String与InputStream互转的几种方法
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/iplayvs2008/article/details/11484627
- /**
- * 利用BufferedReader实现Inputstream转换成String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return String
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_Reader(InputStream in, String encode)
- {
- String str = "";
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, encode));
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null)
- {
- sb.append(str).append("\n");
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1)
- {
- e1.printStackTrace();
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return str;
- }
- /**
- * 利用byte数组转换InputStream------->String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_byteArr(InputStream in, String encode)
- {
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- byte[] b = new byte[1024];
- int len = 0;
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- while ((len = in.read(b)) != -1)
- {
- sb.append(new String(b, 0, len, encode));
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return "";
- }
- /**
- * 利用ByteArrayOutputStream:Inputstream------------>String <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param in
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static String Inputstr2Str_ByteArrayOutputStream(InputStream in,String encode)
- {
- ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
- byte[] b = new byte[1024];
- int len = 0;
- try
- {
- if (encode == null || encode.equals(""))
- {
- // 默认以utf-8形式
- encode = "utf-8";
- }
- while ((len = in.read(b)) > 0)
- {
- out.write(b, 0, len);
- }
- return out.toString(encode);
- }
- catch (IOException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return "";
- }
- /**
- * 利用ByteArrayInputStream:String------------------>InputStream <功能详细描述>
- *
- * @param inStr
- * @return
- * @see [类、类#方法、类#成员]
- */
- public static InputStream Str2Inputstr(String inStr)
- {
- try
- {
- // return new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes());
- // return new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- return new StringBufferInputStream(inStr);
- }
- catch (Exception e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return null;
- }
=====================================
从SDCard保存的txt文件读取中文到android系统中会出现乱码问题,如何解决这个乱码问题,网上有不少解答方法,譬如说利用String temp1 =EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312"); 但并非对所有的情况都适用,解决乱码问题首先要明白为什么会乱码。究其原因,是因为txt文件在win系统上保存时默认为ANSI格式,而android目前只支持UTF-8编码,因此将txt文件的中文读入android系统中会产生乱码。也有人说直接将txt另存为UTF-8编码格式来解决乱码问题,但这种方法指标不治本,不能要求用户手动去更改格式,客户第一嘛。因此还是需要想办法在程序中进行处理。
以下做了一些编码格式的测试:
测试文本: 122.11196,29.90573,北仑固废厂 测试代码段:
reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
strLine=reader.readLine() ;
String temp1 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312");
String temp2 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes("utf-8"),"utf-8");
String temp3 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"utf-8");
将文件存成 Unicode 格式
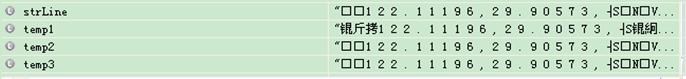
将文件存成utf-8 格式
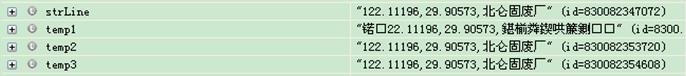
这种方式能得到非乱码的中文显示,但对于 utf-8 格式下取得的经纬度数字利用double lon = Double.parseDouble(lat); 报错 NumberFormatException,原因可能是 parseDouble(lat)方法不能处理存成utf-8格式的带标点小数。 将文件 存成 ANSI 格式

将代码改为:
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filename),"GB2312"));
strLine=reader.readLine() ;
String temp1 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"GB2312");
String temp2 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes("utf-8"),"utf-8");
String temp3 = EncodingUtils.getString(strLine.getBytes(),"utf-8");
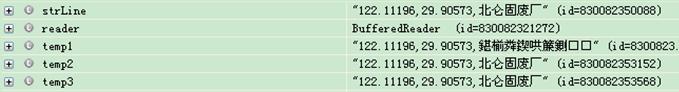
即解决了中文乱码问题,又解决了Double.parseDouble(lat)报错问题。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号