 Map 函数,由 Map函数生成并输出的中间k ey/value pair,并缓存在内存中。
-
缓存中的 key/value pair 通过分区函数分成 R 个区域,之后周期性的写入到本地磁盘上。缓存的 key/value pair 在本地磁盘上的存储位置将被回传给 master,由 master 负责把这些存储位置再传送给 Reduce worker。
-
当 Reduce worker 程序接收到 master 程序发来的数据存储位置信息后,使用 RPC 从 Map worker 所在主机的磁盘上读取这些缓存数据。当 Reduce worker 读取了所有的中间数据后,通过对 key 进行排序后使得具有相同 key 值的数据聚合在一起。由于许多不同的 key 值会映射到相同的 Reduce 任务上,因此必须进行排序。如果中间数据太大无法在内存中完成排序,那么就要在外部进行排序。
-
Reduce worker 程序遍历排序后的中间数据,对于每一个唯一的中间 key 值,Reduce worker 程序将这个 key 值和它相关的中间 value 值的集合传递给用户自定义的 Reduce函数。Reduce 函数的输出被追加到所属分区的输出文件。
-
当所有的 Map 和 Reduce 任务都完成之后,master 唤醒用户程序。在这个时候,在用户程序里的对 MapReduce 调用才返回。
First step
在一开始,目标是至少先让代码跑起来。
首先看懂 mrsequential.go 的逻辑,看懂 coordinator 和 worker 的 rpc 交互流程。然后实现 coordinator 分配任务后 worker 直接把任务打印出来。
worker 通过 rpc 调用 coordinator 的 AssignJob 方法,获取任务,然后直接打印出来。
在 rpc.go 中,定义用到的 rpc 相关的结构体:
type JobType int
const (
Map JobType = iota
Reduce
)
// worker ask for a job
type JobArgs struct{}
// the coordinator reply for the job
type JobReply struct {
JobArgs interface{}
JobType JobType
}
coordinator.go
type JobType int
const (
Map JobType = iota
Reduce
)
// worker ask for a job
type JobArgs struct{}
// the coordinator reply for the job
type JobReply struct {
JobArgs interface{}
JobType JobType
}
func (c *Coordinator) AssignJob(args *JobArgs, reply *JobReply) error {
if c.assigned < len(c.files) {
reply.JobArgs = c.files[c.assigned]
c.assigned++
reply.JobType = Map
} else {
reply.JobType = Reduce
c.nReduce--
}
return nil
}
worker.go
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string,
) {
args := new(JobArgs)
reply := new(JobReply)
ok := call("Coordinator.AssignJob", &args, &reply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("call failed!")
return
} else {
switch reply.JobType {
case Map:
file := reply.JobArgs
fmt.Println("Map: ", file)
case Reduce:
fmt.Println("Reduce: ", reply.JobArgs)
}
}
}
初步实现(暂不考虑worker出现故障、超时以及一些并发引起的问题,先实现成功调用用户 Map 和 Reduce 方法)
定义结构体用于传递 Map 和 Reduce 需要的参数
type MapWorkerArgs struct {
Files []string
WorkerId int // worker id
NReduce int // number of reduce workers
}
type ReduceWorkerArgs struct {
WorkerId int // worker id
}
-
暂时考虑对整个 AssignJob 加互斥锁,若发现这样加锁不能满足要求再行改进。
-
Map worker 将中间文件的文件名传递给 coordinator。
-
coordinator 将需要 Reduce worker 处理的中间文件的文件名传递给对应的 Reduce worker。
rpc.go
package mr
//
// RPC definitions.
//
// remember to capitalize all names.
//
import (
"os"
"strconv"
)
// Add your RPC definitions here.
// the job type enum, Map and Reduce
type JobType int
const (
Map JobType = iota
Reduce
)
// worker ask for a job
type JobArgs struct{}
// the coordinator reply for the job
type JobReply struct {
JobType JobType
MapArgs MapWorkerArgs
ReduceArgs ReduceWorkerArgs
}
type PassFileNamesArgs struct {
IntermediateFileNames []string
}
type PassFileNamesReply struct{}
// Cook up a unique-ish UNIX-domain socket name
// in /var/tmp, for the coordinator.
// Can't use the current directory since
// Athena AFS doesn't support UNIX-domain sockets.
func coordinatorSock() string {
s := "/var/tmp/5840-mr-"
s += strconv.Itoa(os.Getuid())
return s
}
coordinator.go
package mr
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"sync"
)
type Coordinator struct {
files []string
assigned int // number of files assigned
nReduce int // number of reduce workers
mapWorkerNum int // number of map workers created
reduceWorkerNum int // number of reduce workers created
// the file names of the intermediate files
// index i is for the No.i Reduce worker
intermediateFileNames [][]string
mutexLock sync.Mutex
}
// the arguments to pass to the mapWorker
type MapWorkerArgs struct {
File string
WorkerId int // worker id
NReduce int // number of reduce workers
}
// the arguments to pass to the reduceWorker
type ReduceWorkerArgs struct {
WorkerId int // worker id
IntermediateFileNames []string // files for reduce workers to work on
}
// Your code here -- RPC handlers for the worker to call.
func (c *Coordinator) GetJob(args *JobArgs, reply *JobReply) error {
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
if c.assigned < len(c.files) {
reply.MapArgs.WorkerId = c.mapWorkerNum
reply.MapArgs.File = c.files[c.assigned]
reply.MapArgs.NReduce = c.nReduce
c.mapWorkerNum++
c.assigned++
reply.JobType = Map
} else if c.nReduce > c.reduceWorkerNum {
reply.JobType = Reduce
reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId = c.reduceWorkerNum
reply.ReduceArgs.IntermediateFileNames = c.intermediateFileNames[c.reduceWorkerNum]
c.reduceWorkerNum++
} else {
fmt.Println("All Reduce workers are already assigned")
}
return nil
}
func (c *Coordinator) PassFileNames(args *PassFileNamesArgs, reply *PassFileNamesReply) error {
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
intermediateFileNames := args.IntermediateFileNames
for i, intermediateFileName := range intermediateFileNames {
c.intermediateFileNames[i] = append(c.intermediateFileNames[i], intermediateFileName)
}
return nil
}
func (c *Coordinator) server() {
rpc.Register(c)
rpc.HandleHTTP()
// l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
os.Remove(sockname)
l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error:", e)
}
go http.Serve(l, nil)
}
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls Done() periodically to find out
// if the entire job has finished.
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
ret := false
// Your code here.
return ret
}
// create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
// Your code here.
c.assigned = 0
c.files = files
c.mapWorkerNum = 0
c.reduceWorkerNum = 0
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.intermediateFileNames = make([][]string, nReduce)
c.server()
return &c
}
worker.go
package mr
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"hash/fnv"
"io"
"log"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"plugin"
"sort"
)
// Map functions return a slice of KeyValue.
type KeyValue struct {
Key string
Value string
}
// for sorting by key.
type ByKey []KeyValue
// for sorting by key.
func (a ByKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a ByKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a ByKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return a[i].Key < a[j].Key }
// use ihash(key) % NReduce to choose the reduce
// task number for each KeyValue emitted by Map.
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
h.Write([]byte(key))
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
// load the application Map and Reduce functions
// from a plugin file, e.g. ../mrapps/wc.so
func loadPlugin(filename string) (func(string, string) []KeyValue, func(string, []string) string) {
p, err := plugin.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot load plugin %v", filename)
}
xmapf, err := p.Lookup("Map")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Map in %v", filename)
}
mapf := xmapf.(func(string, string) []KeyValue)
xreducef, err := p.Lookup("Reduce")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Reduce in %v", filename)
}
reducef := xreducef.(func(string, []string) string)
return mapf, reducef
}
func mapWorker(args MapWorkerArgs) {
nReduce := args.NReduce
file, err := os.Open(args.File)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", args.File)
}
content, err := io.ReadAll(file)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", args.File)
}
file.Close()
mapf, _ := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
kva := mapf(args.File, string(content))
// divide the key value pairs for each reduce workers
kvalist := make([][]KeyValue, nReduce)
intermediateFileNameList := make([]string, nReduce)
for _, kv := range kva {
num := ihash(kv.Key) % nReduce // the reduce task number for the KeyValue pair
kvalist[num] = append(kvalist[num], kv)
}
// write the divided key value pairs to disk
for i, kva := range kvalist {
intermediateFileName := fmt.Sprintf("mr-%d-%d", args.WorkerId, i)
intermediateFileNameList[i] = intermediateFileName
intermediateFile, err := os.Create(intermediateFileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot create %v", intermediateFileName)
}
enc := json.NewEncoder(intermediateFile)
for _, kv := range kva {
err := enc.Encode(&kv)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot encode %v", kv)
}
}
}
// pass the address (file name) of the key value pairs file to the master
pargs := new(PassFileNamesArgs)
preply := new(PassFileNamesReply)
pargs.IntermediateFileNames = intermediateFileNameList
ok := call("Coordinator.PassFileNames", &pargs, &preply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("call PassFileNames failed")
}
}
func reduceWorker(args ReduceWorkerArgs) {
intermediateFileNames := args.IntermediateFileNames
_, reducef := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
intermediate := make([]KeyValue, 0)
// read key value pairs from intermediate files
for _, fileName := range intermediateFileNames {
intermediateFile, err := os.Open(fileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", fileName)
}
dec := json.NewDecoder(intermediateFile)
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := dec.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
break
}
intermediate = append(intermediate, kv)
}
intermediateFile.Close()
}
sort.Sort(ByKey(intermediate))
// create output file
oname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-out-%v", args.WorkerId)
ofile, _ := os.Create(oname)
//
// call Reduce on each distinct key in intermediate[],
// and print the result to ofile
//
i := 0
for i < len(intermediate) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {
j++
}
values := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)
}
output := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)
// this is the correct format for each line of Reduce output.
fmt.Fprintf(ofile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)
i = j
}
}
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string,
) {
args := new(JobArgs)
reply := new(JobReply)
ok := call("Coordinator.GetJob", &args, &reply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("call GetJob failed!")
return
} else {
switch reply.JobType {
case Map:
fmt.Printf("Running Map No.%d\n", reply.MapArgs.WorkerId)
mapWorker(reply.MapArgs)
case Reduce:
fmt.Printf("Running Reduce No.%d\n", reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId)
reduceWorker(reply.ReduceArgs)
}
}
}
// send an RPC request to the coordinator, wait for the response.
// usually returns true.
// returns false if something goes wrong.
func call(rpcname string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) bool {
// c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("unix", sockname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing:", err)
}
defer c.Close()
err = c.Call(rpcname, args, reply)
if err == nil {
return true
}
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}
对故障和超时的 worker 的识别和处理,以及一些并发相关问题的解决
-
对每一个 worker,coordinator 在分配了任务之后等待10秒,若超出10秒 worker 没有完成任务,就把这个 worker 视为 crashed,将任务分配给其他的 worker。
-
Reduce worker 需要等 Map 全部完成才能开始,在 Map 全部结束之前,利用 channel 阻塞 Reduce worker 的 RPC 调用。
-
定义两个数组用来显示 map 和 reduce 任务的完成情况。两个 int 类型的变量记录尚未完成的 map 和 reduce 任务的数量,Done 函数通过判断这两个变量来判断 coordinator 任务是否结束。
-
利用 channel 作为队列,在 coordinator 中定义两个队列,用于存放后面等待分配的 map 和 reduce 任务。分配之后 coordinator 等待10秒,10 秒后任务没有完成就重新把任务放进队列中。
-
coordinator 在完成对 worker 的调用后新建一个 go routine,等待10秒后判断任务是否已经完成。
-
worker 在任务成功完成后调用一个 RPC 函数告知 coordinator 任务已完成。
一些注意事项(踩过的坑)
-
在编写程序时注意函数和变量以大写开头和以小写开头的区别,RPC 模块涉及到的所有函数,传递的变量(包括结构体内部的变量)开头字母都要大写。
-
使用 go run -race 来检测并发相关的问题。
-
注意,worker 在执行完一个任务之后应该继续向 coordinator 请求下一个任务,而不是直接返回。
-
在 worker 中 sleep 一小段时间来避免所有任务被一个 worker 请求而不能通过 parallelism test。
-
Reduce worker 读取中间文件失败不需要退出,直接尝试读取下一个文件,Map worker 确实可能对于某个 Reduce worker 不产生中间文件。
-
由于可能会有一些 worker 速度慢,并未 crash 而只是超时,所以会出现一个任务由不同的 worker 先后完成,而向 coordinator 先后多次传递任务完成的信息。所以对于记录剩余未完成的任务的数量的变量,不能收到完成消息后简单减一。
-
加了锁的函数要注意防止死锁。如 coordinator 的 GetJob 函数中,如果 channel 队列此时为空,会阻塞直到有下一个数进入队列,但若阻塞时互斥锁是 lock 的状态,下一个数进入队列的程序段也加上了锁,将会出现死锁。事实上 GetJob 函数无需加锁。
一个调试了挺久的问题
在快速解决了一些 bug 之后,最后一个问题是 reduce parallelism test 有概率失败,显示“too few parallel reduces”。
我看了一下 test-mr.sh 中的对应内容,也通过随机数给 worker 编号进行了查看,测试失败的原因是只有一个 worker 执行了所有 reduce 进程。
这是为什么呢,我研究了很久,尝试了很多方法都没有找到问题所在。后来我发现每次只有 reduce parallelism test 有可能会出问题,但是 map parallelism test 每次都能正常通过。这让我把问题范围缩小到 map 和 reduce 任务切换处,才终于发现了问题所在。
我的 GetJob 函数是这样写的:
func (c *Coordinator) GetJob(args *JobArgs, reply *JobReply) error {
// fmt.Println("One worker is asking for job.")
c.mutexLock.Lock()
mapJobsNumLeft := c.mapJobsNumLeft
reduceJobsNumLeft := c.reduceJobsNumLeft
c.mutexLock.Unlock()
if mapJobsNumLeft > 0 {
reply.JobType = Map
reply.MapArgs.WorkerId = <-c.mapQueue
reply.MapArgs.File = c.files[reply.MapArgs.WorkerId]
reply.MapArgs.NReduce = c.nReduce
// fmt.Printf("Assigned Map Job No.%v\n", reply.MapArgs.WorkerId)
go c.waitForWorker(Map, reply.MapArgs.WorkerId)
} else if reduceJobsNumLeft > 0 {
reply.JobType = Reduce
reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId = <-c.reduceQueue
reply.ReduceArgs.IntermediateFileNames = c.intermediateFileNames[reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId]
// fmt.Printf("Assigned Reduce Job No.%v\n", reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId)
go c.waitForWorker(Reduce, reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId)
} else {
reply.JobType = Exit
// fmt.Println("No job left to assign.")
}
return nil
}
判断 worker 是请求 map 任务还是 reduce 任务是通过剩余未完成的 map 任务的数量来实现的。但考虑当 worker A,B 先后执行最后两个 map 任务 的情况,A 执行完 map 任务后继续请求下一个任务。当 A 加锁取出 c.mapJobsNumLeft 的值时,B 并没有完成任务,于是 A 取出的 c.mapJobsNumLeft 的值为1,会继续请求 map 任务。但此时 map 任务已经全部分配出去,c.mapQueue 是空的,A 将会阻塞在 “reply.MapArgs.WorkerId = <-c.mapQueue” 处,并且只要 B 顺利完成最后一个 map 任务,c.mapQueue 将会一直是空的,A 也就会一直阻塞在此处,不能继续执行后面的 reduce 任务了。
解决方案是不将 worker 阻塞在 channel 处,而是直接判断 channel 是否为空,如果为空就让 worker 等待一段时间再重新请求任务。这样就可以给整个 GetJob 函数加上锁。
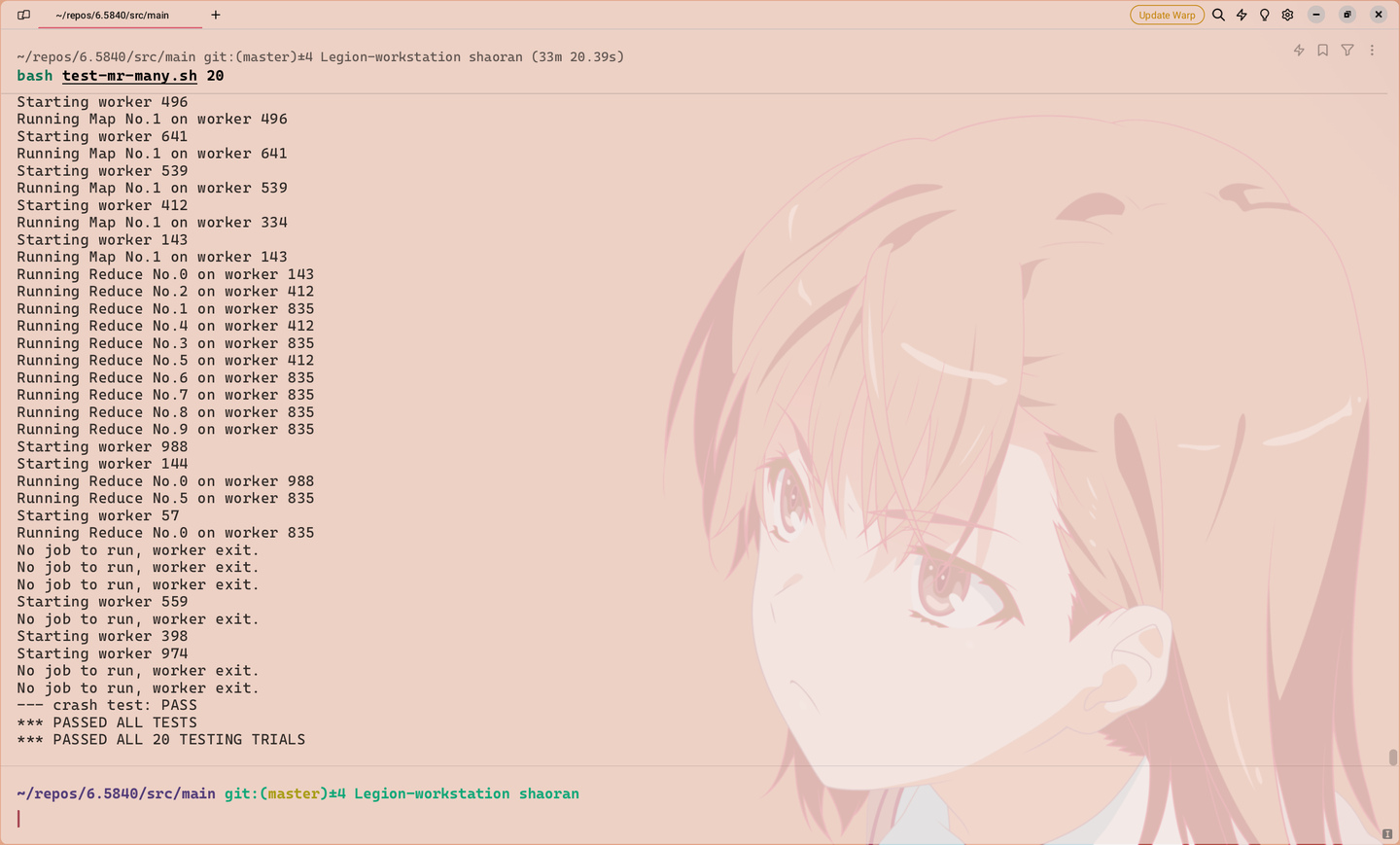
通过全部测试的代码
测试结果如下(进行了20次测试):
rpc.go
package mr
//
// RPC definitions.
//
// remember to capitalize all names.
//
import (
"os"
"strconv"
)
// Add your RPC definitions here.
// the job type enum, Map and Reduce
type JobType int
const (
Map JobType = iota
Reduce
Exit
Wait
)
// worker ask for a job
type JobArgs struct{}
// the coordinator reply for the job
type JobReply struct {
JobType JobType
MapArgs MapWorkerArgs
ReduceArgs ReduceWorkerArgs
}
type PassFileNamesArgs struct {
IntermediateFileNames []string
}
type PassFileNamesReply struct{}
type CompleteJobArgs struct {
TheJobType JobType
JobId int
}
type CompleteJobReply struct{}
// Cook up a unique-ish UNIX-domain socket name
// in /var/tmp, for the coordinator.
// Can't use the current directory since
// Athena AFS doesn't support UNIX-domain sockets.
func coordinatorSock() string {
s := "/var/tmp/5840-mr-"
s += strconv.Itoa(os.Getuid())
return s
}
coordinator.go
package mr
import (
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"sync"
"time"
)
type Coordinator struct {
files []string
nReduce int // number of reduce workers
// the file names of the intermediate files
// index i is for the No.i Reduce worker
intermediateFileNames [][]string
mapJobsNumLeft int // number of map jobs left uncompleted
reduceJobsNumLeft int // number of reduce jobs left uncompleted
mutexLock sync.Mutex
mapQueue chan int // queue of map jobs
reduceQueue chan int // queue of reduce jobs
// the status of the jobs
// 0 : uncompleted
// 1 : successfully completed
mapJobsStatus []int // status of map jobs
reduceJobsStatus []int // status of reduce jobs
}
// the arguments to pass to the mapWorker
type MapWorkerArgs struct {
File string
JobId int // worker id
NReduce int // number of reduce workers
}
// the arguments to pass to the reduceWorker
type ReduceWorkerArgs struct {
JobId int // worker id
IntermediateFileNames []string // files for reduce workers to work on
}
// Your code here -- RPC handlers for the worker to call.
func (c *Coordinator) GetJob(args *JobArgs, reply *JobReply) error {
// fmt.Println("One worker is asking for job.")
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
mapJobsNumLeft := c.mapJobsNumLeft
reduceJobsNumLeft := c.reduceJobsNumLeft
if mapJobsNumLeft > 0 {
if len(c.mapQueue) == 0 {
reply.JobType = Wait
return nil
}
reply.JobType = Map
reply.MapArgs.JobId = <-c.mapQueue
reply.MapArgs.File = c.files[reply.MapArgs.JobId]
reply.MapArgs.NReduce = c.nReduce
// fmt.Printf("Assigned Map Job No.%v\n", reply.MapArgs.WorkerId)
go c.waitForWorker(Map, reply.MapArgs.JobId)
} else if reduceJobsNumLeft > 0 {
if len(c.reduceQueue) == 0 {
reply.JobType = Wait
return nil
}
reply.JobType = Reduce
reply.ReduceArgs.JobId = <-c.reduceQueue
reply.ReduceArgs.IntermediateFileNames = c.intermediateFileNames[reply.ReduceArgs.JobId]
// fmt.Printf("Assigned Reduce Job No.%v\n", reply.ReduceArgs.WorkerId)
go c.waitForWorker(Reduce, reply.ReduceArgs.JobId)
} else {
reply.JobType = Exit
// fmt.Println("No job left to assign.")
}
return nil
}
// worker calls this function to signal that the job has been completed
func (c *Coordinator) CompleteJob(args *CompleteJobArgs, reply *CompleteJobReply) error {
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
jobId := args.JobId
switch args.TheJobType {
case Map:
if c.mapJobsStatus[jobId] == 0 {
c.mapJobsNumLeft--
}
c.mapJobsStatus[jobId] = 1
// fmt.Printf("Completed Map Job No.%v\n", workerId)
case Reduce:
if c.reduceJobsStatus[jobId] == 0 {
c.reduceJobsNumLeft--
}
c.reduceJobsStatus[jobId] = 1
// fmt.Printf("Completed Reduce Job No.%v\n", workerId)
}
return nil
}
// wait the worker for 10 seconds
// if the job is not completed after 10 seconds
// then assume the worker has already crashed
// put the job in the queue, to assign another worker to work on this job
func (c *Coordinator) waitForWorker(jobType JobType, workerId int) {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
switch jobType {
case Map:
if c.mapJobsStatus[workerId] != 1 {
// fmt.Printf("Map job %v timeout\n", workerId)
c.mapQueue <- workerId
}
case Reduce:
if c.reduceJobsStatus[workerId] != 1 {
// fmt.Printf("Reduce job %v timeout\n", workerId)
c.reduceQueue <- workerId
}
}
}
func (c *Coordinator) PassFileNames(args *PassFileNamesArgs, reply *PassFileNamesReply) error {
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
intermediateFileNames := args.IntermediateFileNames
for i, intermediateFileName := range intermediateFileNames {
c.intermediateFileNames[i] = append(c.intermediateFileNames[i], intermediateFileName)
}
return nil
}
func (c *Coordinator) server() {
rpc.Register(c)
rpc.HandleHTTP()
// l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
os.Remove(sockname)
l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)
if e != nil {
log.Fatal("listen error:", e)
}
go http.Serve(l, nil)
}
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls Done() periodically to find out
// if the entire job has finished.
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
c.mutexLock.Lock()
defer c.mutexLock.Unlock()
if c.mapJobsNumLeft == 0 && c.reduceJobsNumLeft == 0 {
return true
}
return false
}
// create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
// Your code here.
c.files = files
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.intermediateFileNames = make([][]string, nReduce)
c.reduceJobsNumLeft = nReduce
c.mapJobsNumLeft = len(files)
c.mapQueue = make(chan int, len(files))
c.reduceQueue = make(chan int, nReduce)
// put all jobs in the queue
for i := 0; i < len(files); i++ {
c.mapQueue <- i
}
for i := 0; i < nReduce; i++ {
c.reduceQueue <- i
}
c.mapJobsStatus = make([]int, len(files))
c.reduceJobsStatus = make([]int, nReduce)
// fmt.Println("----------------------------------------------------------------")
// fmt.Printf("c.files num : %v\n", len(c.files))
// fmt.Printf("c.nReduce = %d\n", c.nReduce)
// fmt.Println("----------------------------------------------------------------")
c.server()
return &c
}
worker.go
package mr
import (
"crypto/rand"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"hash/fnv"
"io"
"log"
"math/big"
"net/rpc"
"os"
"plugin"
"sort"
"time"
)
// Map functions return a slice of KeyValue.
type KeyValue struct {
Key string
Value string
}
// for sorting by key.
type ByKey []KeyValue
// for sorting by key.
func (a ByKey) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a ByKey) Swap(i, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a ByKey) Less(i, j int) bool { return a[i].Key < a[j].Key }
// use ihash(key) % NReduce to choose the reduce
// task number for each KeyValue emitted by Map.
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
h.Write([]byte(key))
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
// load the application Map and Reduce functions
// from a plugin file, e.g. ../mrapps/wc.so
func loadPlugin(filename string) (func(string, string) []KeyValue, func(string, []string) string) {
p, err := plugin.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot load plugin %v", filename)
}
xmapf, err := p.Lookup("Map")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Map in %v", filename)
}
mapf := xmapf.(func(string, string) []KeyValue)
xreducef, err := p.Lookup("Reduce")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot find Reduce in %v", filename)
}
reducef := xreducef.(func(string, []string) string)
return mapf, reducef
}
func mapWorker(args MapWorkerArgs) {
nReduce := args.NReduce
file, err := os.Open(args.File)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", args.File)
return
}
content, err := io.ReadAll(file)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", args.File)
return
}
file.Close()
mapf, _ := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
kva := mapf(args.File, string(content))
// divide the key value pairs for each reduce workers
kvalist := make([][]KeyValue, nReduce)
intermediateFileNameList := make([]string, nReduce)
for _, kv := range kva {
num := ihash(kv.Key) % nReduce // the reduce task number for the KeyValue pair
kvalist[num] = append(kvalist[num], kv)
}
// write the divided key value pairs to disk
for i, kva := range kvalist {
intermediateFileName := fmt.Sprintf("mr-%d-%d", args.JobId, i)
intermediateFileNameList[i] = intermediateFileName
intermediateFile, err := os.Create(intermediateFileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot create %v", intermediateFileName)
}
enc := json.NewEncoder(intermediateFile)
for _, kv := range kva {
err := enc.Encode(&kv)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot encode %v", kv)
return
}
}
}
// pass the address (file name) of the key value pairs file to the master
pargs := new(PassFileNamesArgs)
preply := new(PassFileNamesReply)
pargs.IntermediateFileNames = intermediateFileNameList
ok := call("Coordinator.PassFileNames", &pargs, &preply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("Call PassFileNames failed.")
return
}
// send message to the coordinator that the map job has been completed
cargs := new(CompleteJobArgs)
cargs.TheJobType = Map
cargs.JobId = args.JobId
creply := new(CompleteJobReply)
ok = call("Coordinator.CompleteJob", &cargs, &creply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("Call CompleteJob failed.")
return
}
}
func reduceWorker(args ReduceWorkerArgs) {
intermediateFileNames := args.IntermediateFileNames
_, reducef := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
intermediate := make([]KeyValue, 0)
// read key value pairs from intermediate files
for _, fileName := range intermediateFileNames {
intermediateFile, err := os.Open(fileName)
if err != nil {
// it is possible that map didn't generate this intermediate file
// and it is nomal
continue
}
dec := json.NewDecoder(intermediateFile)
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := dec.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
break
}
intermediate = append(intermediate, kv)
}
intermediateFile.Close()
}
sort.Sort(ByKey(intermediate))
// create output file
oname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-out-%v", args.JobId)
// create temporary file to avoide problems with parallel reduce workers writing to the same file
ofile, _ := os.CreateTemp("./", "mr-out-*")
// ofile, _ := os.Create(oname)
//
// call Reduce on each distinct key in intermediate[],
// and print the result to ofile
//
i := 0
for i < len(intermediate) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {
j++
}
values := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)
}
output := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)
// this is the correct format for each line of Reduce output.
fmt.Fprintf(ofile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)
i = j
}
ofile.Close()
os.Rename(ofile.Name(), oname)
// send message to the coordinator that this reduce job has been completed
cargs := new(CompleteJobArgs)
cargs.TheJobType = Reduce
cargs.JobId = args.JobId
creply := new(CompleteJobReply)
ok := call("Coordinator.CompleteJob", &cargs, &creply)
if !ok {
fmt.Println("Call CompleteJob failed.")
return
}
}
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,
reducef func(string, []string) string,
) {
workerId, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, big.NewInt(1000))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Starting worker %v\n", workerId)
for {
args := new(JobArgs)
reply := new(JobReply)
ok := call("Coordinator.GetJob", &args, &reply)
// sleep for a little while to avoid all jobs being asked by one worker
// time.Sleep(time.Second)
if !ok {
// assume that the coordinator has exited because the job is done
fmt.Println("Call GetJob failed.")
return
} else {
switch reply.JobType {
case Map:
fmt.Printf("Running Map No.%d on worker %v\n", reply.MapArgs.JobId, workerId)
mapWorker(reply.MapArgs)
case Reduce:
fmt.Printf("Running Reduce No.%d on worker %v\n", reply.ReduceArgs.JobId, workerId)
reduceWorker(reply.ReduceArgs)
// time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
case Exit:
fmt.Println("No job to run, worker exit.")
return
case Wait:
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 50)
}
}
}
}
// send an RPC request to the coordinator, wait for the response.
// usually returns true.
// returns false if something goes wrong.
func call(rpcname string, args interface{}, reply interface{}) bool {
// c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
sockname := coordinatorSock()
c, err := rpc.DialHTTP("unix", sockname)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("dialing:", err)
}
defer c.Close()
err = c.Call(rpcname, args, reply)
if err == nil {
return true
}
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本