C#泛型
1、引入泛型
泛型不是一个简单的语法糖,是框架升级支持的
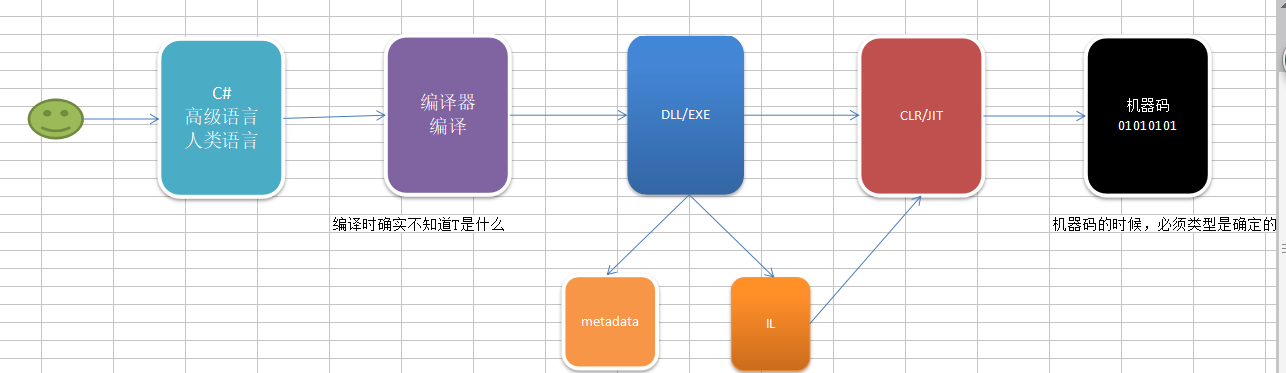
List<string>就是泛型,为什么要有泛型?
List<T>是一个集合,可能是一组int,也可能是一组string,泛型就是用一个东西来满足多种不同类型的需求的。
2、泛型方法
方法名称后面加上尖括号,里面是类型参数,类型参数实际上就是一个类型T声明,方法就可以用这个类型T了。泛型声明方法时,并没有写死类型,T是什么,并不知道,T要等着调用的时候才指定。正式因为没有写死,才拥有了无限的可能。
泛型的设计思想--延迟声明:推迟一切可以推迟的,一切能晚点再做的事,就晚一点再做。泛型不是一个简单的语法糖,是框架升级支持的。泛型方法的性能跟普通方法一致,是最好的,而且还能一个方法满足多个不同类型。
下面来看下代码是怎么写的:
public static void Show<T>(T tParameter)//, T t = default(T { Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(CommonMethod), tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter); }
泛型类、泛型委托等和泛型方法声明类似:
//泛型类 public class GenericClass<T> where T : ISports { } //泛型接口 public interface GenericInterface<S> { } //方形委托 public delegate void Do<T>() where T : ISports;
WebService WCF都不能用泛型,为什么?
因为这些是跨语言的,别的语言也能用,不支持泛型,服务在发布的时候是必须确定的,泛型在编译时确定不了。
3、泛型约束
没有约束,其实很受局限。
基类约束:
where T:BaseModel
1、可以把T当成基类---权利
2、T必须是BaseModel或者其子类
为什么要有约束?
因为有约束才有权利,自由主义的鼻祖洛克先生说过,有了法律,才有自由。
泛型:不同的类型都能进来,任何的类型都能过来,你知道我是谁?
where T:class 引用类型约束;引用类型
where T:struct
where T:new() 无参构造函数约束
public static void Show<T>(T tParameter) //where T : String//密封类约束的不行,因为没有意义 //where T : People //where T : ISports where T : People, ISports, IWork, new() { Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(GenericConstraint), tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter); Console.WriteLine($"{tParameter.Id} {tParameter.Name}"); tParameter.Hi(); //tParameter.Pingpang(); }
public T GetT<T, S>() //where T : class//引用类型约束 //where T : struct//值类型 where T : new()//无参数构造函数 where S : class { //return null; //return default(T);//default是个关键字,会根据T的类型去获得一个默认值 return new T(); //throw new Exception(); }
泛型属性的初始化:
public T Data { get; set; }= System.Activator.CreateInstance<T>();
4、协变、逆变
.net4.0才出现的,只能放在接口或者委托的泛型参数前面
out协变 covariant,修饰返回值,只能作为返回值
in 逆变 contravariant,修饰传输参数,只能作为传入值
public class Bird { public int Id { get; set; } } public class Sparrow : Bird { public string Name { get; set; } } {//协变 IEnumerable<Bird> birdList1 = new List<Bird>(); IEnumerable<Bird> birdList2 = new List<Sparrow>(); Func<Bird> func = new Func<Sparrow>(() => null); ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerList1 = new CustomerListOut<Bird>(); ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerList2 = new CustomerListOut<Sparrow>(); } {//逆变 ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerList2 = new CustomerListIn<Sparrow>(); ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerList1 = new CustomerListIn<Bird>(); ICustomerListIn<Bird> birdList1 = new CustomerListIn<Bird>(); birdList1.Show(new Sparrow()); birdList1.Show(new Bird()); Action<Sparrow> act = new Action<Bird>((Bird i) => { }); } { IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList1 = new MyList<Sparrow, Bird>(); IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList2 = new MyList<Sparrow, Sparrow>();//协变 IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList3 = new MyList<Bird, Bird>();//逆变 IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList4 = new MyList<Bird, Sparrow>();//协变+逆变 }
5、泛型缓存
每个不同的T,都会生成一份不同的副本,适合不同的类型,需要缓存一份数据 场景,效率高
如有不对的地方,希望大家多指教!



