tensorflow GPU版本配置加速环境
import tensorflow as tf
tf.test.is_gpu_available()
- 背景
环境:Anaconda 、tensorflow_gpu==1.4.0 (这里就用1.4.0版本做演示了,虽然现在的已经是2.0版本了)
如下图是各个版本的cuda版本信息,在安装时需要看清楚,并不是所有的gpu版本都是cuda_8.0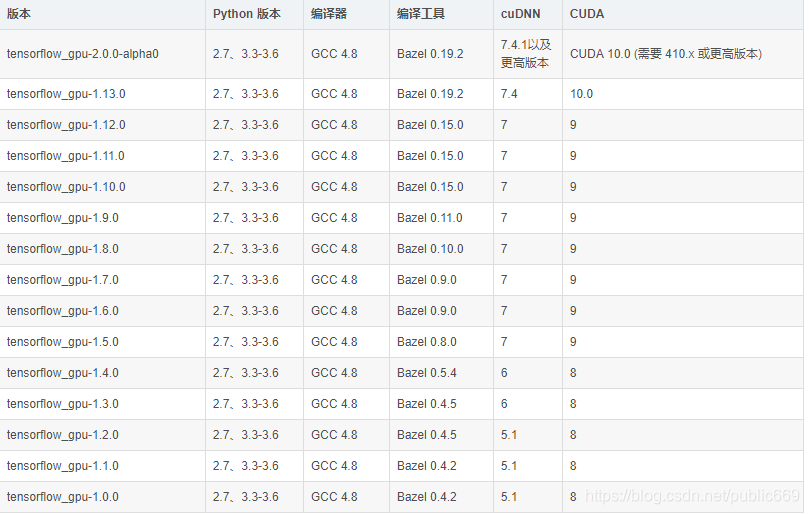
材料:cuda_8.0版本链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lzKSWRLl5lYMrYcLjGbVXw
提取码:2p9i - 安装cuda
下载之后点击执行cuda
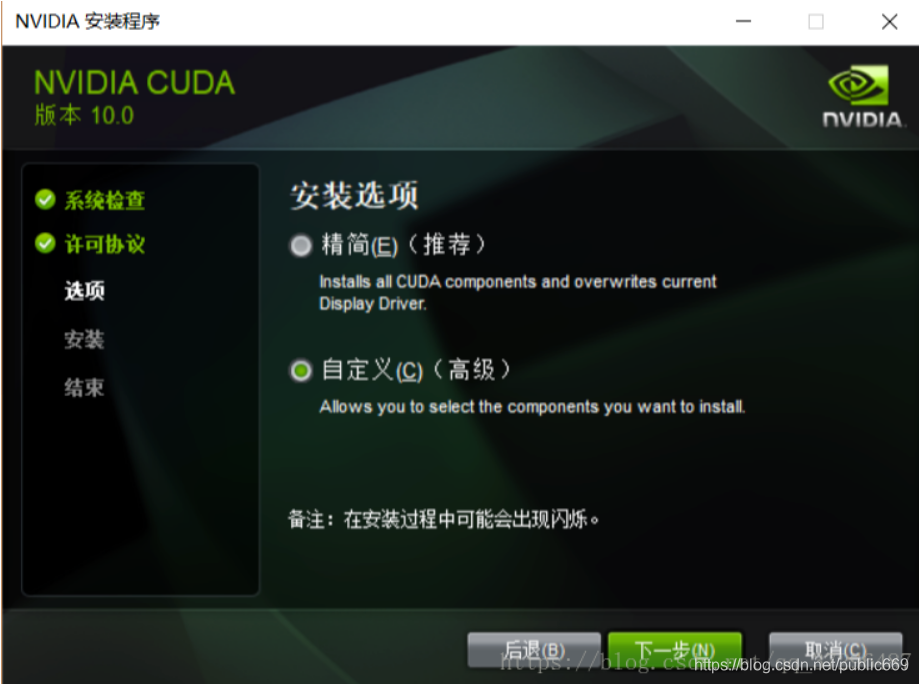
这里可以选择安装的模式:精简也可以选择自定义
安装路径可以自定义,也可以默认。选择自定义得记住安装的路径(后面配置环境变量)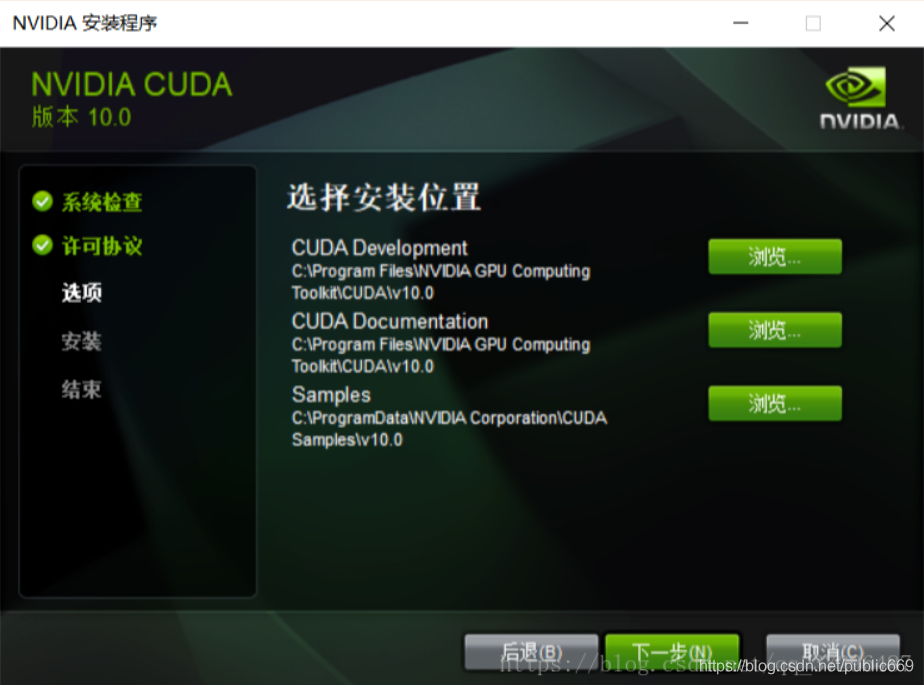
后面的就是一键Next,完成即可 - 配置系统环境变量
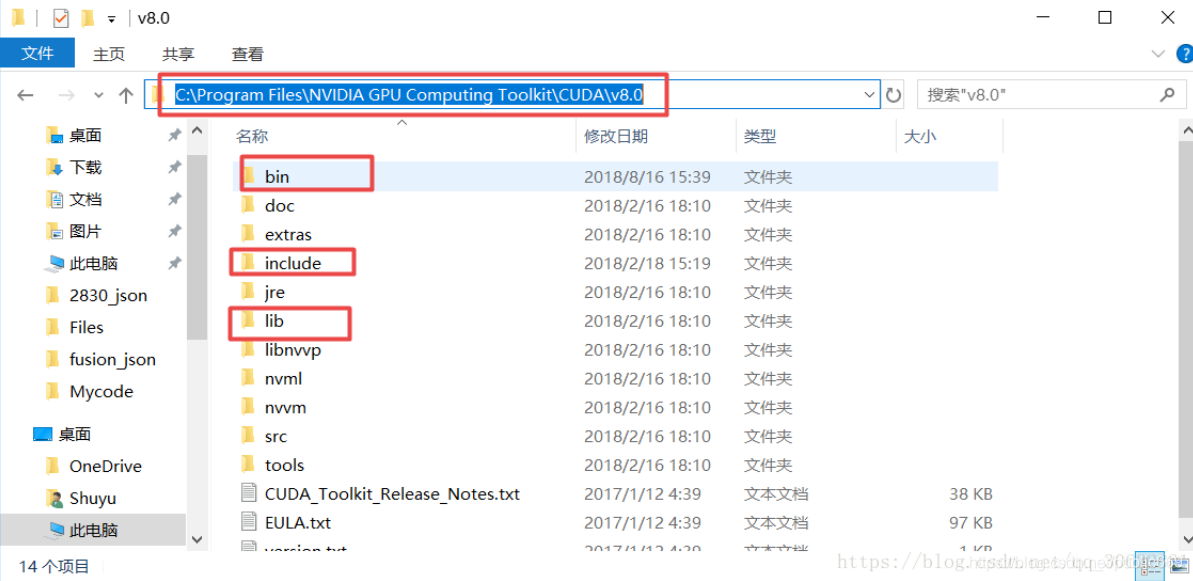
在系统环境变量中配置环境变量,在cuda安装好时会自动的配置两个,另外两个需要自己配置(ps:如果安装路径是自定义的话,需要根据情况自行变动)
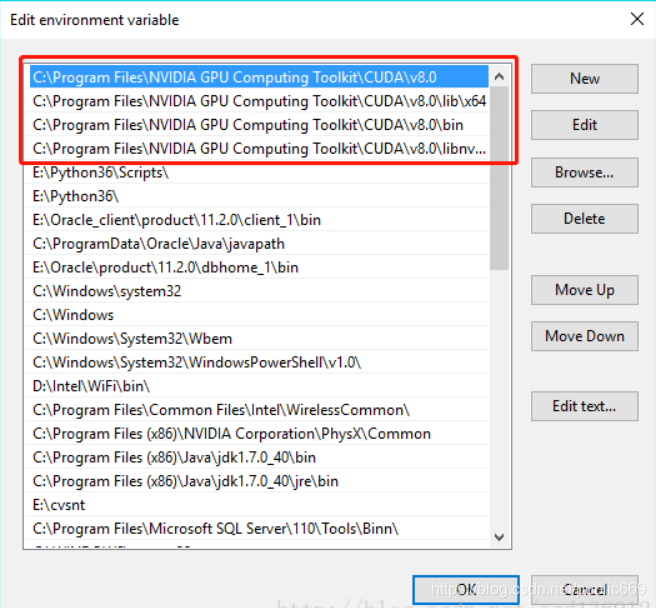
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\bin
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\lib\x64
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\libnvvp
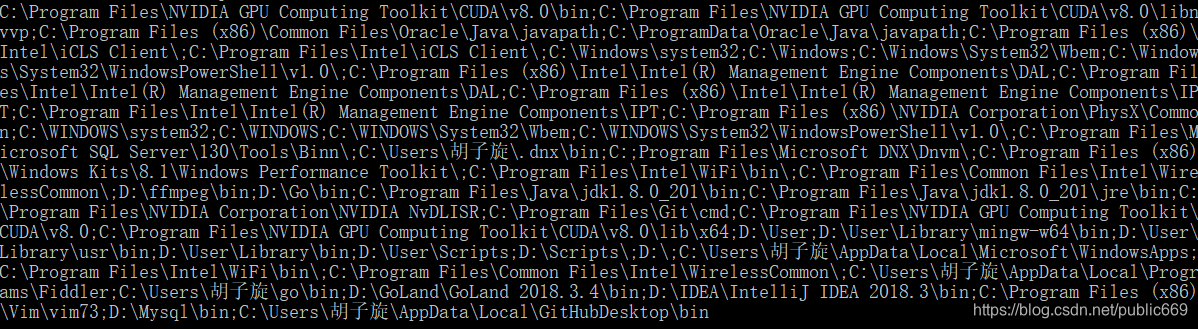
在完成了上述的配置后,可以验证一下是否配置成功:
在cmd中输入如下的代码:
echo %path%
执行结果如下:
4.配置cudnn:
在分享的安装包中有一个压缩包,将其解压会出现三个文件夹:
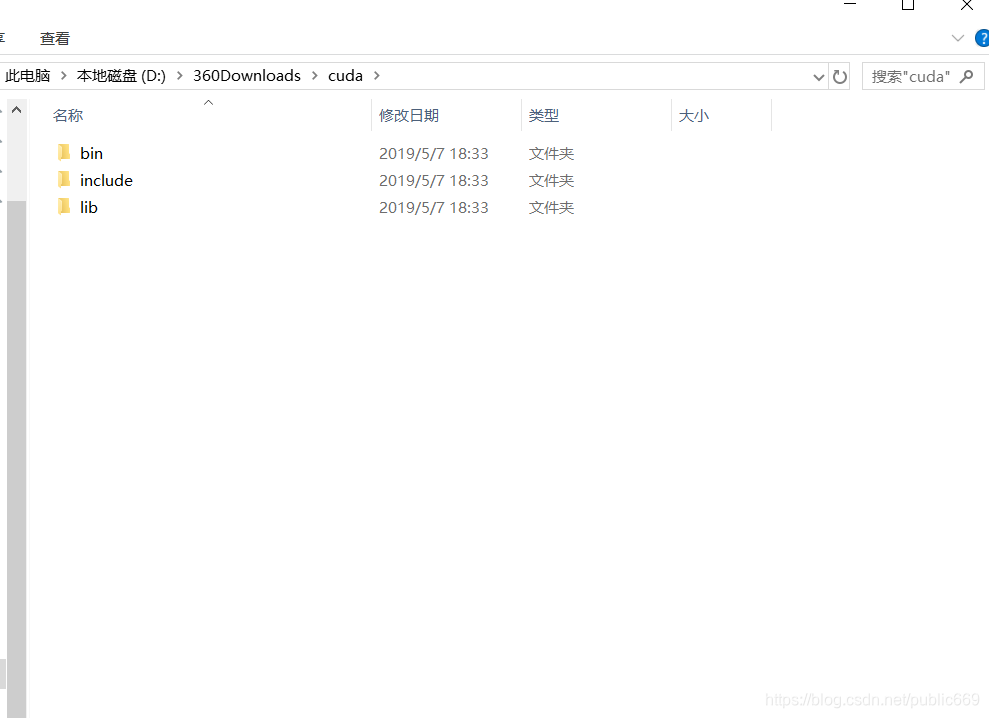
将这三个文件夹里面的文件对应的复制到cuda文件下:
(注意这里是将文件下的文件复制到cuda对应的文件夹里面,而不是将文件夹直接替代cuda下的文件夹(这步特别重要))
4.验证:
完成上述的所有步骤后,基本上就完成了大部分了!!!
验证是否成功:
打开pycharm,在里面输入如下测试代码:(前提是已经安装了相应版本tensorflow_gpu,这里给出1.4.0安装方法:在cmd中输入pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple tensorflow-gpu==1.4.0)
import ctypes
import imp
import sys
def main():
try:
import tensorflow as tf
print("TensorFlow successfully installed.")
if tf.test.is_built_with_cuda():
print("The installed version of TensorFlow includes GPU support.")
else:
print("The installed version of TensorFlow does not include GPU support.")
sys.exit(0)
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: Failed to import the TensorFlow module.")
candidate_explanation = False
python_version = sys.version_info.major, sys.version_info.minor
print("\n- Python version is %d.%d." % python_version)
if not (python_version == (3, 5) or python_version == (3, 6)):
candidate_explanation = True
print("- The official distribution of TensorFlow for Windows requires "
"Python version 3.5 or 3.6.")
try:
_, pathname, _ = imp.find_module("tensorflow")
print("\n- TensorFlow is installed at: %s" % pathname)
except ImportError:
candidate_explanation = False
print("""
- No module named TensorFlow is installed in this Python environment. You may
install it using the command `pip install tensorflow`.""")
try:
msvcp140 = ctypes.WinDLL("msvcp140.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'msvcp140.dll'. TensorFlow requires that this DLL be
installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment
variable. You may install this DLL by downloading Microsoft Visual
C++ 2015 Redistributable Update 3 from this URL:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53587""")
try:
cudart64_80 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudart64_80.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudart64_80.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Download and install CUDA 8.0 from
this URL: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit""")
try:
nvcuda = ctypes.WinDLL("nvcuda.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'nvcuda.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that
this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH%
environment variable. Typically it is installed in 'C:\Windows\System32'.
If it is not present, ensure that you have a CUDA-capable GPU with the
correct driver installed.""")
cudnn5_found = False
try:
cudnn5 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_5.dll")
cudnn5_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudnn64_5.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Note that installing cuDNN is a
separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often found in a
different directory from the CUDA DLLs. You may install the
necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN 5.1 from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
cudnn6_found = False
try:
cudnn = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_6.dll")
cudnn6_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
if not cudnn5_found or not cudnn6_found:
print()
if not cudnn5_found and not cudnn6_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN.")
elif not cudnn5_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 5.1.")
else:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 6.")
print("""
The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that the correct cuDNN DLL be installed
in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment variable. Note that
installing cuDNN is a separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often
found in a different directory from the CUDA DLLs. The correct version of
cuDNN depends on your version of TensorFlow:
* TensorFlow 1.2.1 or earlier requires cuDNN 5.1. ('cudnn64_5.dll')
* TensorFlow 1.3 or later requires cuDNN 6. ('cudnn64_6.dll')
You may install the necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
if not candidate_explanation:
print("""
- All required DLLs appear to be present. Please open an issue on the
TensorFlow GitHub page: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues""")
sys.exit(-1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
如果出现以下结果则表明已经配置成功了:
TensorFlow successfully installed.
The installed version of TensorFlow includes GPU support.
若是出现以下问题则表明环境配置出错了:
Could not load ‘cudart64_80.dll’. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Download and install CUDA 8.0 from
this URL: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit
5.模型gpu加速训练:
# 测试tensorflow_gpu版本加速效果代码
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import os
#os.environ["CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER"] = "PCI_BUS_ID"
#os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
batch_size = 32
num_batches = 100
# 该函数用来显示网络每一层的结构,展示tensor的尺寸
def print_activations(t):
print(t.op.name, ' ', t.get_shape().as_list())
# with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope # 可以将scope之内的variable自动命名为conv1/xxx,便于区分不同组件
def inference(images):
parameters = []
# 第一个卷积层
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 卷积核、截断正态分布
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
# 可训练
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv1)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 再加LRN和最大池化层,除了AlexNet,基本放弃了LRN,说是效果不明显,还会减速?
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn1')
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool1')
print_activations(pool1)
# 第二个卷积层,只有部分参数不同
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 192], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[192], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv2)
# 稍微处理一下
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_activations(pool2)
# 第三个
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 192, 384], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv3)
# 第四层
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv4)
# 第五个
with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv5)
# 之后还有最大化池层
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_activations(pool5)
return pool5, parameters
# 全连接层
# 评估每轮计算时间,第一个输入是tf得Session,第二个是运算算子,第三个是测试名称
# 头几轮有显存加载,cache命中等问题,可以考虑只计算第10次以后的
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
# 进行num_batches+num_steps_burn_in次迭代
# 用time.time()记录时间,热身过后,开始显示时间
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s:step %d, duration = %.3f' % (datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
# 计算每轮迭代品均耗时和标准差sd
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' % (datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
def run_benchmark():
# 首先定义默认的Graph
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# 并不实用ImageNet训练,知识随机计算耗时
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, image_size, image_size, 3], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1))
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False))
sess.run(init)
# 下面直接用pool5传入训练(没有全连接层)
# 只是做做样子,并不是真的计算
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, "Forward")
# 瞎弄的,伪装
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, "Forward-backward")
run_benchmark()
好啦,到这里就大功告成啦~~~~
可以体会gpu给你带来训练时的高速了,个人觉得还是得有一块好的显卡,这样加速效果会更好,速度更快。。。。
6.结束:
有什么问题和建议欢迎给我发邮件:1017190168@qq.com
或者直接联系我:1017190168



