oop4~6次作业心得体会
OOP 4~6次作业心得体会
22201709-刘隽涛
目录
(1)对于oop4~6次作业的理解
(2)设计与分析,测试分析性能,踩坑心得及下次改进的建议
(3)总结与看法:)
关于这几次作业的看法:
这三次题目集较第一次作业难度有进一步提高,考察抽象类、接口等。在写这次作业的同时,不仅要在较短的时间内学习相关知识点,还要会掌握,确实有点难度。题目集4在一次考察对正则表达式的使用,但是相较之前的多项式求导,难度有所降低,但题目复杂程度依然不减。题目集4还考察了继承的用法。题目集5主要依然是考察正则表达式的运用。题目集6旨在掌握类的继承、多态性及其使用方法、使用接口及类实现多态性。
对于OOP4~6次作业难点的理解和出错点分析
第四次作业
1.字符串的使用分割,数组的使用。
2.了解Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
第五次作业
1.通过类图来完成代码的书写,其中必须清楚每个类之间的关系。
2.正则表达式的运用。
3.每个类之间互相聚合和所有类与一个类聚合的书写
第六次作业
1.正则表达式的运用
2.(1)务必注意本题目中的各实体类之间的关系,尤其是一对多的组合关系。 (2)对实体类的设计要做到单一职责原则,且不能缺少规定的实体类。 (3)编程时考虑面向对象中的封装性本题目中的应用以及是否有能够扩展 的衍生需求。
3.(1)务必注意本题目中的各实体类之间的关系,尤其是一对多的组合关系。 (2)对实体类的设计要做到单一职责原则,且不能缺少规定的实体类。 (3)在“合成复用原则”及“单一职责原则”基础上,尽量对上次作业的程 序进行重构,使之符合 “开-闭”原则。
设计与分析
ps:SourceMonitor里图表的含义:
- Lines: 指的是代码总行数
- Statements:语句的行数,语句是以分号结尾的。这个C中有所不同。
- Percent Branch Statement:分支数占总语句数的百分比
- Method Call Statement:方法调用语句数
- Percent Lines with Comments:注释语句占总语句数的百分比
- Classes and Interfaces:类和接口数
- Methods per Class:每个类平均包含函数个数
- Average Statements per Method:每个函数平均包含的语句个数函数深度(Block Depth):函数深度是函数中分支嵌套的层数。
- 对应有最大深度(Max Depth)和平均深度(Avg Depth)。
- Line Number of Complex Method:最复杂函数的行号(最复杂指的是McCabe复杂度值为最高)
- Maximum Complexity:该类中最复杂函数的复杂度(最复杂指的是McCabe复杂度值为最高)
- Line Number of Deepest Block:最深层语句块的行号
-
函数复杂度(Function Complexity)复杂度指1个函数可履行路径的数目,以下语句为复杂度的值贡献1:if/else/for/while语句,3元运算符语句,if/for/while判断条件中的"&&"或“||”,switch语句,
后接break/goto/ return/throw/continue语句的case语句,catch/except语句等。对应有最大复杂度(Max Complexity)和平均复杂度(Avg Complexity)。
第四次作业
7-1 菜单计价程序-3
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish\[\] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\\
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record\[\] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
### 输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
### 输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 table 1 2023/3/22 12/2/3 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 table 1: 38
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 table 1 2023/3/22 17/0/0 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 1 delete end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 table 1: 22
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 table 1 2023/3/22 16/59/59 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 1 delete end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 table 1 out of opening hours
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 table 1 2022/12/5 15/03/02 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2 5 delete 7 delete table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2 7 delete end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist delete error; delete error; table 2: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist delete error; table 1 out of opening hours table 2: 63
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 table 1 2022/12/3 19/5/12 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2 table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02 1 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2 油淋生菜 1 3 3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2 1 4 麻婆豆腐 1 1 7 delete end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist table 2: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist 4 table 2 pay for table 1 12 delete error; table 1: 63 table 2: 75
代码展示:
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Judge judge=new Judge(); Menu menu=new Menu(); ArrayList<Discount> discounts=new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Table> tables=new ArrayList<>(); int tableNumber=0; ArrayList<Order> orders=new ArrayList<>(); while (in.hasNext()){ String str=new String(in.nextLine()); if(str.equals("end")){//判断结束 break; } String[] strSplit=str.split(" "); if(judge.isMenu(strSplit.length,strSplit[1])){//入菜单 menu.addDish(strSplit[0],Integer.parseInt(strSplit[1])); } if(judge.isTable(strSplit)){//输入桌子序号,时间 Discount discount=new Discount(); Order order=new Order(); order.setTableNumber(Integer.parseInt(strSplit[1])); discount.setTime(strSplit[2],strSplit[3]); discounts.add(discount); orders.add(order); tableNumber++; } if(judge.isRecord(strSplit)){//输入订单 int orderNum=Integer.parseInt(strSplit[0]); String dishName=strSplit[1]; int portion=Integer.parseInt(strSplit[2]); int num=Integer.parseInt(strSplit[3]); orders.get(tableNumber-1).addARecord(orderNum,dishName,portion,num); orders.get(tableNumber-1).findRecordByNum(orderNum-1).setDish(menu); } if(judge.isDelete(strSplit.length,strSplit[1])){ //table.setDeleteNumber(Integer.parseInt(strSplit[0])); orders.get(tableNumber-1).setDeleteNumber(Integer.parseInt(strSplit[0])); } } //输出 for(int i=0;i<orders.size();i++){ System.out.println("table "+orders.get(i).getTableNumber()+": "); for(int j=0;j<orders.get(i).getRecordNumber();j++){ System.out.println(j+1+" "+orders.get(i).findRecordByNum(j).getDish().getName()+" "+orders.get(i).findRecordByNum(j).getPrice()); } Table table=new Table(); if(orders.get(i).hasDelete(orders.get(i).getDeleteNumber())){ orders.get(tableNumber-1).delARecordByOrderNum(orders.get(i).getDeleteNumber()); } table.setTototalPrice((int)(orders.get(i).getTotalPrice()*judge.judgeTimeDiscount(discounts.get(i))+0.5)); tables.add(table); } for(int i=0;i<tables.size();i++){ System.out.println("table"+" "+(i+1)+":"+" "+tables.get(i).getTototalPrice()); } } } class Discount{ int year; int month; int day; int hour; int minute; int second; Discount(){} void setTime(String timeDay,String timeHour){ String[] timeDaySplit = timeDay.split("/"); String[] timeHourSplit =timeHour.split("/"); this.year=Integer.parseInt(timeDaySplit[0]); this.month=Integer.parseInt(timeDaySplit[1]); this.day=Integer.parseInt(timeDaySplit[2]); this.hour=Integer.parseInt(timeHourSplit[0]); this.minute=Integer.parseInt(timeHourSplit[1]); this.second=Integer.parseInt(timeHourSplit[2]); } public int getDay() { return day; } public int getHour() { return hour; } public int getMinute() { return minute; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public int getSecond() { return second; } public int getYear() { return year; } } class Judge{ Judge(){} boolean isMenu(int length,String string){ if(length==2&&!string.equals("delete")){ return true; } else{ return false; } } boolean isRecord(String[] strSplit){ if(strSplit.length==4&&!strSplit[0].equals("table")){ return true; } else{ return false; } } boolean isTable(String[] strSplit){ if(strSplit[0].equals("table")){ return true; } else{ return false; } } boolean isDelete(int length,String string){ if(length==2&&string.equals("delete")){ return true; } else{ return false; } } double judgeTimeDiscount(Discount discount){ if(discount.getHour()>=17&&discount.getHour()<20||(discount.getHour()==20&&discount.getMinute()<20)){ return 0.8; } else if((discount.getHour()==10&&discount.getMinute()>=30)||discount.getHour()>11&&discount.getHour()<14||(discount.getHour()==14&&discount.getMinute()<30)){ return 0.6; } return 1; } } class Dish{ String name;//菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 Dish(){} Dish(String name,int unit_price){ this.name=name; this.unit_price=unit_price; } void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } void setUnit_price(int unit_price){ this.unit_price=unit_price; } String getName(){ return this.name; } int getUnit_price(){ return this.unit_price; } int getPrice(int portion){//计算菜品价格 if(portion==1){ return (int)unit_price; } else if(portion==2){ return (int)(unit_price*1.5+0.5); } else if(portion==3){ return (int)unit_price*2; } return 1; } } class Menu{ ArrayList<Dish> dishs=new ArrayList<>();//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 Dish searthDish(String dishName){//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。 for(int i=0;i<dishs.size();i++){ if(dishs.get(i).getName().equals(dishName)){ return dishs.get(i); } } return dishs.get(1); } void addDish(String dishName,int unit_price){//添加一道菜品信息 Dish dish=new Dish(dishName,unit_price); dishs.add(dish); } } class Record{ int orderNum;//序号 Dish d=new Dish();//菜品 int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) int numberOfDish; String dishName; Record(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){ this.orderNum=orderNum; this.dishName=dishName; this.portion=portion; this.numberOfDish=num; } void setDish(Menu menu){//存入订单中 this.d=menu.searthDish(this.dishName); } int getOrderNum(){ return this.orderNum; } Dish getDish(){ return this.d; } int getPortion(){ return this.portion; } int getNumberDish(){ return this.numberOfDish; } void setOrderNum(int orderNum){ this.orderNum=orderNum; } void setDish(Dish dish){ this.d=dish; } void setPortion(int portion){ this.portion=portion; } void setNumberDish(int numberOfDish){ this.numberOfDish=numberOfDish; } int getPrice(){//计价,计算本条记录的价格 return (int)numberOfDish*d.getPrice(portion); } } class Order{ //Record\[\] records; int tableNumber; int deleteNumber=0; ArrayList<Record> records=new ArrayList<>();//保存订单上每一道的记录 int getTotalPrice(){//计算订单的总价 int totalPrice=0; for(int i=0;i<records.size();i++){ totalPrice+=records.get(i).getPrice(); } return totalPrice; } void setTableNumber(int tableNumber){ this.tableNumber=tableNumber; } int getTableNumber(){ return tableNumber; } void addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。 Record record=new Record(orderNum,dishName,portion,num); records.add(record); } void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){//根据序号删除一条记录 records.remove(orderNum-1); } Record findRecordByNum(int orderNum){//根据序号查找一条记录 return records.get(orderNum); } int getRecordNumber(){ return records.size(); } void setDeleteNumber(int deleteNumber){ this.deleteNumber=deleteNumber; } public int getDeleteNumber() { return deleteNumber; } boolean hasDelete(int deleteNumber){ if(deleteNumber==0){ return false; } if(deleteNumber>0&&deleteNumber<records.size()){ return true; } else{ return false; } } } class Table{ int tototalPrice; void setTototalPrice(int tototalPrice){ this.tototalPrice=tototalPrice; } int getTototalPrice(){ return this.tototalPrice; } }
生成报表:
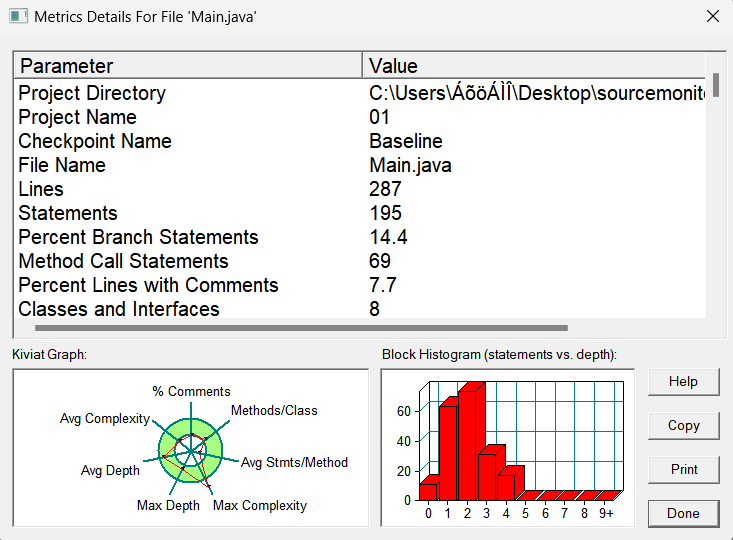
问题:(1)代码复杂度过高
(2)方法模式太少
(3)耦合度过高:类与类间分支嵌套过多。
(4)设计混乱:对各个类中的方法设计混乱。
改进:(1)多设置类,遵循单一职责。
(2)弄清类与类之间的关系。
第五次作业
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
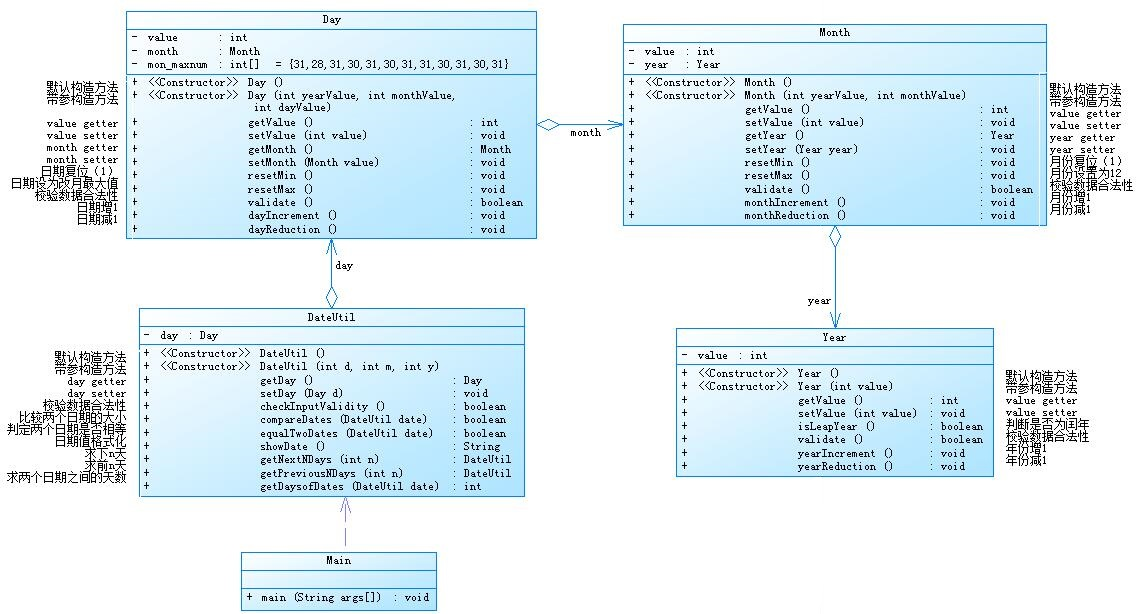
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
- 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
- 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
代码展示:
import java.util.Scanner; //Year类 class Year{ int value; //默认构造方法 public Year(){ } //带参构造方法 public Year(int value){ this.value=value; } //getter public int getValue(){ return value; } //setter public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //判断year是否为闰年 public boolean isLeapYear(){ if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) return true; else return false; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean validate(){ if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) return true; else return false; } //年份增1 public void yearIncrement(){ value=value+1; } //年份减1 public void yearReduction(){ value=value-1; } } //Month类 class Month{ int value; Year year; //默认构造方法 public Month(){ } //带参构造方法 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ this.year=new Year(yearValue); this.value=monthValue; } //get set Value public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //get set Year public Year getYear(){ return year; } public void setYear(Year year){ this.year=year; } //月份复位(1) public void resetMin(){ value=1; } //月份设置为12 public void resetMax(){ value=12; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean validate(){ if(value>=1&&value<=12) return true; else return false; } //月份增1 public void monthIncrement(){ value=value+1; } //月份减1 public void monthReduction(){ value=value-1; } } //Day类 class Day{ int value; Month month; int mon_maxnum[]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; //默认构造方法 public Day(){ } //带参构造方法 public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value=dayValue; } //value getter&setter public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //month getter&setter public Month getMonth(){ return month; } public void setMonth(Month value){ this.month=value; } //日期复位(1) public void resetMin(){ value=1; } //日期设为该月最大值 public void resetMax(){ value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean validate(){ if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; if(value>=1&&value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return true; else return false; } //日期增1 public void dayIncrement() { value=value+1; } //日期减1 public void dayReduction() { value=value-1; } } //DateUtil类 class DateUtil{ Day day; //默认构造方法 public DateUtil(){ } //带参构造方法 public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){ this.day=new Day(d,m,y); } //day getter public Day getDay(){ return day; } //day setter public void setDay(Day d){ this.day=d; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&day.validate()) return true; else return false; } //比较两个日期大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&date.getDay().getValue()<this.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; } //判定两个日期的大小 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if(this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&& this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //日期值格式化 public String showDate(){ return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); } //计算该年的剩余天数 //求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ int a[]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int y=0,m=0,d=0; int i,j; int b=0;//该年剩余天数 for(i=getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;i<=12;i++){ b=b+a[i]; } b=b+a[getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-getDay().getValue(); if(getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)//闰年 b++; if(b>n){//该年剩余天数大于n y=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){//如果是闰年 a[2]=29; } int e=a[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()];//该月的天数 e=e-this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的天数 if(e>=n){//如果n天后在本月 m=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); d=n+this.getDay().getValue(); } else{//如果n天后不在本月 n=n-e; m=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1; i=m; while(n-a[i]>0&&i<=12){//找到月 n=n-a[i]; m++; i++; } d=n;//找到天 } } else{//该年剩余天数小于n n=n-b; y=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1; int c=365;//平年天数 if(new Year(y).isLeapYear()){//闰年天数 c++; } while(n-c>0){//找到年 n=n-c; y++; c=365; if(new Year(y).isLeapYear()) c++; } i=1; while(n-a[i]>0&&i<=12){//找到月 n=n-a[i]; i++; } m=i; d=n;//找到天 } return new DateUtil(y, m, d); } //求前n天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ int a[]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int y=0,m=0,d=0; int i,b=0; for(i=getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;i<=12;i++){ b=b+a[i]; } b=b+a[getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-getDay().getValue(); if(getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)//闰年 b++; b=365-b;//该日期所在年份已经过的天数 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){//如果是闰年 b++; } if (b>n){//如果前n天在该年 y=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); int e=this.getDay().getValue();//本月已经过的天数 if(e>n){//如果前n天在本月 m=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); d=e-n; } else{//如果前n天不在本月 n=n-e; m=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1; i=m; while(n-a[i]>0&&i>=0){//找到月 n=n-a[i]; m--; i--; } d=a[i]-n;//找到天 if(new Year(y).isLeapYear()&&m==2){ d++; } } } else{//如果前n天不在该年 n=n-b; y=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-1; int f=365; if(new Year(y).isLeapYear()){ f++; } while(n-f>0){//找到年 n=n-f; y--; f=365; if(new Year(y).isLeapYear()) f++; } i=12; while(n-a[i]>0&&i>=0){//找到月 n=n-a[i]; i--; } m=i; d=a[i]-n;//找到天 if(new Year(f).isLeapYear()&&m==2){ d++; } } return new DateUtil(y, m, d); } //求两个日期之间的天数 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ DateUtil b1=this; DateUtil b2=date; if(this.equalTwoDates(date)){//如果两天的日期相等 return 0; } else if(!this.compareDates(date)){//如果日期大小不对 b1=date; b2=this; } int a[]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int i,j,ts=0; for(i=b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;i<b2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();i++){//两个日期的年数之和 ts=ts+365; if(new Year(i).isLeapYear()) ts++; } if(b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==b2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==b2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){//年份相同,月份相同,日不同 ts=b2.getDay().getValue()-b1.getDay().getValue(); } else if(b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==b2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=b2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){//年份相同,月份不同 if(b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//是闰年 a[2]=29; ts=ts+a[b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-b1.getDay().getValue();//小日期该月剩余的天数 ts=ts+b2.getDay().getValue();//大日期的天数 for(j=b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=b2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;j++)//月份天数和 ts+=a[j]; } else if(b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()!=b2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()){//年份不同 ts=ts+a[b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-b1.getDay().getValue();//小日期在该月剩余的天数 ts=ts+b2.getDay().getValue();//大日期在该月已经过的天数 for(j=b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++)//小日期在该年剩余的天数 ts=ts+a[j]; for(j=b2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;j>0;j--)//大日期在该年已经过的天数 ts=ts+a[j]; if(b1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&b1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)//如果小日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月 ts++; if(b2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&b2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2)//如果大日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月后 ts++; } return ts; } } //主类 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in); int year=0,month=0,day=0,a,b; a=x.nextInt();//输入判断类型 year=x.nextInt();month= x.nextInt();day=x.nextInt();//输入年月日 DateUtil c=new DateUtil(year,month,day); if(a==1){//求下n天 b=x.nextInt();//输入n if(!c.checkInputValidity()||b<0){//如果数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getNextNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==2){ b=x.nextInt();//输入n if(!c.checkInputValidity()||b<0){//如果数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getPreviousNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==3){ int y1,m1,d1; y1=x.nextInt();m1= x.nextInt();d1=x.nextInt();//输入第二个年月日 DateUtil d=new DateUtil(y1,m1,d1); if(!c.checkInputValidity()||!d.checkInputValidity()){//如果数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getDaysofDates(d)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }
报表展示:

问题:(1)类过于多,但题目要求没办法
(2)方法中复杂程度过高
(3)耦合过高。
改进和踩坑心得:
我做这道题目是按照题目所给的设计方案来完成的,这道题的聚合方式是Year类聚合成Month类,而Month类聚合成Day类,最后是Day类聚合成需求类Dateutil类。Main类通过调用需求类Dateutil类来实现程序的功能。而需求类Dateutil类实现的方式是操纵Day类进而操纵Month类,操纵Month类进而操纵Year类,一层一层地调用来实现相应的数据设置。
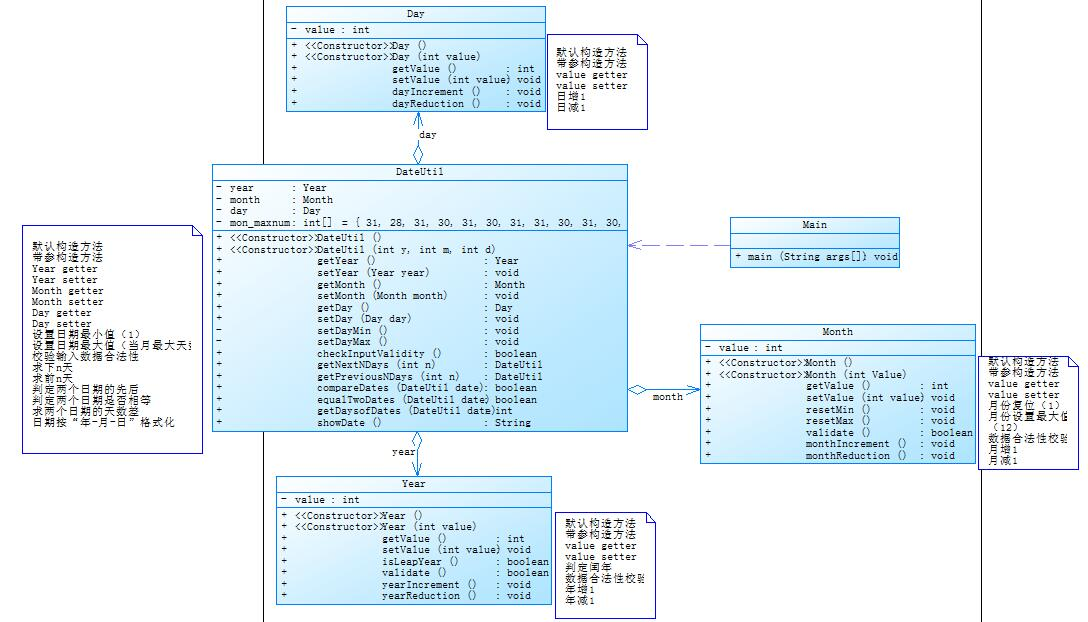
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
import java.util.Scanner; //Year类 class Year{ int value; //默认构造方法 public Year(){ } //带参构造方法 public Year(int value){ this.value=value; } //getter public int getValue(){ return value; } //setter public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //判断year是否为闰年 public boolean isLeapYear(){ if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) return true; else return false; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean validate(){ if(value<=2020&&value>=1820) return true; else return false; } //年份增1 public void yearIncrement(){ value=value+1; } //年份减1 public void yearReduction(){ value=value-1; } } //Month类 class Month{ int value; //默认构造方法 public Month(){ } //带参构造方法 public Month(int Value){ this.value=Value; } //get set Value public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //月份复位(1) public void resetMin(){ value=1; } //月份设置为12 public void resetMax(){ value=12; } //效验数据合法性 public boolean validate(){ if(value>=1&&value<=12) return true; else return false; } //月份增1 public void monthIncrement(){ value=value+1; } //月份减1 public void monthReduction(){ value=value-1; } } //Day类 class Day{ int value; //默认构造方法 public Day(){ } //带参构造方法 public Day(int dayValue){ this.value=dayValue; } //value getter&setter public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } //日期增1 public void dayIncrement() { value=value+1; } //日期减1 public void dayReduction() { value=value-1; } } //DateUtil类 class DateUtil{ private Year year; private Month month; private Day day; private int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; DateUtil(){} DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ year = new Year(y); month = new Month(m); day = new Day(d); } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public Day getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } //设置日期最小值1 public void setDayMin(){ day.setValue(1); } //设置日期为当月最大值 public void setDayMax(){ day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]); } //效验数据合法性 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if(year.validate()&&month.validate()&&day.getValue()>=1&&day.getValue()<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return true; else return false; } //比较两个日期大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//判断两个日期的先后 if(year.getValue()>date.getYear().getValue()){ return true; } else if(year.getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&month.getValue()>date.getMonth().getValue()){ return true; } else if(month.getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&&day.getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()){ return true; } else return false; } //判定两个日期的大小 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if(day.getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()&&month.getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&& year.getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //日期值格式化 public String showDate(){ return year.getValue()+"-"+month.getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); } //计算该年的剩余天数 //求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//求下N天 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ day.dayIncrement(); if(year.isLeapYear()){ mon_maxnum[2]=29; } else mon_maxnum[2]=28; if(day.getValue()>mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]){ day.setValue(1); month.monthIncrement(); if(month.getValue()>12){ month.setValue(1); year.yearIncrement(); } } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue()); } //求前N天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ day.dayReduction(); if(day.getValue()==0){ month.monthReduction(); if(month.getValue()==0){ month.setValue(12); year.yearReduction(); }if(year.isLeapYear()){ mon_maxnum[2]=29; } else mon_maxnum[2]=28; day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]); } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue()); } //求两个日期的天数差 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int n=0; DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue()); while(date1.compareDates(date)){//每次加一天,直到两个日期相等 date.getNextNDays(1); n++; } while(date.compareDates(date1)){ date1.getNextNDays(1); n++; } return n; } } //主类 public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int a = input.nextInt(); if(a==1){ int y=input.nextInt(); int m=input.nextInt(); int d=input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if(date.checkInputValidity()){ int n=input.nextInt(); date.getNextNDays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" next "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else if(a==2){ int y=input.nextInt(); int m=input.nextInt(); int d=input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if(date.checkInputValidity()){ int n=input.nextInt(); date.getPreviousNDays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" previous "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else if(a==3){ int y=input.nextInt(); int m=input.nextInt(); int d=input.nextInt(); int y1=input.nextInt(); int m1=input.nextInt(); int d1=input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(y1,m1,d1); if(date.checkInputValidity()&&date1.checkInputValidity()){ int n = date.getDaysofDates(date1); System.out.println("The days between "+y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" and "+y1+"-"+m1+"-"+d1+" are:"+n); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }
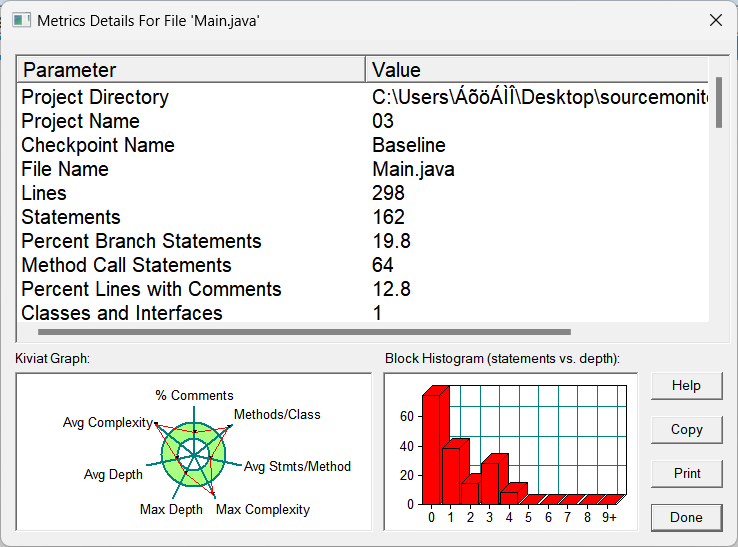
问题:(1)类过于多,但题目要求没办法
(2)方法中复杂程度过高
(3)耦合过高。
改进和踩坑心得:聚合二和上面的聚合一的思路不同,在聚合二中首先是Day类与DateUtil类聚合,Month类再与DateUtil类聚合,Year类再与DateUtil类聚合,每一个类都是一个单独的部分,没有关联。当我们需要运用到某一个类时,必须要对这些聚合在DateUtil类的类统一进行调整,实现DateUtil类更加复杂,但是没有聚合一那么多的嵌套关系。但是聚合一只要考虑好不同聚合之间的调用关系,那么还是比较简单的。第六次作业
7-4 ATM机类结构设计(一)
输入格式:
每一行输入一次业务操作,可以输入多行,最终以字符#终止。具体每种业务操作输入格式如下:
- 存款、取款功能输入数据格式:
卡号 密码 ATM机编号 金额(由一个或多个空格分隔),
其中,当金额大于0时,代表取款,否则代表存款。 - 查询余额功能输入数据格式:
卡号
输出格式:
①输入错误处理
- 如果输入卡号不存在,则输出
Sorry,this card does not exist.。 - 如果输入ATM机编号不存在,则输出
Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong.。 - 如果输入银行卡密码错误,则输出
Sorry,your password is wrong.。 - 如果输入取款金额大于账户余额,则输出
Sorry,your account balance is insufficient.。 - 如果检测为跨行存取款,则输出
Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported.。
②取款业务输出
输出共两行,格式分别为:
[用户姓名]在[银行名称]的[ATM编号]上取款¥[金额]
当前余额为¥[金额]
其中,[]说明括起来的部分为输出属性或变量,金额均保留两位小数。
③存款业务输出
输出共两行,格式分别为:
[用户姓名]在[银行名称]的[ATM编号]上存款¥[金额]
当前余额为¥[金额]
其中,[]说明括起来的部分为输出属性或变量,金额均保留两位小数。
④查询余额业务输出
¥[金额]
金额保留两位小数。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6222081502001312390 88888888 06 -500.00 #
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
张无忌在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上存款¥500.00 当前余额为¥10500.00
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6217000010041315709 88888888 02 3500.00 #
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
杨过在中国建设银行的02号ATM机上取款¥3500.00 当前余额为¥6500.00
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6217000010041315715 #
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
¥10000.00
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6222081502001312390 88888888 06 -500.00 6222081502051320786 88888888 06 1200.00 6217000010041315715 88888888 02 1500.00 6217000010041315709 88888888 02 3500.00 6217000010041315715 #
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
张无忌在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上存款¥500.00 当前余额为¥10500.00 韦小宝在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上取款¥1200.00 当前余额为¥8800.00 杨过在中国建设银行的02号ATM机上取款¥1500.00 当前余额为¥8500.00 杨过在中国建设银行的02号ATM机上取款¥3500.00 当前余额为¥5000.00 ¥5000.00
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Objects; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //输入 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String input = in.nextLine(); //截止到#前输入 while(!input.equals("#")) { String[] gets = input.split("\\s+"); if(gets.length==1) { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm.checkmoney(gets[0]); }else { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm = atm.getATM(gets[2]); if(atm == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); }else { atm.Outmoney(gets[0],gets[1],Double.parseDouble(gets[3]));//将字符串转化为double类 } } input = in.nextLine(); } } } class Account { String num; Card[] cards;//数组化 double money = 10000;//钱的初始值 public Account(){ } public Account(String num,Card[] cards){ super(); this.num = num; this.cards = cards; } } class ATM{ String id; String BankName; public ATM(){ } //判断银行 public ATM(String id){ super(); this.id = id; if(Objects.equals(id, "01") || Objects.equals(id, "02")||Objects.equals(id,"03")||Objects.equals(id,"04")){ this.BankName = "中国建设银行"; }else{ this.BankName = "中国工商银行"; } } //银行对应的编号 public ATM getATM(String nubmer) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); for(Bank bank:union.banks) { for(ATM atm:bank.atms) { if(nubmer.equals(atm.id)) { return atm; } } } return null; } //取钱 public void Outmoney(String cardnumber,String password,double money) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); String username = ""; String bankname = ""; Account account = null; Card card = null; for(Bank bank:union.banks) {//替换 bankname = bank.name; for(User user:bank.users) { username = user.name; for(Account accounts:user.accounts) { account = accounts; for(Card cardo:account.cards) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { card = cardo; break; } } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); return; } if(!card.password.equals(password)) { System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); return; } if(!this.BankName.equals(bankname)) { System.out.println("Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported."); return; } if(money<=0) { account.money -= money; System.out.println(username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); }else { if(account.money<money) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); return; }else { account.money -= money; System.out.println(username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } } System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+String.format("%.2f", account.money)); } //查询 public void checkmoney(String cardnumber) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); String username = ""; String bankname = ""; Account account = null; Card card = null; for(Bank bank:union.banks) {//替换 bankname = bank.name; for(User user:bank.users) { username = user.name; for(Account accounts:user.accounts) { account = accounts; for(Card cardo:account.cards) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { card = cardo; break; } } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); return; } System.out.println("¥"+String.format("%.2f", account.money)); } } class Bank{ String name; User[] users; ATM[] atms; public Bank(){ } public Bank(String name,User[] users,ATM[] atms){ super(); this.name = name; this.users = users; this.atms = atms; } } class Card { String num; String password = "88888888"; public Card(){ } public Card(String num){ super(); this.num = num; } } class UnionPay { //银联只有一个,使用单例 public static UnionPay union = null; Bank[] banks =new Bank[2]; //必须静态化,否则在ATM类中调用会报错 public static UnionPay getUnionPay(){ if(union!= null){ return union; } union = new UnionPay(); return union; } public UnionPay() { Card[] card1 = {new Card("6217000010041315709"),new Card("6217000010041315715")}; Card[] card2 = {new Card("6217000010041315718")}; Card[] card3 = {new Card("6217000010051320007")}; Card[] card4 = {new Card("6222081502001312389")}; Card[] card5 = {new Card("6222081502001312390")}; Card[] card6 = {new Card("6222081502001312399"),new Card("6222081502001312400")}; Card[] card7 = {new Card("6222081502051320785")}; Card[] card8 = {new Card("6222081502051320786")}; Account[] account1 = {new Account("3217000010041315709",card1),new Account("3217000010041315715",card2)}; Account[] account2 = {new Account("3217000010051320007",card3)}; Account[] account3 = {new Account("3222081502001312389",card4),new Account("3222081502001312390",card5),new Account("3222081502001312399",card6)}; Account[] account4 = {new Account("3222081502051320785",card7),new Account("3222081502051320786",card8)}; User[] user1 = {new User(account1,"杨过"),new User(account2,"郭靖")}; User[] user2 = {new User(account3,"张无忌"),new User(account4,"韦小宝")}; ATM[] atm1 = {new ATM("01"),new ATM("02"),new ATM("03"),new ATM("04")}; ATM[] atm2 = {new ATM("05"),new ATM("06")}; banks[0] = new Bank("中国建设银行",user1,atm1); banks[1] = new Bank("中国工商银行",user2,atm2); } } class User { Account[] accounts; String name; public User(){ } public User(Account[] accounts,String name){ super(); this.accounts = accounts; this.name = name; } }
报表展示:

问题:(1)方法用的过多,但总体来说不错
几个类之间的联系,几个类之间的关系非常的微妙。
比如银联只能有一个,所以我使用了单例。
比如银行里存储的信息,是用户包含了账户信息然后包含卡
还是一张卡对应一个用户。
非常值得深思。
7-4 ATM机类结构设计(一)
输入格式:
每一行输入一次业务操作,可以输入多行,最终以字符#终止。具体每种业务操作输入格式如下:
- 存款、取款功能输入数据格式:
卡号 密码 ATM机编号 金额(由一个或多个空格分隔),
其中,当金额大于0时,代表取款,否则代表存款。 - 查询余额功能输入数据格式:
卡号
输出格式:
①输入错误处理
- 如果输入卡号不存在,则输出
Sorry,this card does not exist.。 - 如果输入ATM机编号不存在,则输出
Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong.。 - 如果输入银行卡密码错误,则输出
Sorry,your password is wrong.。 - 如果输入取款金额大于账户余额,则输出
Sorry,your account balance is insufficient.。 - 如果检测为跨行存取款,则输出
Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported.。
②取款业务输出
输出共两行,格式分别为:
[用户姓名]在[银行名称]的[ATM编号]上取款¥[金额]
当前余额为¥[金额]
其中,[]说明括起来的部分为输出属性或变量,金额均保留两位小数。
③存款业务输出
输出共两行,格式分别为:
业务:取款 [用户姓名]在[银行名称]的[ATM编号]上取款¥[金额]
当前余额为¥[金额]
其中,[]说明括起来的部分为输出属性或变量,金额均保留两位小数。
④查询余额业务输出
业务:查询余额 ¥[金额]
金额保留两位小数。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6222081502001312390 88888888 06 500.00
#
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
业务:取款 张无忌在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上取款¥500.00
当前余额为¥9500.00
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6217000010041315709 88888888 06 3500.00
#
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
业务:取款 杨过在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上取款¥3500.00
当前余额为¥6395.00
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6217000010041315715
#
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
业务:查询余额 ¥10000.00
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6222081502001312390 88888888 01 500.00
6222081502051320786 88888888 06 1200.00
6217000010041315715 88888888 02 1500.00
6217000010041315709 88888888 02 3500.00
6217000010041315715
#
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
业务:取款 张无忌在中国建设银行的01号ATM机上取款¥500.00
当前余额为¥9490.00
业务:取款 韦小宝在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上取款¥1200.00
当前余额为¥8800.00
业务:取款 杨过在中国建设银行的02号ATM机上取款¥1500.00
当前余额为¥8500.00
业务:取款 杨过在中国建设银行的02号ATM机上取款¥3500.00
当前余额为¥5000.00
业务:查询余额 ¥5000.00
输入样例5:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6640000010045442002 88888888 09 3000
6640000010045442002 88888888 06 8000
6640000010045442003 88888888 01 10000
6640000010045442002
#
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
业务:取款 张三丰在中国农业银行的09号ATM机上取款¥3000.00
当前余额为¥6880.00
业务:取款 张三丰在中国工商银行的06号ATM机上取款¥8000.00
当前余额为¥-1416.00
业务:取款 张三丰在中国建设银行的01号ATM机上取款¥10000.00
当前余额为¥-11916.00
业务:查询余额 ¥-11916.00
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Objects; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //输入 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String input = in.nextLine(); //截止到#前输入 while(!input.equals("#")) { String[] gets = input.split("\\s+"); if(gets.length==1) { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm.checkMoney(gets[0]); }else { ATM atm = new ATM(); atm = atm.getATM(gets[2]); if(atm == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); }else { atm.Outmoney(gets[0],gets[1],Double.parseDouble(gets[3]));//将字符串转化为double类 } } input = in.nextLine(); } } } class ATM{ String name; String id; String BankName; String bankname = ""; public ATM(){ } //判断银行 public ATM(String id){ this.id = id; if(Objects.equals(id, "01") || Objects.equals(id, "02")||Objects.equals(id,"03")||Objects.equals(id,"04")){ bankname = "中国建设银行"; }else if(Objects.equals(id, "05") || Objects.equals(id, "06")){ bankname = "中国工商银行"; }else if(Objects.equals(id, "07") || Objects.equals(id, "08")||Objects.equals(id,"09")||Objects.equals(id,"10")||Objects.equals(id,"11")){ bankname = "中国农业银行"; } } //银行对应的编号 public ATM getATM(String nubmer) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); for(Bank bank:union.banks) { for(ATM atm:bank.atms) { if(nubmer.equals(atm.id)) { return atm; } } } return null; } //取钱 public void Outmoney(String cardnumber,String password,double money) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); String username = ""; Account account = null; Card card = null; for(Bank bank:union.banks) {//替换 this.BankName = bank.name; for(User user:bank.users) { username = user.name; for(Account accounts:user.accounts) { account = accounts; for(Card cardo:account.cards) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { card = cardo; break; } } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); return; } if(!card.password.equals(password)) { System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); return; } if(!this.BankName.equals(bankname)&&money<=0) { if(!this.BankName.equals("中国建设银行")&&bankname.equals("中国建设银行")){ account.money -= money*1.02; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } if(!this.BankName.equals("中国工商银行")&&bankname.equals("中国工商银行")){ account.money -= money*1.03; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } if(!this.BankName.equals("中国农业银行")&&bankname.equals("中国农业银行")){ account.money -= money*1.04; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } } if(!this.BankName.equals(bankname)&&money>0&&account.money>=money){ if(!this.BankName.equals("中国建设银行")&&bankname.equals("中国建设银行")){ account.money -= money*1.02; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } if(!this.BankName.equals("中国工商银行")&&bankname.equals("中国工商银行")){ account.money -= money*1.03; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money)));} if(!this.BankName.equals("中国农业银行")&&bankname.equals("中国农业银行")){ account.money -= money*1.04; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } } if(this.BankName.equals(bankname)&&money<=0) { account.money -= money; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } if(this.BankName.equals(bankname)&&money>0&&account.money>=money){ account.money -= money; System.out.println("业务:取款"+username+"在"+bankname+"的"+this.id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(money))); } } //查询 public void checkMoney(String cardnumber) { UnionPay union = UnionPay.getUnionPay(); String username = ""; String bankname = ""; Account account = null; Card card = null; for(Bank bank:union.banks) {//替换 bankname = bank.name; for(User user:bank.users) { username = user.name; for(Account accounts:user.accounts) { account = accounts; for(Card cardo:account.cards) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { if(cardo.num.equals(cardnumber)) { card = cardo; break; } } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card!=null) { break; } } if(card == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); return; } System.out.println("业务:查询余额 ¥"+String.format("%.2f", account.money)); } } class Card { String num; String password = "88888888"; public Card(){ } public Card(String num){ super(); this.num = num; } } class Account { String num; Card[] cards;//数组化 double money = 10000;//钱的初始值 public Account(){ } public Account(String num,Card[] cards){ super(); this.num = num; this.cards = cards; } } class Bank{ String name; User[] users; ATM[] atms; public Bank(){ } public Bank(String name,User[] users,ATM[] atms){ super(); this.name = name; this.users = users; this.atms = atms; } } class User { Account[] accounts; String name; public User(){ } public User(Account[] accounts,String name){ super(); this.accounts = accounts; this.name = name; } } class UnionPay { //银联只有一个,使用单例 public static UnionPay union = null; Bank[] banks =new Bank[3]; //必须静态化,否则在ATM类中调用会报错 public static UnionPay getUnionPay(){ if(union!= null){ return union; } union = new UnionPay(); return union; } public UnionPay() { Card[] card1 = {new Card("6217000010041315709"),new Card("6217000010041315715")}; Card[] card2 = {new Card("6217000010041315718")}; Card[] card3 = {new Card("6217000010051320007")}; Card[] card4 = {new Card("6222081502001312389")}; Card[] card5 = {new Card("6222081502001312390")}; Card[] card6 = {new Card("6222081502001312399"),new Card("6222081502001312400")}; Card[] card7 = {new Card("6222081502051320785")}; Card[] card8 = {new Card("6222081502051320786")}; Card[] card9 = {new Card("6640000010045442002"),new Card("6640000010045442003")}; Card[] card10 = {new Card("6640000010045442003")}; Card[] card11 = {new Card("6630000010033431001")}; Card[] card12 = {new Card("6630000010033431008")}; Account[] account1 = {new Account("3217000010041315709",card1),new Account("3217000010041315715",card2)}; Account[] account2 = {new Account("3217000010051320007",card3)}; Account[] account3 = {new Account("3222081502001312389",card4),new Account("3222081502001312390",card5),new Account("3222081502001312399",card6)}; Account[] account4 = {new Account("3222081502051320785",card7),new Account("3222081502051320786",card8)}; Account[] account5 = {new Account("3640000010045442002",card9)}; Account[] account6 = {new Account("3640000010045441009",card10)}; Account[] account7 = {new Account("3640000010045441009",card11)}; Account[] account8 = {new Account("3630000010033431008",card12)}; User[] user1 = {new User(account1,"杨过"),new User(account2,"郭靖"),new User(account5,"张三丰")}; User[] user2 = {new User(account3,"张无忌"),new User(account4,"韦小宝"),new User(account6,"令狐冲")}; User[] user3 = {new User(account7,"乔峰"),new User(account8,"洪七公")}; ATM[] atm1 = {new ATM("01"),new ATM("02"),new ATM("03"),new ATM("04")}; ATM[] atm2 = {new ATM("05"),new ATM("06")}; ATM[] atm3 = {new ATM("07"),new ATM("08"),new ATM("09"),new ATM("10"),new ATM("11"),new ATM("12")}; banks[0] = new Bank("中国建设银行",user1,atm1); banks[1] = new Bank("中国工商银行",user2,atm2); banks[2] = new Bank("中国农业银行",user3,atm3); } }
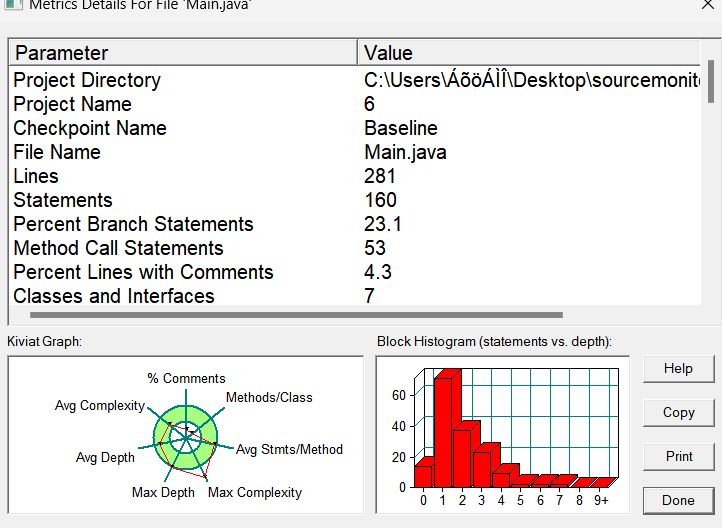
问题:(1)注释过少,单体复杂度较高
(2)算法不明确,不理解题目意思导致题目没有做对
(3)贷款收费是叠加的,只有account.money<0时才开始透支
改进:增加借贷账户和贷款账户俩类,分别用于计算俩种不同的情况
总结
对于这三次作业来说,比上一次作业难度有所增加,阅读题目方面的阅读量需求更大了,要更加清楚面向对象的对象提出的需求,面向对象进行编程,而不是面向测试点进行编程。
老师上课所讲述的原则模式方法得融会贯通,运用进去,才能真正的掌握。

