YOLOV5、YOLOV7使用onnx转tensorrt(engine)
近几日完成ResNet相关实现engine方法,但仅仅基于基于简单分类网络实现转换,且基于Tensorrt C++ API 构建YLOV5实现engine转换相关资料较多,然调用ONNX解析转换engine相关资料较少,因此本文将介绍如何使用onnx构建engine,并推理。
版本:tensorrt版本8.4,可使用8.0以上版本
一.yolov5转onnx方法:
这里我将重点说明,我使用官方export.py能成功导出onnx文件,也能使用python的onnx runtime预测出正确结果,且也能转rknn模型完成测试,但使用tensorrt的onnx解析构建engine时候,便会出错。若知道答案可帮忙回答,万分感谢!
方法一:
需使用github:https://github.com/linghu8812/yolov5 成功转onnx,能被tensorrt的onnx解析,实现网络构建。
其解析构建网络代码:
const char* onnx_path = "./best.onnx"; INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(1U); //此处重点1U为OU就有问题 IParser* parser = createParser(*network, gLogger); parser->parseFromFile(onnx_path, static_cast<int32_t>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING)); //解析有错误将返回 for (int32_t i = 0; i < parser->getNbErrors(); ++i) { std::cout << parser->getError(i)->desc() << std::endl; } std::cout << "successfully parse the onnx model" << std::endl;
方法二(修改时间:2022-0905):
可用github yolov7的转换代码https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7/tree/u5 ,已测试可行。同时也测试了yolov7转换,任然可运行。
二.基于C++ 使用onnx转engine且推理
(1)yolov5 使用onnx转为engine代码,此代码比较原始,未做后处理逻辑而保存代码。
可忽略该版本代码直接使用(2)中代码。

#include "NvInfer.h" #include "cuda_runtime_api.h" #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <chrono> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> // onnx转换头文件 #include "NvOnnxParser.h" using namespace nvonnxparser; using namespace std; #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) struct alignas(float) Detection { //center_x center_y w h float bbox[4]; float conf; // bbox_conf * cls_conf float class_id; }; // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = 640; static const int INPUT_W = 640; static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 25200*85; //1000 * sizeof(Detection) / sizeof(float) + 1; const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "images"; const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "output"; using namespace nvinfer1; //static Logger gLogger; //构建Logger class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } } gLogger; // Creat the engine using only the API and not any parser. ICudaEngine* createEngine(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config) { const char* onnx_path = "./best.onnx"; INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(1U); //此处重点1U为OU就有问题 IParser* parser = createParser(*network, gLogger); parser->parseFromFile(onnx_path, static_cast<int32_t>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING)); //解析有错误将返回 for (int32_t i = 0; i < parser->getNbErrors(); ++i) { std::cout << parser->getError(i)->desc() << std::endl; } std::cout << "successfully parse the onnx model" << std::endl; // Build engine builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16); // 设置精度计算 //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kINT8); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); std::cout << "successfully convert onnx to engine!!! " << std::endl; //销毁 network->destroy(); parser->destroy(); return engine; } void APIToModel(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IHostMemory** modelStream) { // Create builder IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network, then set the outputs and create an engine ICudaEngine* engine = createEngine(maxBatchSize, builder, config); assert(engine != nullptr); // Serialize the engine (*modelStream) = engine->serialize(); // Close everything down engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); } void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) { const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); //const int inputIndex = 0; //const int outputIndex = 1; // Create GPU buffers on device cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float)); cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float)); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); } //加工图片变成拥有batch的输入, tensorrt输入需要的格式,为一个维度 void ProcessImage(cv::Mat image, float input_data[]) { //只处理一张图片,总之结果为一维[batch*3*INPUT_W*INPUT_H] //以下代码为投机取巧了 cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); std::vector<cv::Mat> InputImage; InputImage.push_back(image); int ImgCount = InputImage.size(); //float input_data[BatchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; for (int b = 0; b < ImgCount; b++) { cv::Mat img = InputImage.at(b); int w = img.cols; int h = img.rows; int i = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h; ++row) { uchar* uc_pixel = img.data + row * img.step; for (int col = 0; col < INPUT_W; ++col) { input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i] = (float)uc_pixel[2] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[1] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + 2 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[0] / 255.0; uc_pixel += 3; ++i; } } } } int get_trtengine() { IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; APIToModel(1, &modelStream); assert(modelStream != nullptr); std::ofstream p("./best.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); modelStream->destroy(); return 0; } int infer() { //加载engine引擎 char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("./best.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } //反序列为engine,创建context IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); delete[] trtModelStream; //*********************推理-循环推理*********************// float time_read_img = 0.0; float time_infer = 0.0; static float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // 处理图片为固定输出 auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 std::string path = "./1.jpg"; std::cout << "img_path=" << path << endl; static float data[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(path); ProcessImage(img, data); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_read_img = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_read_img; //Run inference start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 doInference(*context, data, prob, 1); end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_infer = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_infer; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; //输出后处理 //std::cout <<"prob="<<prob << std::endl; float cls_float = prob[0]; int cls_id = 0; for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++) { if (cls_float < prob[i]) { cls_float = prob[i]; cls_id = i; } } std::cout << "i=" << i << "\tcls_id=" << cls_id << "\t cls_float=" << cls_float << std::endl; } std::cout << "C++ 2engine" << "mean read img time =" << time_read_img / 1000 << "ms\t" << "mean infer img time =" << time_infer / 1000 << "ms" << std::endl; // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { //string mode = argv[1]; string mode = "-d"; //适用windows编译,固定指定参数 //if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-s") { if (mode == "-s") { get_trtengine(); } //else if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-d") { else if (mode == "-d") { infer(); } else { return -1; } return 0; }
(2)yolov5 使用onnx转为engine代码,完整代码。
代码重要步骤有解释,具体查看代码。
代码平台:windows10 visual studio 相关安装可参考我以往博客点击这里 和 这里末尾
本代码实现功能如下:
①.onnx转engine;
②.engine推理;
③CPU实现NMS方法

#include "NvInfer.h" #include "cuda_runtime_api.h" #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <chrono> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> // onnx转换头文件 #include "NvOnnxParser.h" using namespace nvonnxparser; using namespace std; #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) struct Detection { //center_x center_y w h float bbox[4]; float conf; // bbox_conf * cls_conf int class_id; int index; }; // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = 640; static const int INPUT_W = 640; static const int cls_num = 80; static const int anchor_output_num = 25200; //不同输入尺寸anchor:640-->25200 | 960-->56700 static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1* anchor_output_num *(cls_num+5); //1000 * sizeof(Detection) / sizeof(float) + 1; const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "images"; const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "output"; using namespace nvinfer1; //static Logger gLogger; //构建Logger class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } } gLogger; // Creat the engine using only the API and not any parser. ICudaEngine* createEngine(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config) { const char* onnx_path = "./best.onnx"; INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(1U); //此处重点1U为OU就有问题 IParser* parser = createParser(*network, gLogger); parser->parseFromFile(onnx_path, static_cast<int32_t>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING)); //解析有错误将返回 for (int32_t i = 0; i < parser->getNbErrors(); ++i) { std::cout << parser->getError(i)->desc() << std::endl; } std::cout << "successfully parse the onnx model" << std::endl; // Build engine builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16); // 设置精度计算 //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kINT8); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); std::cout << "successfully convert onnx to engine!!! " << std::endl; //销毁 network->destroy(); parser->destroy(); return engine; } void APIToModel(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IHostMemory** modelStream) { // Create builder IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network, then set the outputs and create an engine ICudaEngine* engine = createEngine(maxBatchSize, builder, config); assert(engine != nullptr); // Serialize the engine (*modelStream) = engine->serialize(); // Close everything down engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); } void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) { const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); //const int inputIndex = 0; //const int outputIndex = 1; // Create GPU buffers on device cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float)); cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float)); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); } int get_trtengine() { IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; APIToModel(1, &modelStream); assert(modelStream != nullptr); std::ofstream p("./best.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); modelStream->destroy(); return 0; } //加工图片变成拥有batch的输入, tensorrt输入需要的格式,为一个维度 void ProcessImage(cv::Mat image, float input_data[]) { //只处理一张图片,总之结果为一维[batch*3*INPUT_W*INPUT_H] //以下代码为投机取巧了 cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); std::vector<cv::Mat> InputImage; InputImage.push_back(image); int ImgCount = InputImage.size(); //float input_data[BatchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; for (int b = 0; b < ImgCount; b++) { cv::Mat img = InputImage.at(b); int w = img.cols; int h = img.rows; int i = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h; ++row) { uchar* uc_pixel = img.data + row * img.step; for (int col = 0; col < INPUT_W; ++col) { input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i] = (float)uc_pixel[2] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[1] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + 2 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[0] / 255.0; uc_pixel += 3; ++i; } } } } //********************************************** NMS code **********************************// /* struct Detection { //center_x center_y w h float bbox[4]; float conf; // bbox_conf * cls_conf int class_id; int index; }; */ struct Bbox { int x; int y; int w; int h; }; float iou(Bbox box1, Bbox box2) { int x1 = max(box1.x, box2.x); int y1 = max(box1.y, box2.y); int x2 = min(box1.x + box1.w, box2.x + box2.w); int y2 = min(box1.y + box1.h, box2.y + box2.h); int w = max(0, x2 - x1); int h = max(0, y2 - y1); float over_area = w * h; return over_area / (box1.w * box1.h + box2.w * box2.h - over_area); } int get_max_index(vector<Detection> pre_detection) { //获得最佳置信度的值,并返回对应的索引值 int index; float conf; if (pre_detection.size() > 0) { index = 0; conf = pre_detection.at(0).conf; for (int i = 0; i < pre_detection.size(); i++) { if (conf < pre_detection.at(i).conf) { index = i; conf = pre_detection.at(i).conf; } } return index; } else { return -1; } } bool judge_in_lst(int index, vector<int> index_lst) { //若index在列表index_lst中则返回true,否则返回false if (index_lst.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < index_lst.size(); i++) { if (index == index_lst.at(i)) { return true; } } } return false; } vector<int> nms(vector<Detection> pre_detection, float iou_thr) { /* 返回需保存box的pre_detection对应位置索引值 */ int index; vector<Detection> pre_detection_new; //Detection det_best; Bbox box_best, box; float iou_value; vector<int> keep_index; vector<int> del_index; bool keep_bool; bool del_bool; if (pre_detection.size() > 0) { pre_detection_new.clear(); // 循环将预测结果建立索引 for (int i = 0; i < pre_detection.size(); i++) { pre_detection.at(i).index = i; pre_detection_new.push_back(pre_detection.at(i)); } //循环便利获得保留box位置索引-相对输入pre_detection位置 while (pre_detection_new.size() > 0) { index = get_max_index(pre_detection_new); if (index >= 0) { keep_index.push_back(pre_detection_new.at(index).index); //保留索引位置 // 更新最佳保留box box_best.x = pre_detection_new.at(index).bbox[0]; box_best.y = pre_detection_new.at(index).bbox[1]; box_best.w = pre_detection_new.at(index).bbox[2]; box_best.h = pre_detection_new.at(index).bbox[3]; for (int j = 0; j < pre_detection.size(); j++) { keep_bool = judge_in_lst(pre_detection.at(j).index, keep_index); del_bool = judge_in_lst(pre_detection.at(j).index, del_index); if ((!keep_bool) && (!del_bool)) { //不在keep_index与del_index才计算iou box.x = pre_detection.at(j).bbox[0]; box.y = pre_detection.at(j).bbox[1]; box.w = pre_detection.at(j).bbox[2]; box.h = pre_detection.at(j).bbox[3]; iou_value = iou(box_best, box); if (iou_value > iou_thr) { del_index.push_back(j); //记录大于阈值将删除对应的位置 } } } //更新pre_detection_new pre_detection_new.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < pre_detection.size(); j++) { keep_bool = judge_in_lst(pre_detection.at(j).index, keep_index); del_bool = judge_in_lst(pre_detection.at(j).index, del_index); if ((!keep_bool) && (!del_bool)) { pre_detection_new.push_back(pre_detection.at(j)); } } } } } del_index.clear(); del_index.shrink_to_fit(); pre_detection_new.clear(); pre_detection_new.shrink_to_fit(); return keep_index; } vector<Detection> postprocess(float* prob, float conf_thr = 0.2, float nms_thr = 0.4) { /* #####################此函数处理一张图预测结果######################### prob为[x y w h score multi-pre] 如80类-->(1,anchor_num,85) */ vector<Detection> pre_results; vector<int> nms_keep_index; vector<Detection> results; bool keep_bool; Detection pre_res; float conf; int tmp_idx; float tmp_cls_score; for (int i = 0; i < anchor_output_num; i++) { tmp_idx = i * (cls_num + 5); pre_res.bbox[0] = prob[tmp_idx + 0]; pre_res.bbox[1] = prob[tmp_idx + 1]; pre_res.bbox[2] = prob[tmp_idx + 2]; pre_res.bbox[3] = prob[tmp_idx + 3]; conf = prob[tmp_idx + 4]; //是为目标的置信度 tmp_cls_score = prob[tmp_idx + 5] * conf; pre_res.class_id = 0; pre_res.conf = 0; for (int j = 1; j < cls_num; j++) { tmp_idx = i * (cls_num + 5) + 5 + j; //获得对应类别索引 if (tmp_cls_score < prob[tmp_idx] * conf) { tmp_cls_score = prob[tmp_idx] * conf; pre_res.class_id = j; pre_res.conf = tmp_cls_score; } } if (conf >= conf_thr) { pre_results.push_back(pre_res); } } //使用nms nms_keep_index=nms(pre_results,nms_thr); for (int i = 0; i < pre_results.size(); i++) { keep_bool = judge_in_lst(i, nms_keep_index); if (keep_bool) { results.push_back(pre_results.at(i)); } } pre_results.clear(); pre_results.shrink_to_fit(); nms_keep_index.clear(); nms_keep_index.shrink_to_fit(); return results; } cv::Mat draw_rect(cv::Mat image, vector<Detection> results) { /* image 为图像 struct Detection { float bbox[4]; //center_x center_y w h float conf; // 置信度 int class_id; //类别id int index; //可忽略 }; */ float x; float y; float y_tmp; float w; float h; string info; cv::Rect rect; for (int i = 0; i < results.size(); i++) { x = results.at(i).bbox[0]; y= results.at(i).bbox[1]; w= results.at(i).bbox[2]; h=results.at(i).bbox[3]; x = (int)(x - w / 2); y = (int)(y - h / 2); w = (int)w; h = (int)h; info = "id:"; info.append(to_string(results.at(i).class_id)); info.append(" s:"); info.append( to_string((int)(results.at(i).conf*100) ) ); info.append("%"); rect= cv::Rect(x, y, w, h); cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, 1, 0);//矩形的两个顶点,两个顶点都包括在矩形内部 cv::putText(image, info, cv::Point(x, y), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.4, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 0.4, 1, false); } return image; } int infer() { //加载engine引擎 char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("./best.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } //反序列为engine,创建context IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); delete[] trtModelStream; //*********************推理-循环推理*********************// float time_read_img = 0.0; float time_infer = 0.0; float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; vector<Detection> results; for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // 处理图片为固定输出 auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 std::string path = "./7.jpg"; std::cout << "img_path=" << path << endl; static float data[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(path); ProcessImage(img, data); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_read_img = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_read_img; //Run inference start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 doInference(*context, data, prob, 1); end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_infer = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_infer; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; //输出后处理 //std::cout <<"prob="<<prob << std::endl; results.clear(); results=postprocess(prob, 0.3, 0.4); cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); img=draw_rect(img,results); cv::imshow("www", img); cv::waitKey(0); cout << "ok" << endl; } std::cout << "C++ 2engine" << "mean read img time =" << time_read_img / 1000 << "ms\t" << "mean infer img time =" << time_infer / 1000 << "ms" << std::endl; // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { //string mode = argv[1]; string mode = "-d"; //适用windows编译,固定指定参数 //if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-s") { if (mode == "-s") { get_trtengine(); } //else if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-d") { else if (mode == "-d") { infer(); } else { return -1; } return 0; }
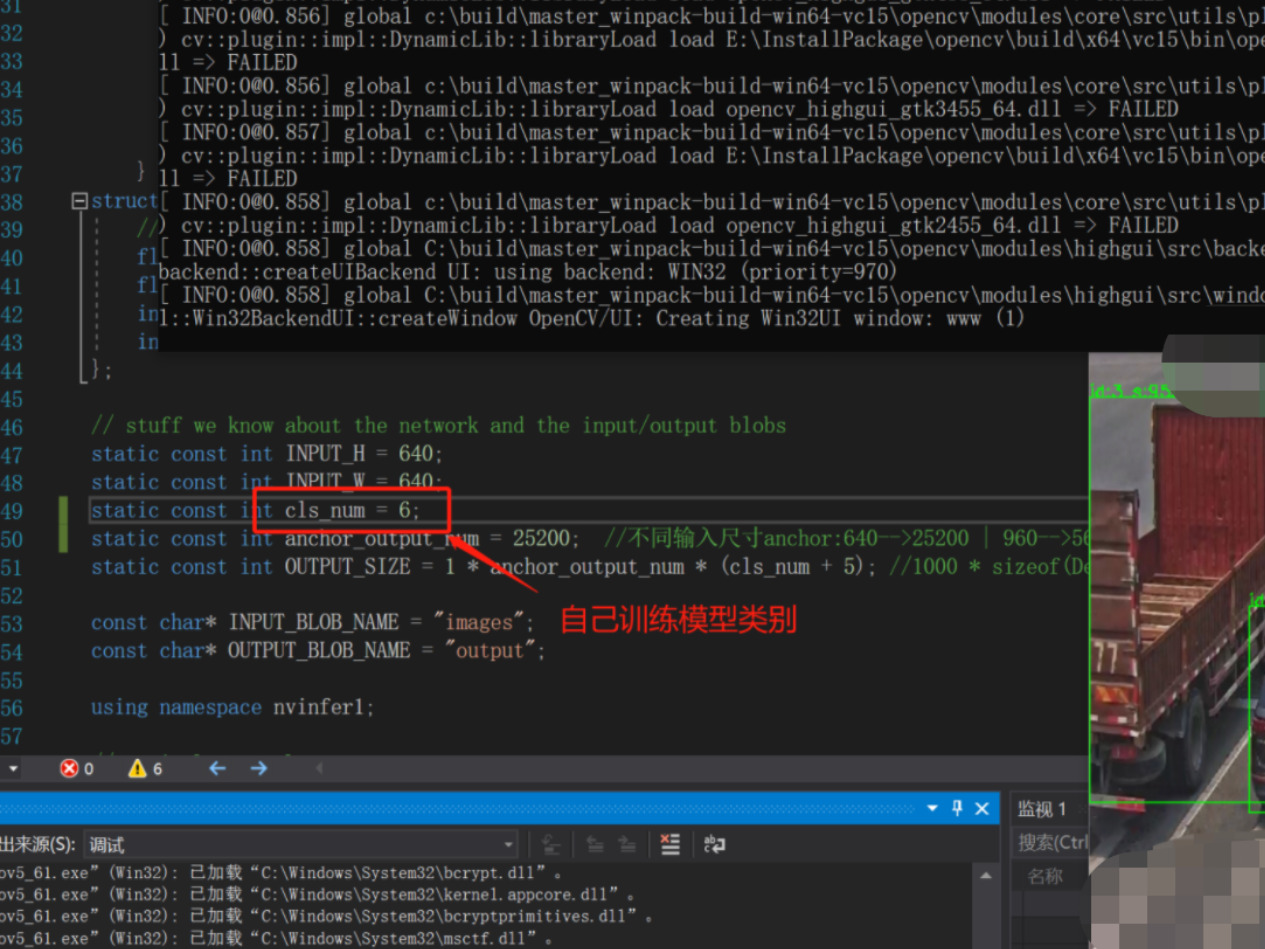
三.预测结果展示:
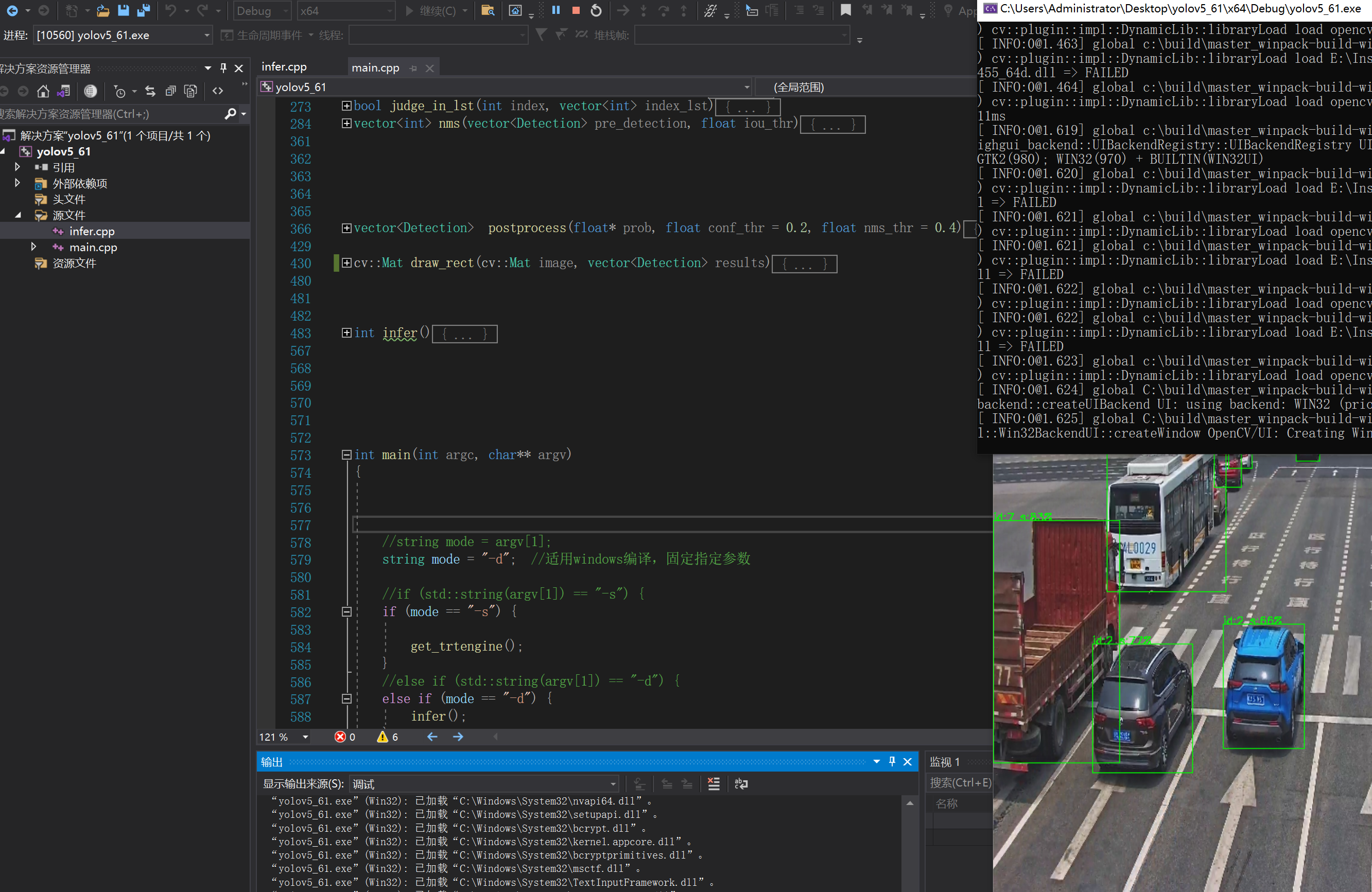
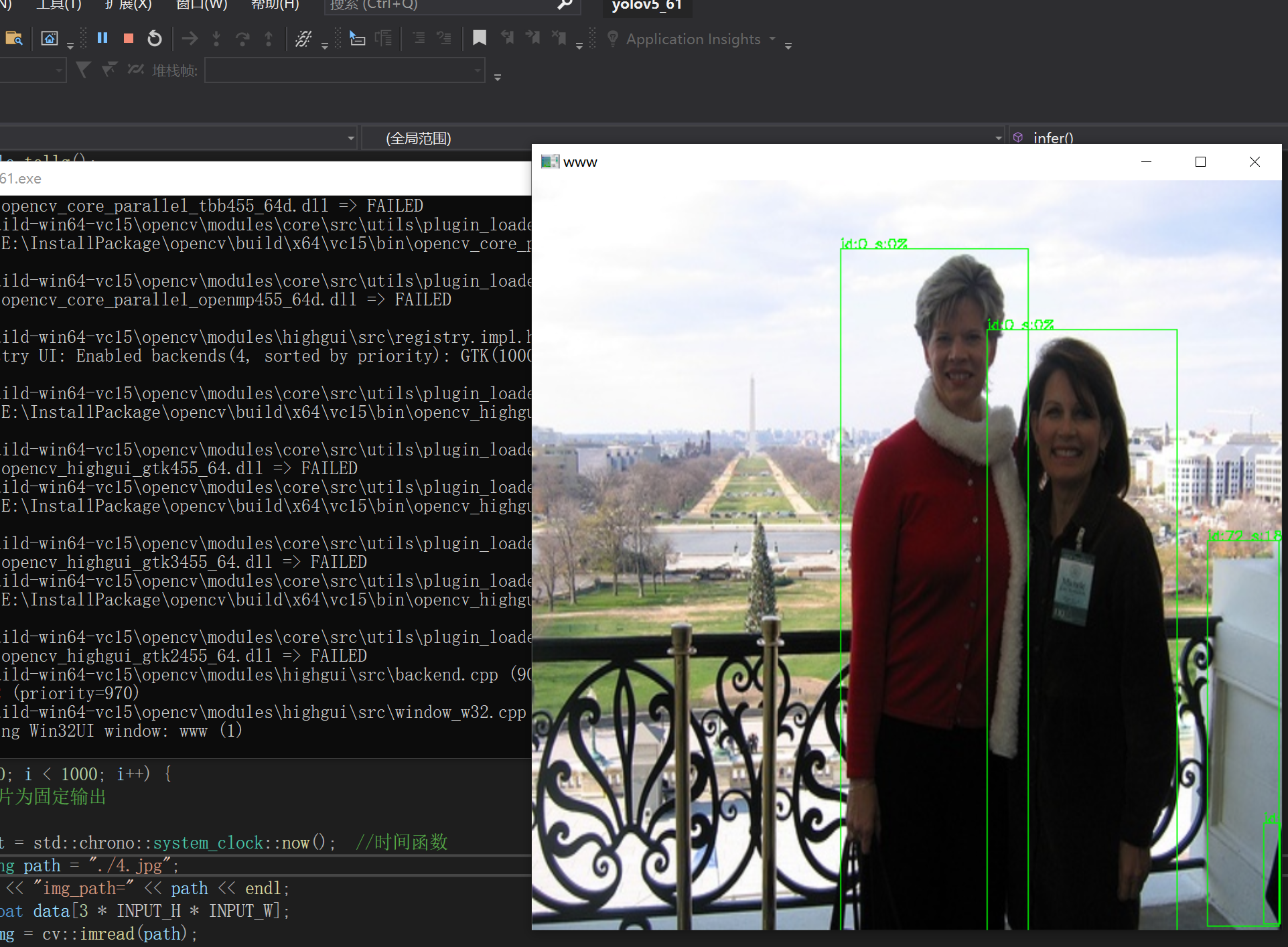
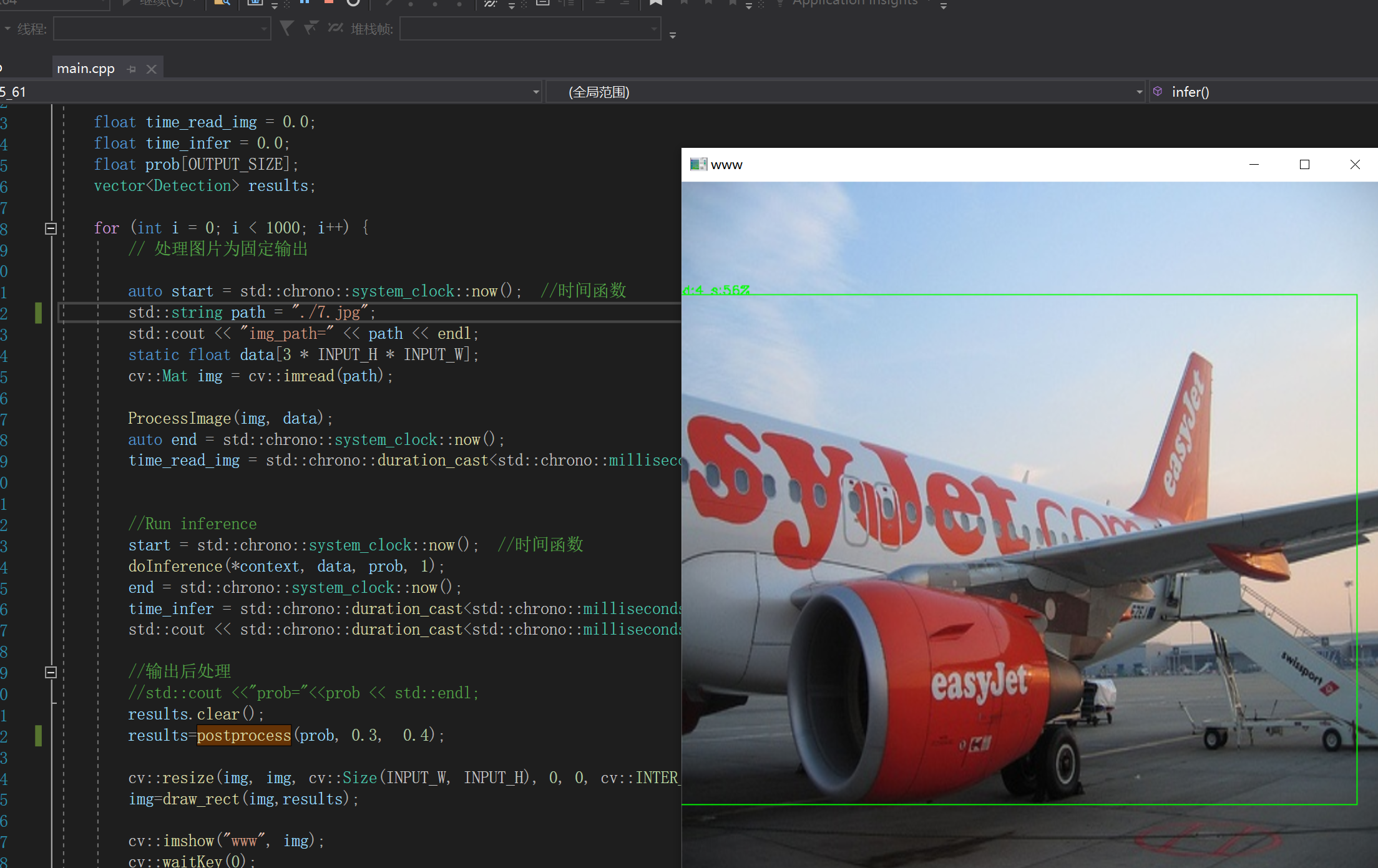
自己训练模型转换测试结果:
四.CMakeLists.txt编写(添加:2022-1006)
介绍如何使用编译命令在ubuntu(linux)环境中运行,以下代码适用YOLO Onnx及C++ 源码构建,其中target_link_libraries(yolo /home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/stubs/libnvonnxparser.so)此库的onnx需要调用,若C++则可忽略。
引用链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tangjunjun/p/16624566.html
engine的CMakeLists.txt构建:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6) project(yolo) add_definitions(-std=c++11) option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug) include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) # include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different # cuda include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include) link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64) # tensorrt include_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/include/) link_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/) include_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/samples/common/) #link_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/stubs/) # opencv find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED) include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}) add_executable(yolo ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cpp) target_link_libraries(yolo nvinfer) target_link_libraries(yolo cudart) target_link_libraries(yolo ${OpenCV_LIBS}) target_link_libraries(yolo /home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/stubs/libnvonnxparser.so) add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号