Spring 声明式事物控制
一,编程式事务控制
事务控制是对一一些操作用事务管理的方式来解决从而保证数据的一致新问题。而spring中的事务控制有编程式事务控制(需要我们自己调用或实现sping接口来实现事务控制),或者是申明式事务控制。我们在这里采用的是申明式事务控制。
1.1 编程式事物控制相关对象
1.1.1 PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager 接口是 spring 的事务管理器,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法。
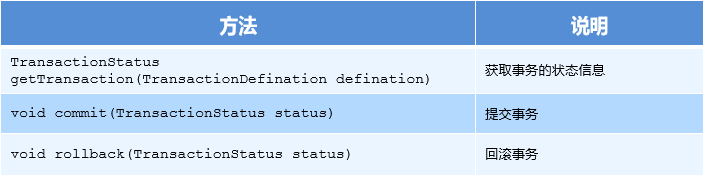
注意:
PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类,
例如:
Dao 层技术是jdbc 或 mybatis 时:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
Dao 层技术是hibernate时:org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager
1.1.2 TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition 是事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法:
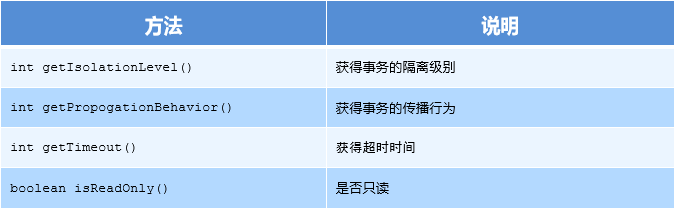
事务隔离级别:
设置隔离级别,可以解决事务并发产生的问题,如脏读、不可重复读和虚读。
ISOLATION_DEFAULT
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE
事务传播行为:
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值) SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务) MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常 REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。 NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起 NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常 NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作 超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置 是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
1.1.3 TransactionStatus
TransactionStatus 接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法介绍如下。以下方法为自动执行的方法:
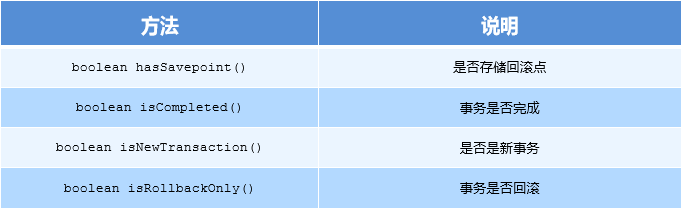
以上的几个对象不需要我们自己去实现事务控制,我们可以采用声明式事务控制的方式来帮助我们实现事务的控制。
二,基于XML的声明式事物控制
2.1 声明式事物控制定义
Spring 的声明式事务顾名思义就是采用声明的方式来处理事务。这里所说的声明,就是指在配置文件中声明,用在 Spring 配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。
作用:
事务管理不侵入开发的组件。具体来说,业务逻辑对象就不会意识到正在事务管理之中,事实上也应该如此,因为事务管理是属于系统层面的服务,
而不是业务逻辑的一部分,如果想要改变事务管理策划的话,也只需要在定义文件中重新配置即可
在不需要事务管理的时候,只要在设定文件上修改一下,即可移去事务管理服务,无需改变代码重新编译,这样维护起来极其方便
注意:底层是采用AOP的形式来实现事务控制
2.2 实现方式
1.在配置文件中引入命名空间和约束:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" // 申明式事务的命名空间 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> // 声明式事务的约束
2.配置事务增强
<!--平台事物管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--事物增强即参数配置--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!--这里是对所有的方法都采用统一的配置,也可以单独配置也可以不配置--> <tx:method name="*"></tx:method> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--事物的AOP增强--> <aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itcast.com.itcast.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut> <!--这里的配置是配置需要在哪些方法进行事务控制,这里是service.impl下的所有类和方法--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:advisor> </aop:config>
注意上面的dataSource:如下配置 采用C3P0连接池和JDBCTemplate,需要导入这两者的依赖以及数据库的依赖
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///db3?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="qwe123"></property> </bean> <bean id="template" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean>
测试:
package com.itcast.com.itcast.service.impl; import com.itcast.com.itcast.service.AccountService; import com.itcast.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDaoImpl accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDaoImpl accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } public void transfer() { accountDao.out("wallace", 50.0); // int i = 1/0; 通过异常来测试该事务控制是否成功 accountDao.in("laowang", 50.0); } }
2.3 事务参数配置
上面的实例中的tx:即事务增强我们只设置了*,哪还有那些可以设置呢?
<!--事物增强即参数配置--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!--这里是对所有的方法都采用统一的配置,也可以单独配置也可以不配置--> <tx:method name="*"></tx:method> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice>
该切点有如下配置:
<tx:method> 代表切点方法的事务参数的配置,例如: <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/> name:切点方法名称 isolation:事务的隔离级别 propogation:事务的传播行为 timeout:超时时间 read-only:是否只读
三,基于注解的声明式事物控制
3.1 注解式事务实现
1.编写DAO实现类
package com.itcast.dao.impl; import com.itcast.dao.AccountDao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate template; public void setTemplate(JdbcTemplate template){ this.template = template; } public void out(String outMan, double money) { String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?"; System.out.println(template); template.update(sql,money, outMan); } public void in(String inMan, double money){ String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?"; template.update(sql,money, inMan); } }
2.编写调用接口的service
package com.itcast.service.impl; import com.itcast.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itcast.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service("accountService") @Transactional public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDaoImpl accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDaoImpl accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } @Transactional( isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public void transfer() { accountDao.out("wallace", 50.0); // int i = 1/0; accountDao.in("laowang", 50.0); } }
3.配置文件启动组件扫描和事务驱动启动
<!—之前省略datsSource、jdbcTemplate、平台事务管理器的配置--> <!--组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itcast"/> <!--事务的注解驱动--> <tx:annotation-driven/>
以上是使用注解进行声明式事务控制的实现。有如下注意事项需要注意:
使用 @Transactional 在需要进行事务控制的类或是方法上修饰,注解可用的属性同 xml 配置方式,例如隔离级别、传播行为等。 注解使用在类上,那么该类下的所有方法都使用同一套注解参数配置。 使用在方法上,不同的方法可以采用不同的事务参数配置。 Xml配置文件中要开启事务的注解驱动<tx:annotation-driven />

