链表篇
链表篇
跳-移除链表元素-203-力扣
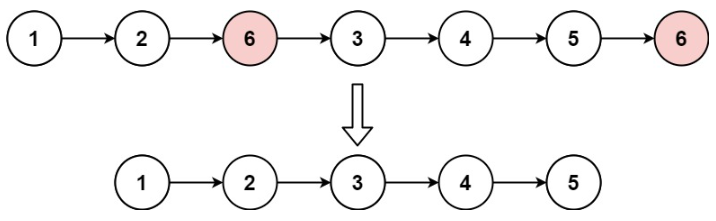
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
带虚拟头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 带虚拟头结点
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode first = dummy.next;
ListNode last = dummy;
while (first != null) {
if (first.val == val) {
last.next = first.next;
} else {
last = first;
}
first = first.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
不带虚拟头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 不带虚拟头结点
// 判断链表是否为空 or 判断head头的情况
while (head==null || head.val==val) {
if (head == null) return head;
head = head.next;
}
// 下面常规操作
ListNode first = head.next;
ListNode last = head;
while (first != null) {
if (first.val == val) {
last.next = first.next;
} else {
last = first;
}
first = first.next;
}
return head;
}
}
跳-设计链表-707-力扣
class MyLinkedList {
public:
// 定义链表节点结构体
struct LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode* next;
LinkedNode(int val):val(val), next(nullptr){}
};
// 初始化链表
MyLinkedList() {
_dummyHead = new LinkedNode(0); // 这里定义的头结点 是一个虚拟头结点,而不是真正的链表头结点
_size = 0;
}
// 获取到第index个节点数值,如果index是非法数值直接返回-1, 注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
int get(int index) {
if (index > (_size - 1) || index < 0) {
return -1;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while(index--){ // 如果--index 就会陷入死循环
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur->val;
}
// 在链表最前面插入一个节点,插入完成后,新插入的节点为链表的新的头结点
void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在链表最后面添加一个节点
void addAtTail(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr){
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在第index个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果index大于链表的长度,则返回空
// 如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > _size) return;
if(index < 0) index = 0;
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 删除第index个节点,如果index 大于等于链表的长度,直接return,注意index是从0开始的
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= _size || index < 0) {
return;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur ->next;
}
LinkedNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
//delete命令指示释放了tmp指针原本所指的那部分内存,
//被delete后的指针tmp的值(地址)并非就是NULL,而是随机值。也就是被delete后,
//如果不再加上一句tmp=nullptr,tmp会成为乱指的野指针
//如果之后的程序不小心使用了tmp,会指向难以预想的内存空间
tmp=nullptr;
_size--;
}
// 打印链表
void printLinkedList() {
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (cur->next != nullptr) {
cout << cur->next->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
int _size;
LinkedNode* _dummyHead;
};
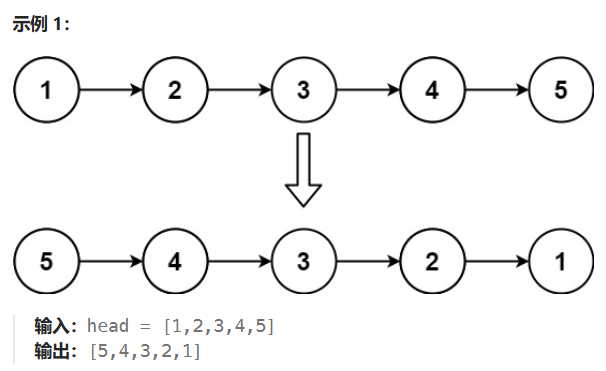
做-翻转链表-206-力扣
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
双指针法
// 法一:双指针法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
递归
// 法二:递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
我的感觉:一个指向当前节点,再有一个指向前一个节点,因为当前节点的下一个节点可以通过指针很容易得到。
两两交换链表中的节点
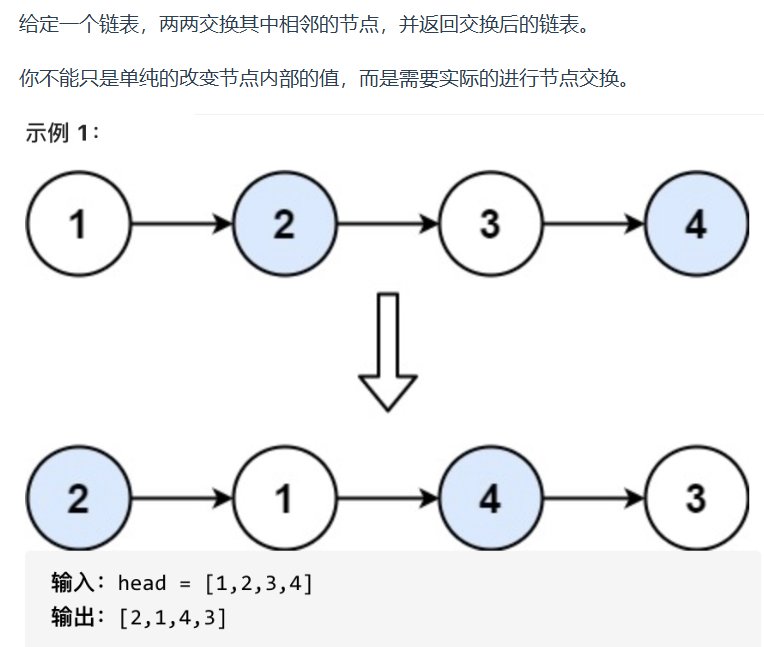
// 递归版本
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// base case 退出提交
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 获取当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
// 进行递归
ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);
// 这里进行交换
next.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return next;
}
}
比如交换3和4,主要思想还是要能够找到3前面的那个元素,要提前知道,不然交换不了3和4.不清楚3和4前面的那个元素,可能3和4在交换的过程中前面的就和它们断开了。
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode cur = dumyhead;
ListNode temp; // 临时节点,保存两个节点后面的节点
ListNode firstnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第一个节点
ListNode secondnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第二个节点
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
temp = cur.next.next.next;
firstnode = cur.next;
secondnode = cur.next.next;
cur.next = secondnode; // 步骤一
secondnode.next = firstnode; // 步骤二
firstnode.next = temp; // 步骤三
cur = firstnode; // cur移动,准备下一轮交换
}
return dumyhead.next;
}
}
删除链表的倒数第N个节点

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
for (int i=1; i<=n+1; i++) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
}
while (fastIndex != null) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
}
#slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next; 这个地方我之前用的这个,存在空指针异常的情况。
if (slowIndex.next != null) {
slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
链表相交

public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
for (curA != null) {
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
for (curB != null) {
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
if (lenA > lenB) {
int sublen = lenA - lenB;
while (sublen != 0) {
headA = headA.next;
sublen--;
}
} else {
int sublen = lenB - lenA;
while (sublen != 0) {
headB = headB.next;
sublen--;
}
}
while (headA != null) {
if (headA == headB) {
return headA;
}
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
环形链表||

我自己写的代码:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fastIndex = head;
ListNode slowIndex = head;
/***
if (fastIndex != null && fastIndex.next != null) 这个是后来改的判断条件,一开始的是if (fastIndex.next != null) 直接报空指针异常
*/
if (fastIndex != null && fastIndex.next != null) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
} else {
return null;
}
while (fastIndex != slowIndex) {
if (fastIndex != null && fastIndex.next != null) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
} else {
return null;
}
}
fastIndex = head;
while (fastIndex != slowIndex) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
}
return fastIndex;
}
}
官方代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {// 有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
// 两个指针,从头结点和相遇结点,各走一步,直到相遇,相遇点即为环入口
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
这道题主要还是要掌握其中的窍门,尤其公式的推导。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号