Linux-基础知识(一)
系统管理
Linux中的进程与服务
计算机中,一个正在执行的程序或者命令,被叫做“进程”(process)
启动之后一直存在、常驻内存的进程,一般被称作“服务”(service)
service服务管理(CentOS6版本-了解)
1)基本语法
service 服务名 start|stop|restart|status
2)经验技巧
查看服务的方法:/etc/init.d/服务名,发现只有两个服务保留在service
3)案例实操
(1)查看网络服务的状态
[root@localhost init.d]# service network status
(2)停止网络服务
[root@localhost init.d]# service network status
(3)启动网络服务
[root@localhost init.d]# service network start
chkconfig设置后台服务的自启配置(CentOS 6版本)
1)基本语法
chkconfig (功能描述:查看所有服务器自启配置)
chkconfig 服务名 off (功能描述:关掉指定服务的自动启动)
chkconfig 服务名 on (功能描述:开启指定服务的自动启动)
chkcpnfig 服务名 --list (功能描述:查看服务开启启动状态)
2)案例实操
(1)开启/关闭network(网络)服务的自动启动
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig network on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig network off
(2)开启/关闭network服务指定级别的自动启动
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 指定级别 network on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 指定级别 network off
systemctl (CentOS 7版本-重点)
1)基本语法
systemctl start|stop|restart|status 服务名
2)经验技巧
查看服务的方法:/usr/lib/systemd/system
[root@localhost system]# pwd
/usr/lib/systemd/system
[root@localhost system]# ls -al
总用量 1460
drwxr-xr-x. 27 root root 20480 1月 9 17:12 .
drwxr-xr-x. 13 root root 4096 11月 9 15:10 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 275 8月 13 2019 abrt-ccpp.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 380 8月 13 2019 abrtd.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 361 8月 13 2019 abrt-oops.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 266 8月 13 2019 abrt-pstoreoops.service
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 262 8月 13 2019 abrt-vmcore.service
3)案例实操
(1)查看防火墙服务的状态
[root@localhost system]# systemctl status firewalld
(2)停止防火墙服务
[root@localhost system]# systemctl stop firewalld
(3)启动防火墙服务
[root@localhost system]# systemctl start firewalld
(3)重启防火墙服务
[root@localhost system]# systemctl restart firewalld
systemctl设置后台服务的自启配置
1)基本语法
systemctl list-unit-files (功能描述:查看服务开机启动状态)
systemctl disable service_name (功能描述:关掉指定服务的自动启动)
systemctl enable service_name (功能描述:开启指定服务的自动启动)
2)案例实操
(1)开启/关闭iptables(防火墙)服务的自动启动
[root@localhost system]# systemctl enable firewalld.service
[root@localhost system]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
系统运行级别
1)Linux运行级别[CentOS 6],如下图所示:
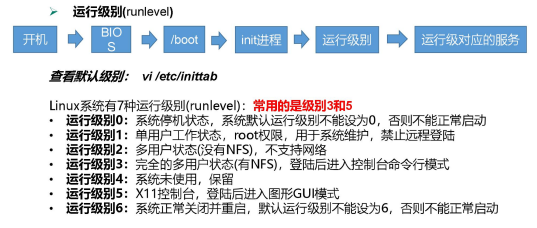
2)CentOS7的运行级别简化为:
multi-user.target 等价于原运行级别 3(多用户有网,无图形界面)
graphical.target 等价于原运行级别 5(多用户有网,有图形界面)
3)查看当前运行级别:
systemctl get-default
4)修改当前运行级别
systemctl set-default TARGET.target(这里TARGET取multi-user或者graphical)
关闭防火墙
1)临时关闭防火墙
(1)查看防火墙的状态
[root@localhost system]# systemctl status firewalld
(2)临时关闭防火墙
[root@localhost system]# systemctl stop firewalld
2)开机启动时关闭防火墙
(1)查看防火墙开机启动状态
[root@localhost system]# systemctl enable firewalld.service
(2)设置开机时关闭防火墙
[root@localhost system]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
关机重启命令
在Linux领域内大多用在服务器上,很少遇到关机的操作。毕竟服务器上跑一个服务是永无止境的,除非特殊情况下,不得已才会关机。
1)基本语法
(1)sync (功能描述:将数据有内存同步到硬盘中)
(2)halt (功能描述:停机,关闭系统,但不断电)
(3)poweroff (功能描述:关机,断电)
(4)reboot (功能描述:重启,等同于shutdown -r now)
(5)shutdown [选项] 时间
| 选项 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -h | 相当于--halt,停机 |
| -r | -r=reboot 重启 |
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| now | 立刻关机 |
| 时间 | 等待多久后关机(时间单位是分钟)。 |
2)经验技巧
Linux系统为了提高磁盘的续写效率,对磁盘采取了“预读迟写”操作方式。当用户保存文件时,Linux核心并不一定立即将保存的数据写入到磁盘中,而是将数据保存在缓冲区中,等缓冲区满时再写入磁盘,这种方式可以极大的提高磁盘写入数据的效率。但是,也带来了安全隐患,如果数据还未写入磁盘时,系统掉电或者其他严重问题出现,则将导致数据丢失。使用sync指令可以立即将缓冲区的数据写入磁盘。
3)案例实操
(1)将数据同步到硬盘中
[root@localhost system]# sync
(2)重启
[root@localhost system]# reboot
(3)停机(不断电)
[root@localhost ~]# halt
(4)计算机将在1分钟后关机,并且会显示在登录用户的当前屏幕中
[root@localhost ~]# shutdown -h 1 ‘This server will shutdown after 1 mins’
(5)立马关机(等同于poweroff)
[root@localhost ~]# shutdown -h now
(6)系统立马重启(等同于reboot)
[root@localhost ~]# shutdown -r now


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号