MNIST手写数字识别:分类应用入门(实践篇)
慕课:《深度学习应用开发-TensorFlow实践》
章节:第七讲 MNIST手写数字识别:分类应用入门
TensorFlow版本为2.3
理论篇:MNIST手写数字识别:分类应用入门(理论篇)
数据集加载与预处理
数据集下载与导入
有关数据集下载在理论篇里讲了,这里就只放代码,想知道详细的可以去看看理论篇
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
tf.__version__
mnist=tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(train_images,train_labels),(test_images,test_labels)=mnist.load_data()
划分验证集
在TF2中,没有单独划分验证集,而在TF1中是有进行划分的,因此我们要自己划分一下验证集
total_num=len(train_images)
valid_split=0.2# 验证集占20%
train_num=int(total_num*(1-valid_split))
train_x=train_images[:train_num]
train_y=train_labels[:train_num]
valid_x=train_images[train_num:]
valid_y=train_labels[train_num:]
test_x=test_images
test_y=test_labels
接下来我们把(28,28)的结构拉直为一行784
train_x=train_x.reshape(-1,784)# -1表示不指定,他会在计算过程自动生成
valid_x=valid_x.reshape(-1,784)
test_x=test_x.reshape(-1,784)
特征数据归一化
train_x=tf.cast(train_x/255.0,tf.float32)
valid_x=tf.cast(valid_x/255.0,tf.float32)
test_x=tf.cast(test_x/255.0,tf.float32)
独热编码
我们要将标签数据进行独热编码,这一步同样是TF1已经做好了,但TF2没做。
train_y=tf.one_hot(train_y,depth=10)
valid_y=tf.one_hot(valid_y,depth=10)
test_y=tf.one_hot(test_y,depth=10)
构建模型
def model(x,w,b):
pred=tf.matmul(x,w)+b
return tf.nn.softmax(pred)
模型训练
定义变量
W=tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([784,10],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32))
B=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),dtype=tf.float32)
定义交叉熵损失函数
def loss(x,y,w,b):
pred=model(x,w,b)
loss_=tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true=y,y_pred=pred)
return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)
设置超参数
training_epochs=20
batch_size=50
lr=0.001
定义梯度计算函数
def grad(x,y,w,b):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss_=loss(x,y,w,b)
return tape.gradient(loss_,[w,b])# 返回梯度向量
选择优化器
我们依旧选用Adam优化器
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=lr)
定义准确率
def accuracy(x,y,w,b):
pred=model(x,w,b)
corr=tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(corr,tf.float32))
训练
total_step=int(train_num/batch_size)
loss_list_train=[]#train loss
loss_list_valid=[]
acc_list_train=[]#train loss
acc_list_valid=[]
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for step in range(total_step):
xs=train_x[step*batch_size:(step+1)*batch_size,:]
ys=train_y[step*batch_size:(step+1)*batch_size]
grads=grad(xs,ys,W,B)#计算梯度
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads,[W,B]))#优化器调参
loss_train=loss(train_x,train_y,W,B).numpy()
loss_valid=loss(valid_x,valid_y,W,B).numpy()
acc_train=accuracy(train_x,train_y,W,B).numpy()
acc_vaild=accuracy(valid_x,valid_y,W,B).numpy()
loss_list_train.append(loss_train)
loss_list_valid.append(loss_valid)
acc_list_train.append(acc_train)
acc_list_valid.append(acc_vaild)
print(f"epoch={epoch+1},train_loss={loss_train},valid_loss={loss_valid},train_accuracy={acc_train},valid_accuracy={acc_vaild}")
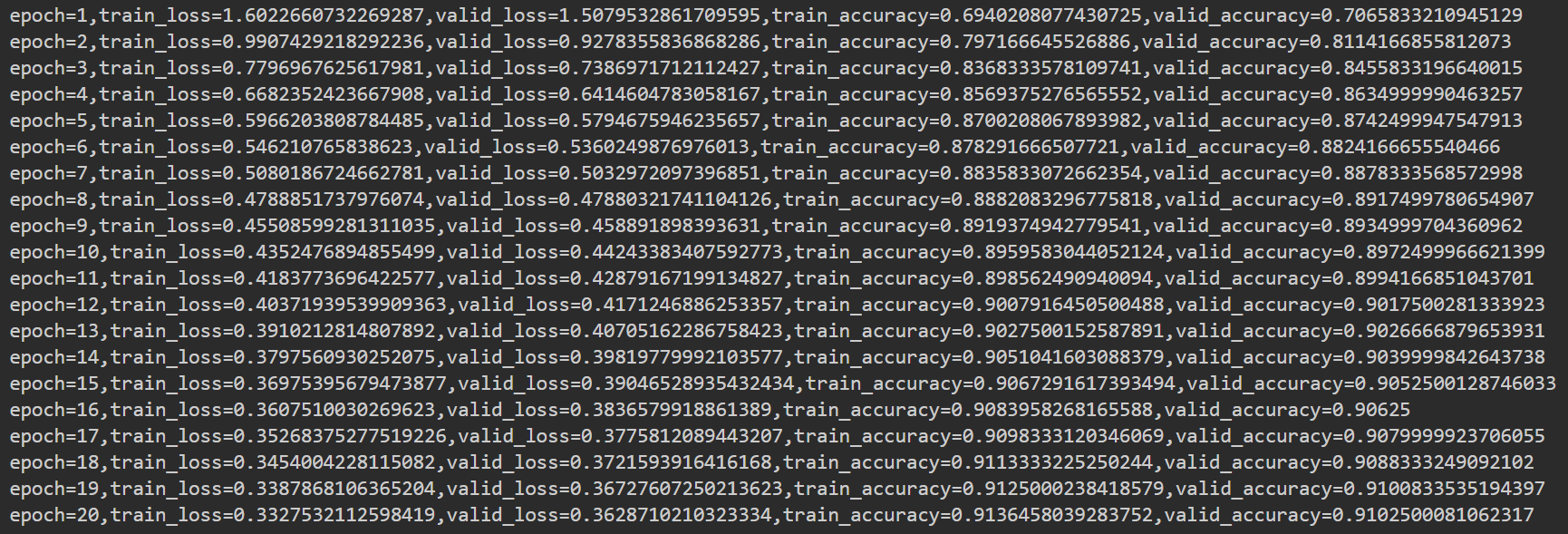
我们可以可视化一下训练过程
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.plot(loss_list_train,'blue',label="Train Loss")
plt.plot(loss_list_valid,'red',label='Valid Loss')
plt.legend(loc=1)

模型评估
acc_test=accuracy(test_x,test_y,W,B).numpy()
print(f'Test acc={acc_test}')
输出
Test acc=0.9061999917030334
学习笔记,仅供参考,如有错误,敬请指正!


