3.基于梯度的攻击——PGD
PGD攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf
1.PGD攻击的原理
PGD(Project Gradient Descent)攻击是一种迭代攻击,可以看作是FGSM的翻版——K-FGSM (K表示迭代的次数),大概的思路就是,FGSM是仅仅做一次迭代,走一大步,而PGD是做多次迭代,每次走一小步,每次迭代都会将扰动clip到规定范围内。
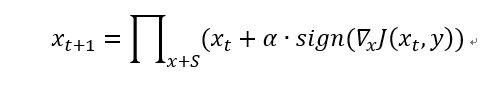
一般来说,PGD的攻击效果比FGSM要好,那么原理是什么呢?首先,如果目标模型是一个线性模型,那么用FGSM就可以了,因为此时loss对输入的导数是固定的,换言之,使得loss下降的方向是明确的,即使你多次迭代,扰动的方向也不会改变。而对于一个非线性模型,仅仅做一次迭代,方向是不一定完全正确的,这也是为什么FGSM的效果一般的原因了。

用画图软件画了一个很丑的图,但大致能够表达我的看法,黑圈是输入样本,假设样本只有两维,那么样本可以改变的就有八个方向,坐标系中显示了loss等高线,以及可以扰动的最大范围(因为是无穷范数,所以限制范围是一个方形,负半轴的范围没有画出来),黑圈每一次改变,都是以最优的方向改变,最后一次由于扰动超出了限制,所以直接截断,如果此时迭代次数没有用完,那么就在截断处继续迭代,直到迭代次数用完。
2.PGD的代码实现

1 class PGD(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self,model): 3 super().__init__() 4 self.model=model#必须是pytorch的model 5 self.device=torch.device("cuda" if (torch.cuda.is_available()) else "cpu") 6 def generate(self,x,**params): 7 self.parse_params(**params) 8 labels=self.y 9 10 adv_x=self.attack(x,labels) 11 return adv_x 12 def parse_params(self,eps=0.3,iter_eps=0.01,nb_iter=40,clip_min=0.0,clip_max=1.0,C=0.0, 13 y=None,ord=np.inf,rand_init=True,flag_target=False): 14 self.eps=eps 15 self.iter_eps=iter_eps 16 self.nb_iter=nb_iter 17 self.clip_min=clip_min 18 self.clip_max=clip_max 19 self.y=y 20 self.ord=ord 21 self.rand_init=rand_init 22 self.model.to(self.device) 23 self.flag_target=flag_target 24 self.C=C 25 26 27 def sigle_step_attack(self,x,pertubation,labels): 28 adv_x=x+pertubation 29 # get the gradient of x 30 adv_x=Variable(adv_x) 31 adv_x.requires_grad = True 32 loss_func=nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 33 preds=self.model(adv_x) 34 if self.flag_target: 35 loss =-loss_func(preds,labels) 36 else: 37 loss=loss_func(preds,labels) 38 # label_mask=torch_one_hot(labels) 39 # 40 # correct_logit=torch.mean(torch.sum(label_mask * preds,dim=1)) 41 # wrong_logit = torch.mean(torch.max((1 - label_mask) * preds, dim=1)[0]) 42 # loss=-F.relu(correct_logit-wrong_logit+self.C) 43 44 self.model.zero_grad() 45 loss.backward() 46 grad=adv_x.grad.data 47 #get the pertubation of an iter_eps 48 pertubation=self.iter_eps*np.sign(grad) 49 adv_x=adv_x.cpu().detach().numpy()+pertubation.cpu().numpy() 50 x=x.cpu().detach().numpy() 51 52 pertubation=np.clip(adv_x,self.clip_min,self.clip_max)-x 53 pertubation=clip_pertubation(pertubation,self.ord,self.eps) 54 55 56 return pertubation 57 def attack(self,x,labels): 58 labels = labels.to(self.device) 59 print(self.rand_init) 60 if self.rand_init: 61 x_tmp=x+torch.Tensor(np.random.uniform(-self.eps, self.eps, x.shape)).type_as(x).cuda() 62 else: 63 x_tmp=x 64 pertubation=torch.zeros(x.shape).type_as(x).to(self.device) 65 for i in range(self.nb_iter): 66 pertubation=self.sigle_step_attack(x_tmp,pertubation=pertubation,labels=labels) 67 pertubation=torch.Tensor(pertubation).type_as(x).to(self.device) 68 adv_x=x+pertubation 69 adv_x=adv_x.cpu().detach().numpy() 70 71 adv_x=np.clip(adv_x,self.clip_min,self.clip_max) 72 73 return adv_x
PGD攻击的参数并不多,比较重要的就是下面这几个:
eps: maximum distortion of adversarial example compared to original input
eps_iter: step size for each attack iteration
nb_iter: Number of attack iterations.
我在上面代码中注释的这行代码是CW攻击的PGD形式,这个在防御论文https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf中有体现,以后说到CW攻击再细说。
1 # label_mask=torch_one_hot(labels) 2 # 3 # correct_logit=torch.mean(torch.sum(label_mask * preds,dim=1)) 4 # wrong_logit = torch.mean(torch.max((1 - label_mask) * preds, dim=1)[0]) 5 # loss=-F.relu(correct_logit-wrong_logit+self.C)
最后再提一点就是,在上面那篇防御论文中也提到了,PGD攻击是最强的一阶攻击,如果防御方法对这个攻击能够有很好的防御效果,那么其他攻击也不在话下了。
2019-03-29 20:43:40






