利用堆排序找出数组中前n大的元素
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <memory.h> #define MAX_SIZE (1000 * 10000 + 1) #define PARENT(i) (i/2) #define RIGHT(i) (i*2 + 1) #define LEFT(i) (i*2) #define EXCHANGE(a,b,t) do{t=a;a=b;b=t;}while(0) // 生成不重复的随机数序列写入文件 void gen_test_data(uint32_t cnt) { if( cnt >= MAX_SIZE){printf("cnt too largr\n");return;} //uint32_t i = 0; //char *buf = (char*)malloc(MAX_SIZE); //for(;i < cnt;++i){buf[i] = 1;} uint32_t n = 0; char file_name[256]; snprintf(file_name,256,"test_data_%d.txt",cnt); FILE *fp = fopen(file_name,"w"); if(NULL == fp){printf("open %s error!\n",file_name);return;} while(n < cnt) { int32_t nRand = rand() % cnt; //while(buf[nRand] == 0)nRand = (nRand + 1)%cnt; //buf[nRand] = 0; fprintf(fp,"%d ",nRand); ++n; } fclose(fp); printf("gen %s finished\n",file_name); } // 读取文件 void read_data(int32_t arr[],const uint32_t size,uint32_t *cnt,const uint32_t data_cnt) { FILE *fp = NULL; *cnt = 0; char file_name[256]; if(data_cnt > size){printf("data_cnt too largr\n");return;} snprintf(file_name,256,"test_data_%d.txt",data_cnt); fp = fopen(file_name,"r"); if(NULL == fp){printf("open %s error!\n",file_name);return;} while(!feof(fp) && *cnt < size) { fscanf(fp,"%d ",&arr[*cnt]); (*cnt)++; } fclose(fp); } // 快速排序 void quick_sort(int32_t arr[],int32_t low,int32_t high) { if(low >= high)return; int32_t i = low,j = high,tmp = arr[i]; while(i<j) { while(i<j && arr[j] <= tmp)j--; if(i<j){arr[i] = arr[j];i++;} while(i<j && arr[i] > tmp)i++; if(i<j){arr[j] = arr[i];j--;} } arr[i] = tmp; quick_sort(arr,low,i-1); quick_sort(arr,i+1,high); } void get_topn_quick(int32_t arr[],int32_t low,int32_t high,const int32_t topn) { if(low >= high || topn > high)return; int32_t i = low,j = high,tmp = arr[i]; while(i<j) { while(i<j && arr[j] < tmp)j--; if(i<j)arr[i++] = arr[j]; while(i<j && arr[i] >= tmp)i++; if(i<j)arr[j--] = arr[i]; } arr[i] = tmp; int32_t n = i - low + 1; if (n == topn)return; else if (n > topn) get_topn_quick(arr, low, i-1, topn); else if (n < topn) get_topn_quick(arr, i+1, high, topn - n); } void max_heapify(int32_t arr[],const uint32_t size,uint32_t i) { uint32_t left = LEFT(i),right = RIGHT(i),largest = 0,tmp = 0; if(left<size && arr[left] > arr[i])largest = left; else largest = i; if(right<size && arr[right] > arr[largest])largest = right; if(largest != i) { EXCHANGE(arr[i],arr[largest],tmp); max_heapify(arr,size,largest); } } void min_heapify(int32_t arr[],const uint32_t size,uint32_t i) { uint32_t left = LEFT(i),right = RIGHT(i),largest = 0,tmp = 0; if(left<size && arr[left] < arr[i])largest = left; else largest = i; if(right<size && arr[right] < arr[largest])largest = right; if(largest != i) { EXCHANGE(arr[i],arr[largest],tmp); min_heapify(arr,size,largest); } } void get_topn_heap(int32_t arr[], const int32_t arr_size, const int32_t topn) { int32_t i = topn / 2, tmp = 0; // 在[0--topn)范围内构建最小堆,即优先级队列 while (i >= 0)min_heapify(arr, topn, i--); for (i = topn; i < arr_size; ++i) { if (arr[i] <= arr[0])continue; //小于最小值,没有判断的必要 EXCHANGE(arr[0], arr[i], tmp); min_heapify(arr, topn, 0); } } void dump1(int32_t arr[],const uint32_t cnt) { uint32_t i = 0; for(;i < cnt;++i) { printf("%4d ",arr[i]); } printf("\n"); } void dump2(int32_t arr[],const uint32_t start,const uint32_t end) { uint32_t i = start; for(;i < end;++i) { printf("%5d ",arr[i]); } printf("\n"); } int32_t main(int32_t argc, char *argv[]) { uint32_t t = 0; int32_t *arr = (int32_t*)malloc(sizeof(int32_t)*MAX_SIZE); int32_t *heap = (int32_t*)malloc(sizeof(int32_t)*MAX_SIZE); int32_t *quick = (int32_t*)malloc(sizeof(int32_t)*MAX_SIZE); uint32_t cnt = 0,data_cnt = 0; for(cnt = 10;cnt <= MAX_SIZE;cnt*=10) { gen_test_data(cnt); } for(data_cnt = 10;data_cnt <= MAX_SIZE;data_cnt*=10) { read_data(arr, MAX_SIZE, &cnt, data_cnt); memcpy(heap,arr,sizeof(int32_t)*MAX_SIZE); printf("cnt=%d\n",cnt); t = clock(); get_topn_heap(heap,cnt,cnt/10); printf("heap use time:%ld\n",clock()-t); quick_sort(heap,0,cnt/2-1); //dump2(heap,0,cnt/10); memcpy(quick,arr,sizeof(int32_t)*MAX_SIZE); t = clock(); get_topn_quick(quick,0,cnt-1,cnt/10); printf("quick use time:%ld\n",clock()-t); quick_sort(quick,0,cnt/2-1); //dump2(quick,0,cnt/10); if(memcmp(heap,quick,sizeof(int32_t)*(cnt/10-1)) == 0)printf("OK\n"); } return 0; }
函数 get_topn_heap 实现了用最小堆查找数组arr中最大topn个数字,并将它们放置在数组中[0-tonp)的位置
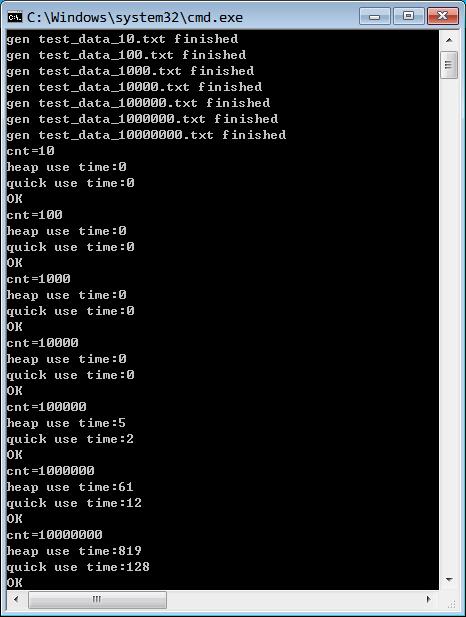
与前面的用快速排序的方法相比,用最小堆的方法效率稍低一些,快速排序方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/tangxin-blog/p/5617736.html
对比数据: