NetScaler 10.1的配置以及结合StoreFront的部署
2015-03-19 14:23 tao先生 阅读(1603) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报工作需要,所以英文+中文,绝壁不是装逼。。。(关于这点勿喷)
This post will cover only the basics for getting NetScaler up and running to support XenDesktop\XenApp. It in no way will help you do some other more advanced NetScaler stuff.
MIPS's and SNIP's and NSIP's and VIP's, Oh My!
Before we get started, let's get some terminology out of the way. The main thing to know is the four different IP addresses that the NetScaler uses.
MIP – Mapped IP address. You use MIP addresses to connect to the back-end servers and Reverse Network Address Translation (NAT). The MIP address is one of the NetScaler owned IP addresses. You must specify at least one MIP address when you configure the appliance for the first time.
SNIP – Subnet IP Address. This is an IP address that enables you to access a NetScaler appliance from an external host that exists on another subnet. When you add an SNIP address, the appliance adds an entry in the routing table. The SNIP enables the NetScaler appliance to connect to the subnet, which is different than that of the MIP and NSIP addresses, similar to local.
NSIP – NetScaler IP Address. The NSIP address is the IP address at which you access the NetScaler for management purposes. The NetScaler can have only one NSIP, which is also called the Management IP address network of the appliance.
VIP – Virtual Server IP Address. A VIP is the IP address associated with a virtual server. It is the public IP address to which clients connect. A NetScaler managing a wide range of traffic may have many VIPs configured.
首先,我们可以从www.citrix.com(需要citrix账号)上下载Citrix NetScaler VPX,然后申请一个90天的试用版本的license文件,如何申请license文件,稍后会有一篇相关的文档.
我们可以根据Hypervisor的版本下载不同的VPX

这里我们下载的是for XenServer的版本,
我们将下载后的NetScaler VPX 导入到XenServer中,

选择正确的host为Citrix NetScaler:

选择合适的Storage:

选择所需要的NetWork: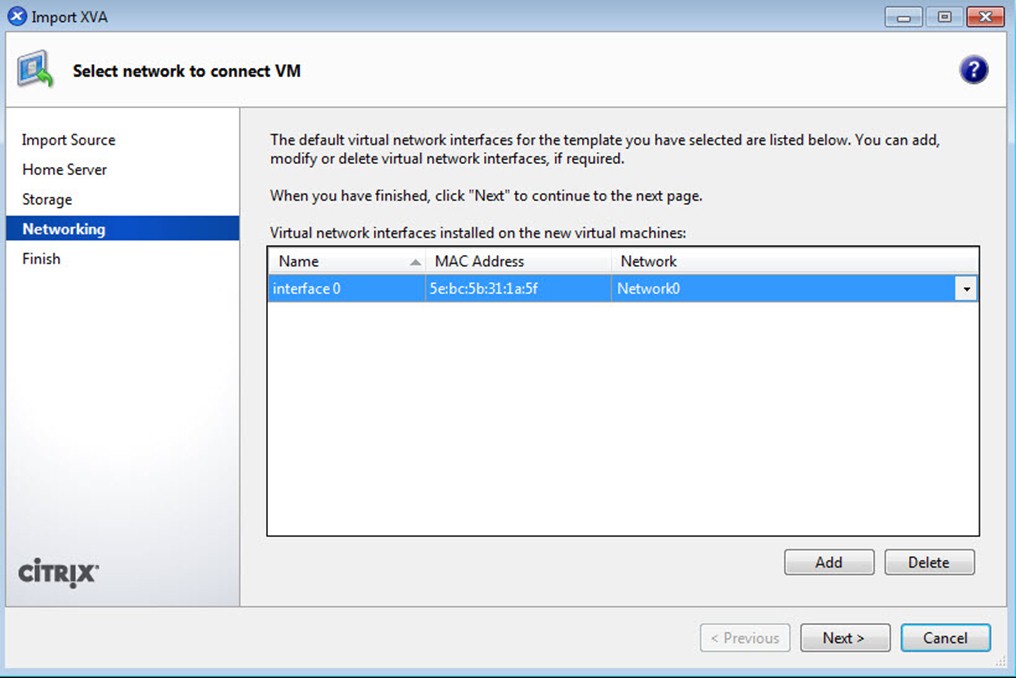
点击Finish,等待大概2分钟,Citrix NetScaler VPX就会成功的导入到XenServer Host 中:
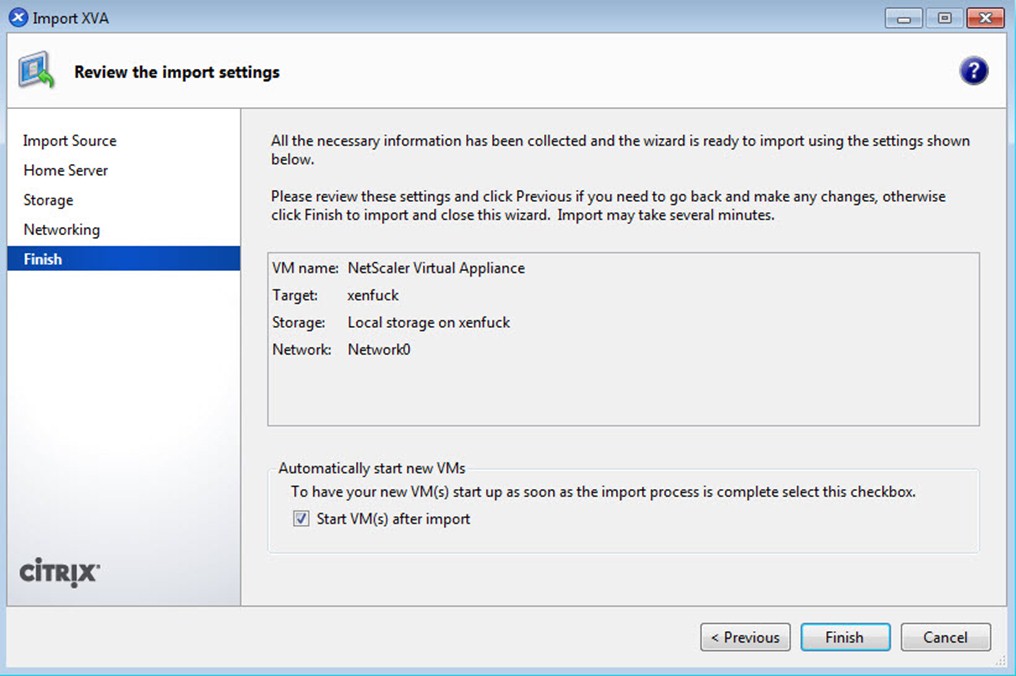
In order to access the appliance via the console remotely, it must have an IP first. Once IP'd all management is done via a web browser.
Go to the console of the newly created NetScaler virtual appliance. The console should be prompting for an Ipv4 address. The IP address it is looking for is the NSIP (NetScaler IP Address). This is the management IP of NetScaler.
Enter the desired IP, subnet mask, and default gateway of the NSIP. Once completed choose Option 4to Save and Quit.

Input associate information:

Once the NetScaler appliance has an IP, the rest of the NetScaler services will start. This takes about a minute or so. Once the console shows "Login:", that should indicate that you can now access the device through a web browser.
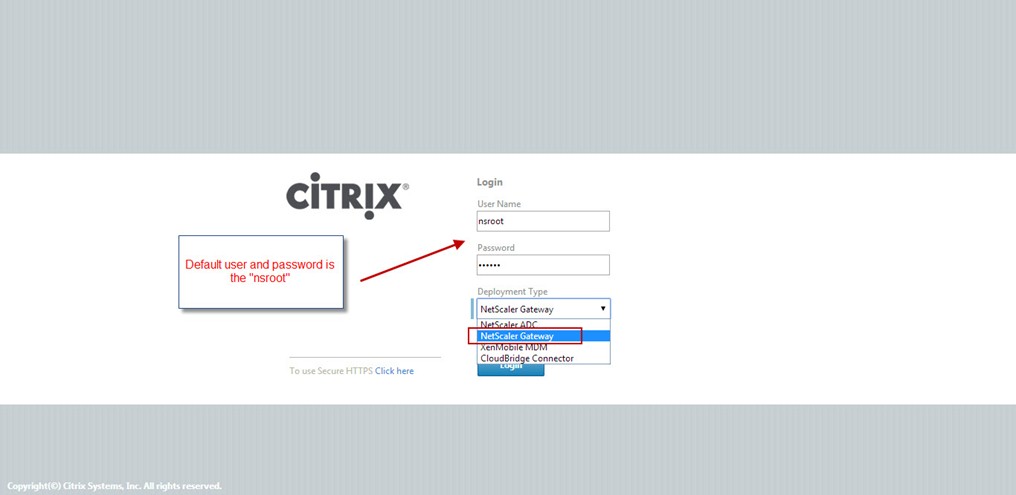
Open Internet Explorer and type the NSIP into the address bar. The default credentials for a NetScaler device is user nsroot for both username and password.
Note: The NetScaler web console requires a Java plug-in(Maybe JDK1.6+ is useful, don't use the latest JDK(7.x+)). If prompted by IE, allow the plug-in to run.
Once into the console, launch the Setup Wizard located towards the bottom of the web console

Import the License File:

Finish the wizard:

Reboot teh Citrix NetScaler:

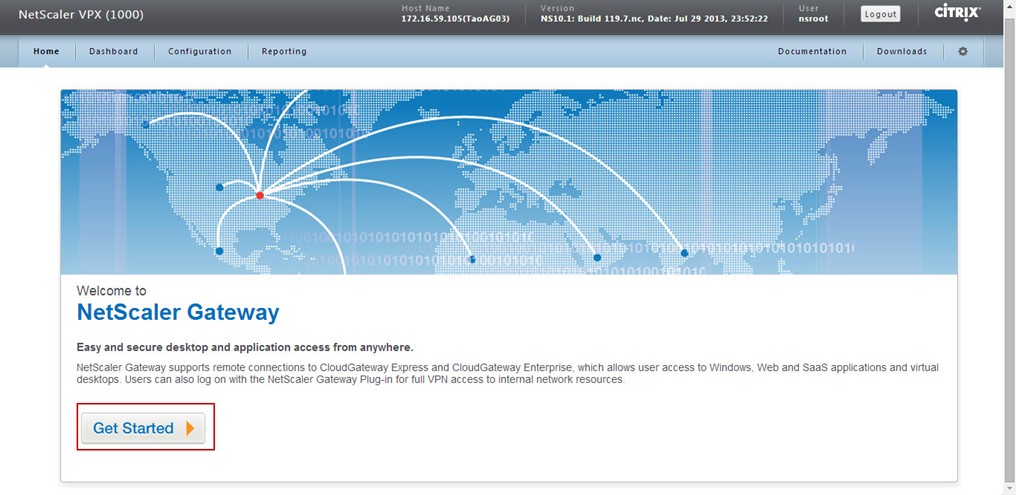
When NetScaler reboots and you login again by choosing 'NetScaler Gateway' option, an interface to configure NetScaler Gateway virtual server is presented. Click on 'Get Started' button.
Note – When you experience this wizard, it is advisable to go through each section and complete the wizard by clicking on 'Done' button at the end.
Configure the Certificate:
Certificates…The Bane of Every IT Person's Existence
When it comes to Access Gateway, the only way you can connect is via SSL (443) with a certificate. This means that any Access Gateway implementation must start with installing a certificate, and if necessary, the certificate chain.
For the purpose of this blog, I am going to use an internal Microsoft CA (Certificate Authority) for the certificate.
The first step is to create a certificate key. Navigate to SSL in the NetScaler GUI. Click on Create RSA Key. Use the following for inputting to the required fields:
Name: XDAG1.key (or anything that makes sense to you)
Key Size (bits): 2048
Key Format: PEM
PEM Encoding Algorithm: NONE

Next, we need to create a request that we are going to send over to the CA. Navigate to SSL in the NetScaler GUI. Click on Create CSR (Certificate Signing Request). Use the following for inputting to the required fields:
Request File Name: XDAG1.req (or anything that makes sense to you)
Key File Name: XDAG1.key (browse for the key created in previous step)
Key Format: PEM
PEM Passphrase: password (same password used to create the key in the previous step)
Common Name: XDAG1.tms.local (this is the name that users will type into their browsers)
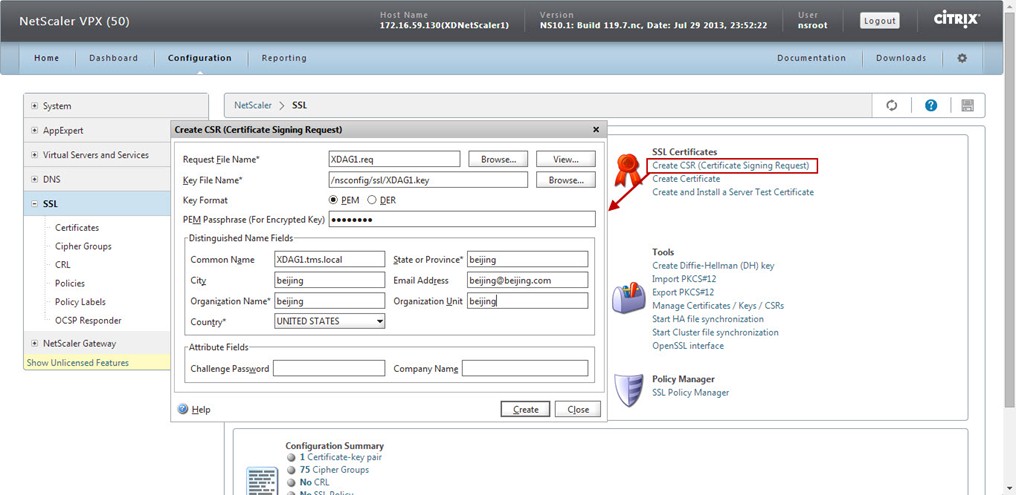
Now, we need to download our request file to use for importing to the CA. Navigate to SSL in the NetScaler GUI. Click on Manage Certificates / Keys / CSRs (found under the Tools section). Find the request file (AG.req) created in the previous step then click Download. In the Download Files window click Browsethen save the file somewhere convenient.

Now, let's submit the request to the CA. Open a web browser and type in http://<yourCAname>/certsrv. Click on Request a certificate -> advanced certificate request -> submit a certificate request by using a base-64… Open the request file (AG.req) in notepad and copy all the contents. Paste the contents into the Saved Request box. Under Certificate Template select Web Server (If Web Server does not show try opening Internet Explorer as an "administrator"). Click Submit to continue.

Now, time to download the certificate that the CA created for us. Click the radio button for Base 64 encoded, then click Download certificate.
And rename the file to "XDAG1.cer"
Install the Certificates:
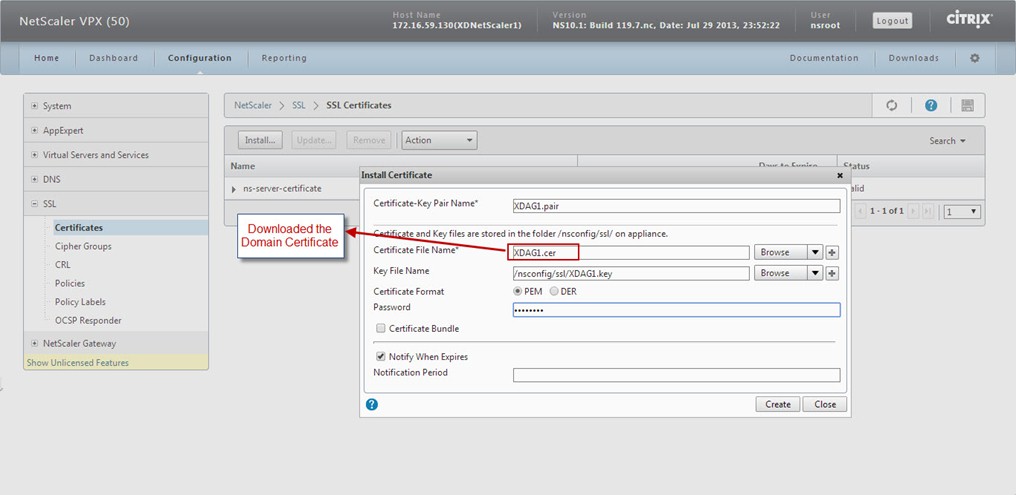
install the CA ROOT Certificate:
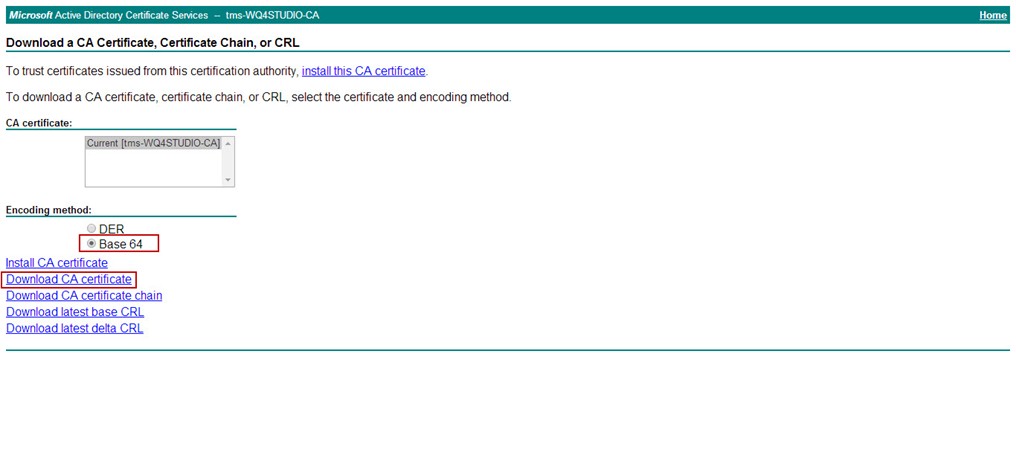
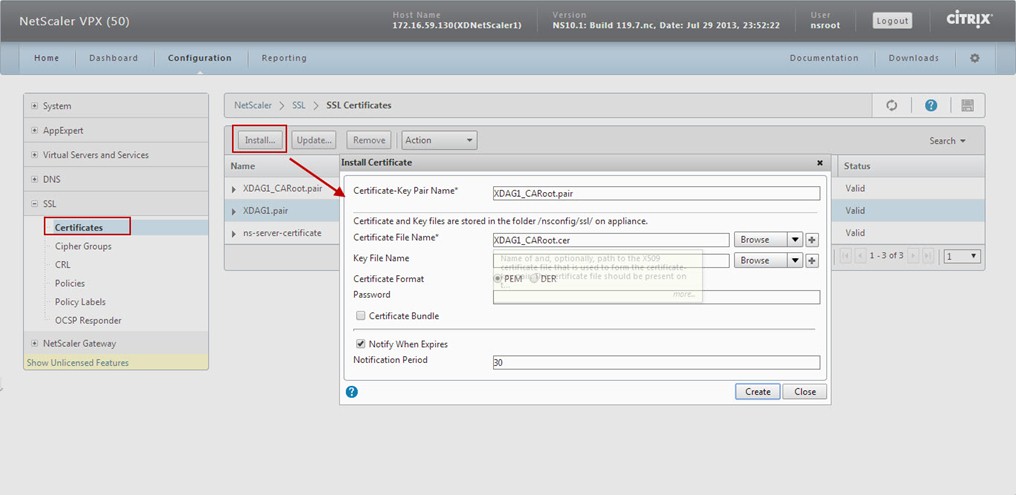
Open a web browser and type in http://<yourCAname>/certsrv. Click on Download a CA certificate, certificate chain, or CRL -> Download CA certificate, and rename the file to "XDAG1_CARoot.cer"
install the CA ROOT Certificate:
 NetScaler Gateway Session Policies and Profiles
NetScaler Gateway Session Policies and Profiles
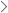 Profiles
Profiles



Create the Sessssion Policy:

Add the Expression:

 Servers
Servers
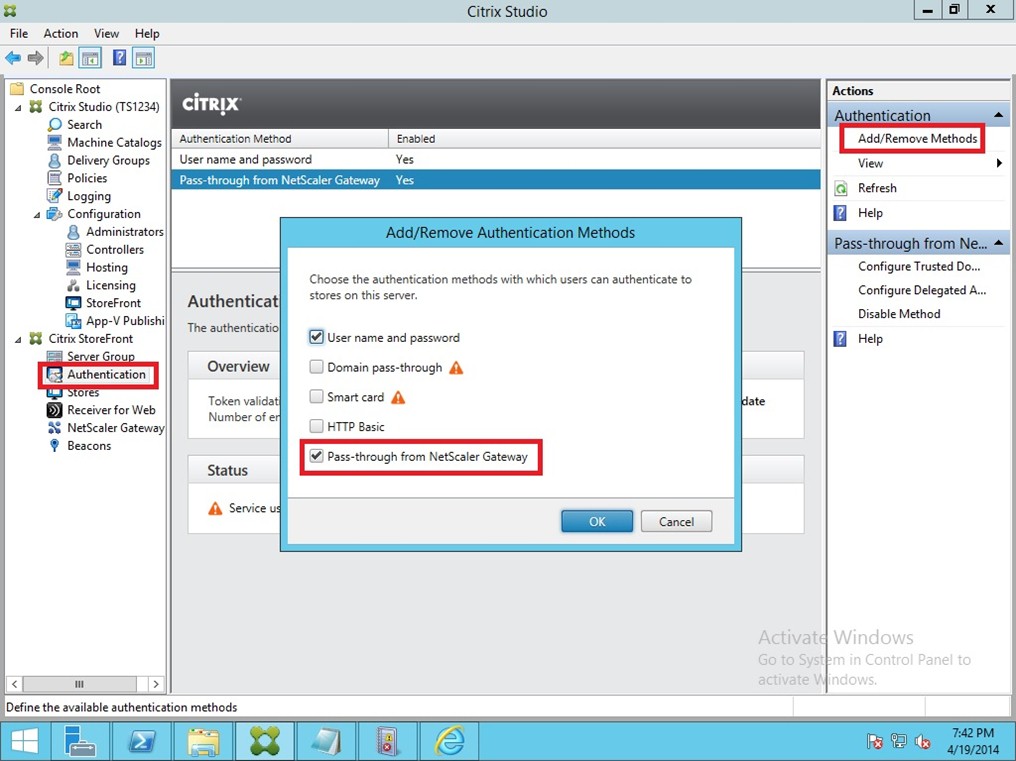
Let's Add Some Authentication…LDAP
To add LDAP to the Access Gateway virtual server, we start my creating an LDAP server on NetScaler. To do this, navigate to System -> Authentication. Click on the Servers tab then click Add at the bottom of the screen. Use the following for inputting to the required fields:
Name: AD (or whatever name you want to give it)
Authentication Type: LDAP
IP Address: 172.16.57.42 (use the IP address of one of your domain controllers)
Base DN: DC=tms,DC=local (use the DN for your domain)
Administrator Bind DN: xendesktop\UserAdmin (does not need to be an admin. Use domain\user for the format)
Administrator Password: password (the password to the above user)
Click the Retrieve Attributes link to test the connection.

Now, let's go create the LDAP policy that NetScaler needs to bind to the Access Gateway virtual server. To create the policy navigate to Authentication->LDAP. Click on the Policies tab then click Add at the bottom of the screen. Use the following for inputting to the required fields:
Name: XDAG1_ADPolicy (or any name that you like)
Authentication Type: LDAP
Server: AD (this is the server created in the previous step)
Expression: Match Any Expression -> General -> True value (then click Add Expression)

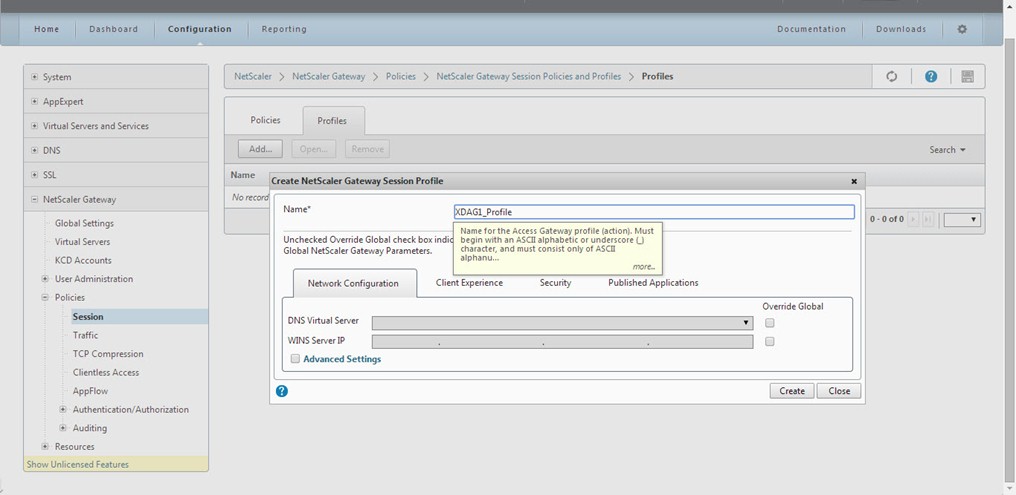
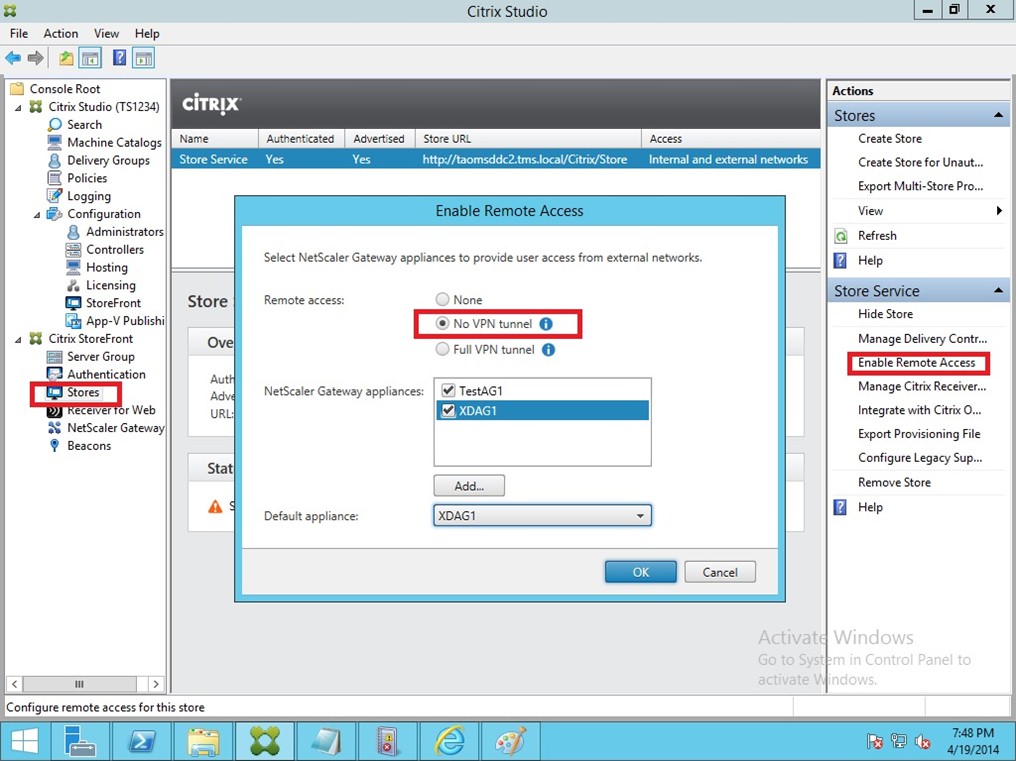
Define NetScaler Gateway virtual server name, IP Address (VIP) and Port. Also, you can enable NetScaler Gateway to redirect HTTP connection to HTTPS secure connection. Click 'Continue' to get next section.
Note – You cannot configure more than one virtual server with the same IP Address (VIP) but different Ports through this wizard.
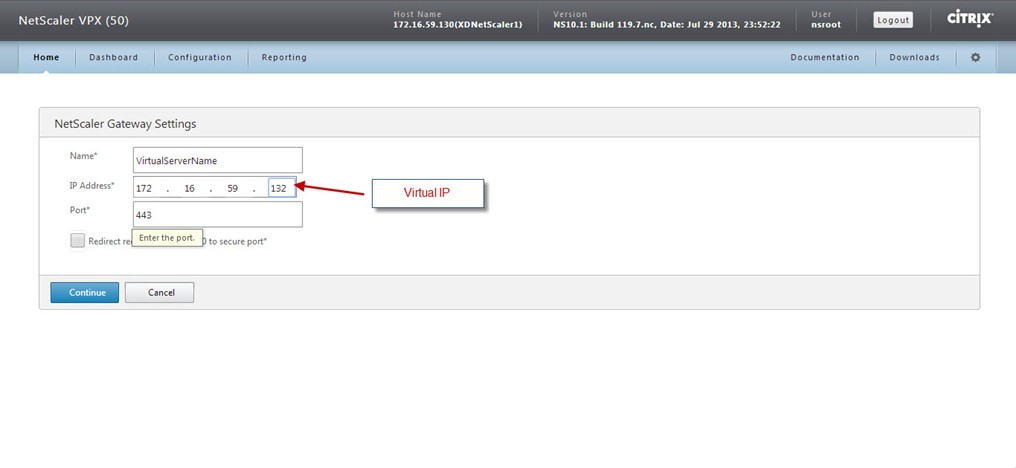
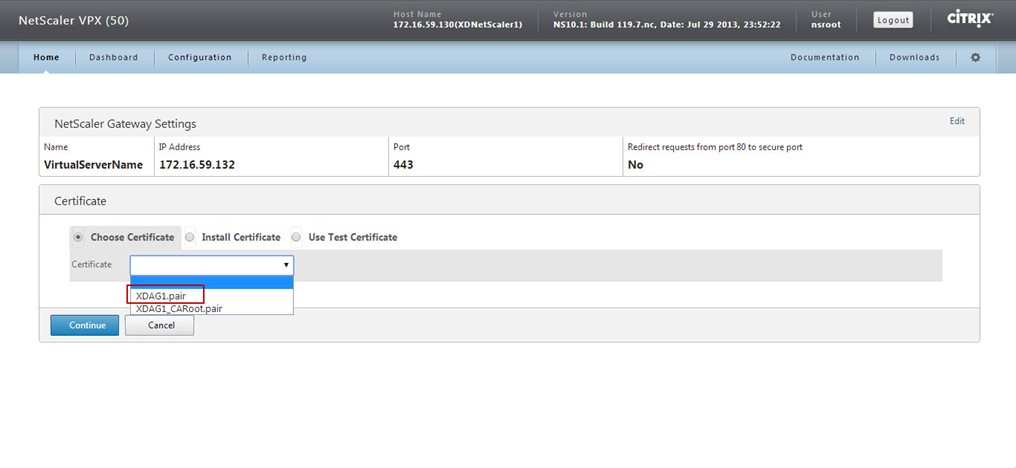

Now, you get a section to define your deployment type and settings related to that deployment type.
-
XenApp / XenDesktop– This allows configuring Web Interface or StoreFront deployment.
-
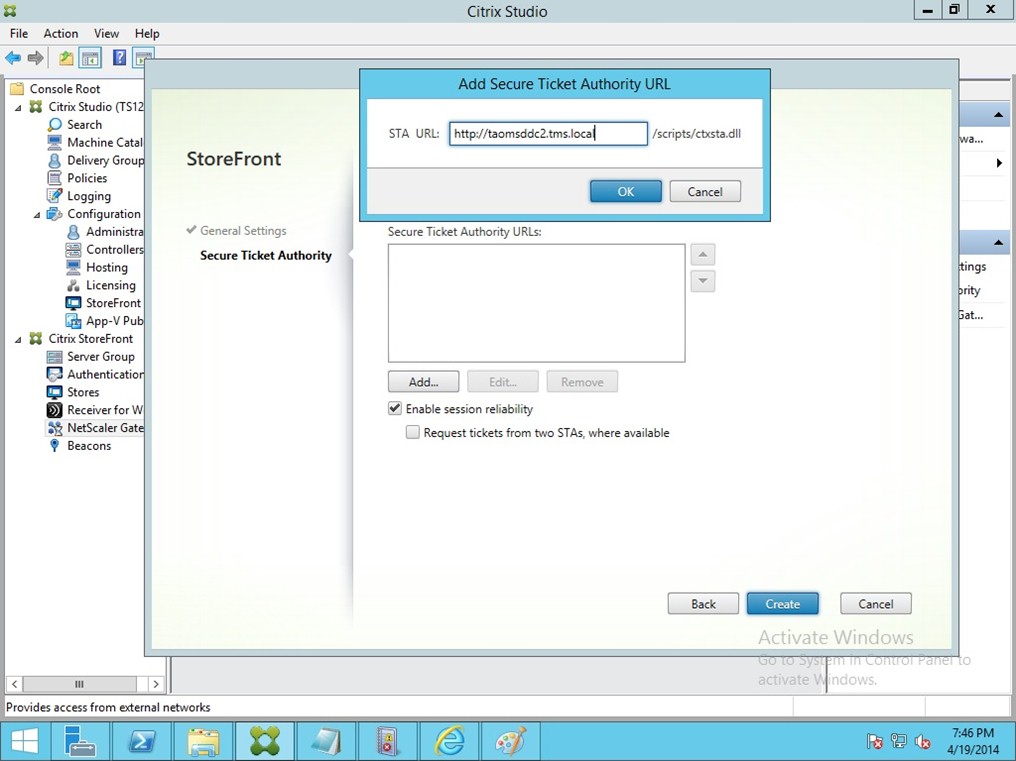
In Web Interface deployment, enter the complete address of XenApp Site e.g.http://Xenapp1.systest.agee/Citrix/XenApp and XenApp Service Services Site e.g.http://Xenapp1.systest.agee/Citrix/PNAgent/Config.xml. Enter the Single Sign-on Domain and STA (Secure Ticket Authority) URL either using IP address or FQDN.
-
In StoreFront deployment, enter the StoreFront FQDN, Receiver for Web Path, Single Sign-on Domain and STA (Secure Ticket Authority) URL either using IP address or FQDN.
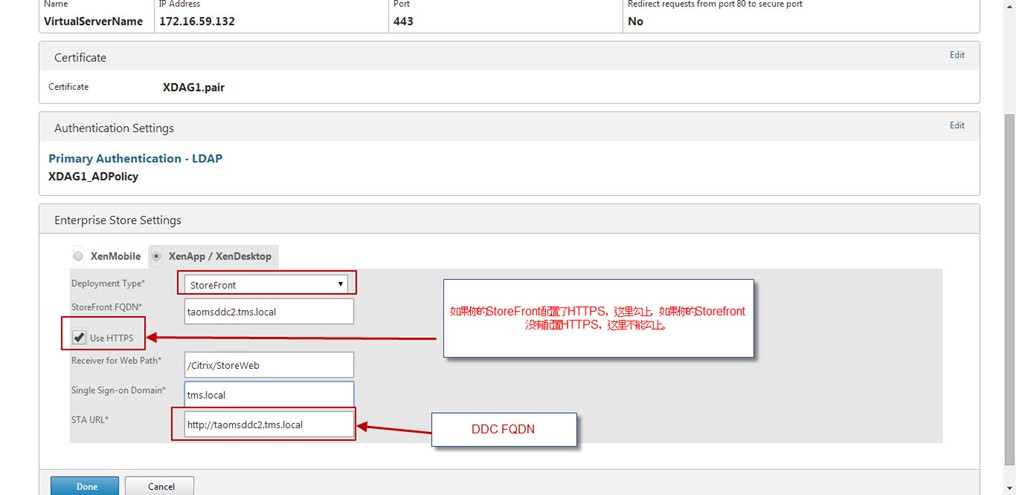
Configure the StoreFront

if your client is not in the Domain, you need add the virtual IP information into the Client Host File:
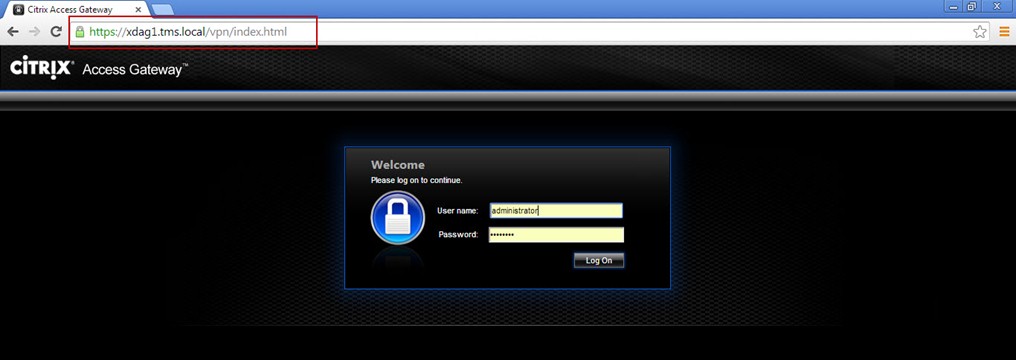

Note:
On the DDC, you need to edit the information
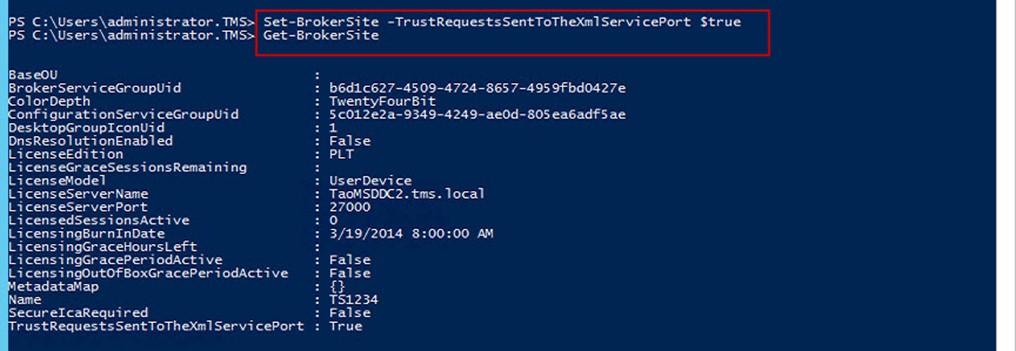
PS: 附加一些额外信息关于NetScaler拓扑图以及端口的调用图
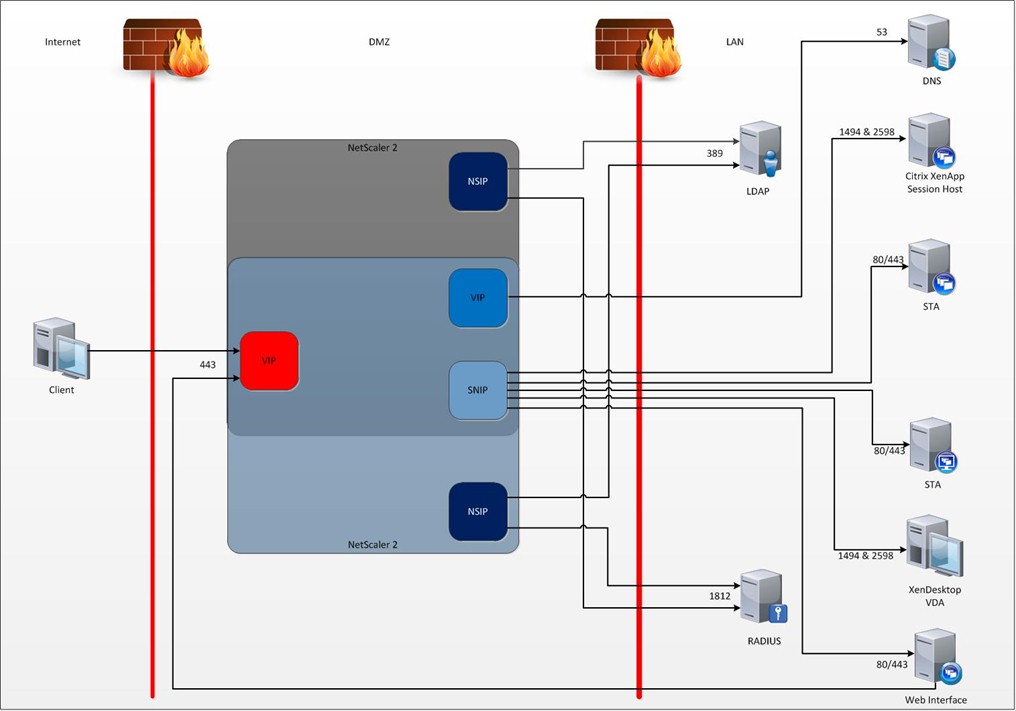
Firewall rule table
|
Source IP |
Destination IP |
Protocol |
Port |
Function |
|
Client IPs |
Access Gateway VIP |
TCP |
443 |
Secure traffic from internet clients to AGEE VIP |
|
NetScaler NSIP |
LDAP Servers 1 |
TCP |
389 |
LDAP authentication traffic from NetScaler IP to LDAP servers. |
|
NetScaler NSIP |
RADIUS servers |
TCP/UDP |
1812 |
RADIUS traffic from Access Gateway to RADIUS server (for RSA dual factor authentication) |
|
NetScaler VIP2 |
DNS Servers |
TCP |
53 |
DNS traffic from VIP to DNS servers |
|
NetScaler SNIP |
Web Interface Servers |
TCP |
80/4433 |
Traffic from Access Gateway to Web Interface servers |
|
Web Interface Servers |
Access Gateway VIP |
TCP |
443 |
Web Interface call back traffic to Access Gateway VIP4 |
|
NetScaler SNIP |
All XenApp session host servers and all XenDesktop Desktops (virtual, physical etc) |
TCP |
1494 & 25986 |
ICA traffic from the Access Gateway to all Citrix XenApp or XenDesktop endpoints |
|
Management Server |
NetScaler SNIP |
TCP |
80/3010 |
Console and Java Applet traffic to NetScaler (for management |
1. In most cases these will be your Active Directory domain controllers – always use more than one.
2. Normally this comes from the NSIP but due to the fact that ICMP is used to verify if the DNS servers are available the DNS servers will show as down unless your security team allow ICMP through the firewall which is very unlikely. Therefore, setup an internal DNS load balancer with a DNS lookup monitor and point your NetScalers at the internal load balancer.
3. Normally port 80. Port 443 if you secure your Web Interface servers with a certificate
4. Ensure that from a browser on your Web Interface server you can type the FQDN of the AGEE and get the logon page with NO errors
5. Normally port 80. Port 443 if you secure your Web Interface servers with a certificate.
6. Port 2598 is for session reliability
Remember that if you have your NetScalers configured in an HA pair traffic originating from the NSIP can come from either NetScaler depending on which one is hosting the AGEE VIP at the time. For anything that comes from the NSIP you can load balance it using a VIP if you want the traffic to originate from one IP.
————————————————————————————————
WHOOOOSHHHHHHHHHHHH…………
Blimey what was that?
That was your life mate
Oh, I was not quite ready. Can I have another go?
Sorry mate, only one per person.







【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步