(笔记)linux内核链表实现(含示例)
背景:Linux内核实现的是双向循环链表,提供了链表操作的基本功能(参见my_list.h)。
一、my_list.h(链表实现)
#ifndef __MY_LIST_H__ #define __MY_LIST_H__ struct list_head { struct list_head *prev; struct list_head *next; }; #define INIT_LIST_HEAD(ptr) do { \ (ptr)->next = (ptr); \ (ptr)->prev = (ptr); \ } while(0) static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { next->prev = new; new->next = next; new->prev = prev; prev->next = new; } static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head, head->next); } static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head->prev, head); } static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; } #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x0) #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x0) static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = LIST_POISON1; entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; } static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head) { return head->next == head; } #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \ const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \ (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );}) #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \ container_of(ptr, type, member) #define list_for_each(pos, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) #define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \ pos = n, n = pos->next) #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) #define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \ for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \ n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \ &pos->member != (head); \ pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) #endif
二、my_list.c(链表使用示例)
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "my_list.h"
//定义链表大结构体 typedef struct Student
{ struct list_head list; unsigned int id; char name[32]; unsigned int score; } T_Student; struct list_head g_stu_list; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { char tmp[32] = { 0 };
//初始化链表 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&g_stu_list); int i = 0; for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { T_Student* pstu = NULL; pstu = (T_Student*)malloc(sizeof(T_Student)); memset(pstu, 0, sizeof(T_Student)); pstu->id = i; memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(tmp)); snprintf(tmp, sizeof(tmp) - 1, "mt-0%d", i); strcpy(pstu->name, tmp); pstu->score = 90 + i; printf("i: %d, id: %d, name: %s, score: %d, &list = %p\n", i, pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score, &pstu->list); list_add(&pstu->list, &g_stu_list); } printf("\r\n"); printf("........................list_for_each start....................\n"); struct list_head* pos = NULL, * temp = NULL; T_Student* pstu = NULL, * pstuTemp = NULL; list_for_each(pos, &g_stu_list) { pstu = list_entry(pos, T_Student, list); printf("id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); } printf("........................list_for_each end....................\n"); printf("\r\n"); printf("........................list_for_each_safe start....................\n"); list_for_each_safe(pos, temp, &g_stu_list) { pstu = list_entry(pos, T_Student, list); printf("id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); } printf("........................list_for_each_safe end....................\n"); printf("\r\n"); printf("........................list_for_each_entry start....................\n"); list_for_each_entry(pstu, &g_stu_list, list) { printf(">>>>id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); } printf("........................list_for_each_entry end....................\n"); printf("\r\n"); printf("........................list_for_each_entry_safe start....................\n"); list_for_each_entry_safe(pstu, pstuTemp, &g_stu_list, list) { printf(">>>>id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); } printf("........................list_for_each_entry_safe end....................\n"); printf("\r\n"); printf("........................list_for_each_safe delete node start....................\n"); //list_for_each(pos, &g_stu_list) //list_for_each遍历时若删除了pos指向的当前元素,则会导致pos节点的prev和next指针从链表断开,无法继续遍历, list_for_each_safe(pos, temp, &g_stu_list) { pstu = list_entry(pos, T_Student, list); printf("id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); if (pstu->id == 4) //delete node { list_del(&pstu->list); } } printf("........................list_for_each_safe delete and print list....................\n"); list_for_each_safe(pos, temp, &g_stu_list) { pstu = list_entry(pos, T_Student, list); printf("id: %d---name: %s---score: %d\n", pstu->id, pstu->name, pstu->score); } printf("........................list_for_each_safe delete node end....................\n"); return 0; }
三、链表示例运行结果
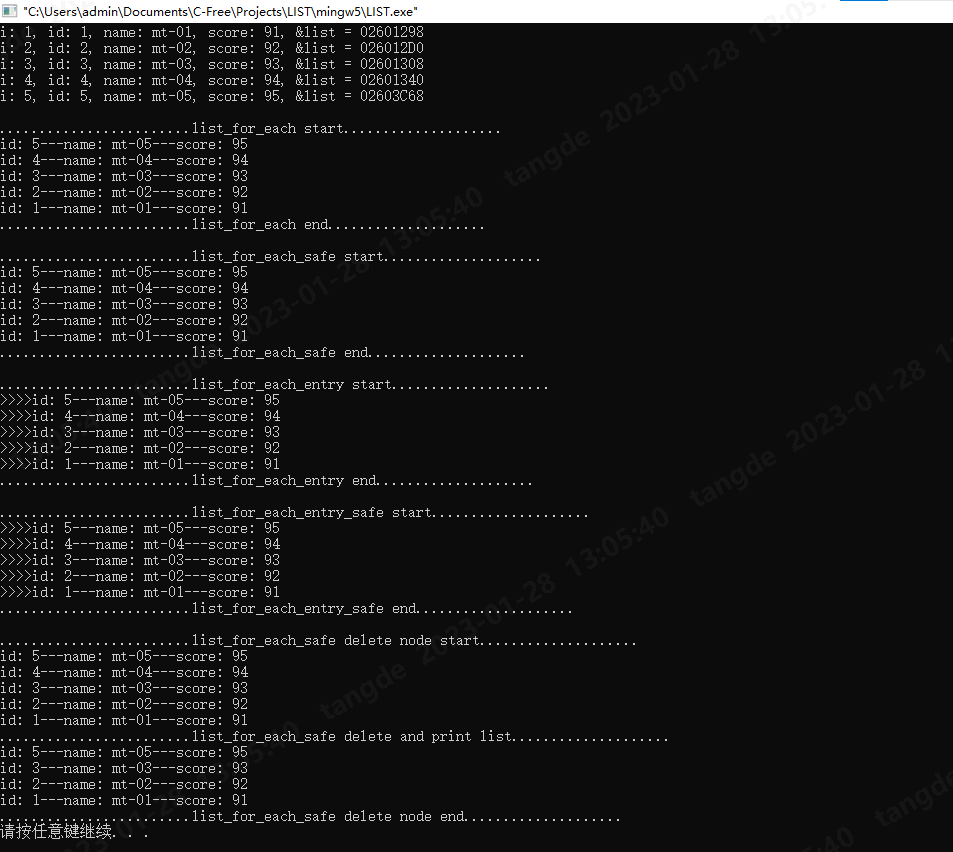
作者:tdyizhen1314(一位从事软硬件开发十年以上的老兵的故事,希望与大家一起交流,共同进步)
邮箱:495567585@qq.com
分类:
C/C++
posted on 2023-01-28 13:15 tdyizhen1314 阅读(498) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具