基于RESNET网络实现tensorrt转换教程(onnx转engine和wts转engine)
近日很想验证使用pytorch训练模型转tensorrt各种关系,更深理解基于C++ API接口engine加速理论(Python API接口稍微简单,将不在验证),本文基于ResNet分类网络。
本文内容主要分为六个内容,第一个内容介绍使用python构建网络,获取pt/wts/onnx文件;第二个内容介绍基于C++ API构建engine;第三个内容介绍基于C++使用onnx构建
engine;第四个内容介绍windows性能及linux性能(添加于20220914);第五个内容介绍验证;第六个内容介绍如何在Linux环境下编译engine且运行。
代码:ResNet.zip
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ujX19IUV0EPSIMyIcBnClA?pwd=r63z
提取码:r63z
版本:tensorrt版本8.4,可使用8.0以上版本
一.使用torchvision获得wts onnx 编译语言:python
①.此代码通过调用torchvision获得resnet18分类权重,并转换为wts和onnx

from torchvision.transforms import transforms import torch import torchvision.models as models import struct transform_train = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) transforms_test = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)) ]) def build_model(): model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) model = model.eval() model = model.cuda() torch.save(model, "./resnet18.pth") def get_wts(model_path='./resnet18.pth',save_wts_path="./resnet18.wts"): net = torch.load(model_path) net = net.cuda() net = net.eval() print('model: ', net) # print('state dict: ', net.state_dict().keys()) tmp = torch.ones(1, 3, 224, 224).cuda() print('input: ', tmp) out = net(tmp) print('output:', out) f = open(save_wts_path, 'w') f.write("{}\n".format(len(net.state_dict().keys()))) for k, v in net.state_dict().items(): print('key: ', k) print('value: ', v.shape) vr = v.reshape(-1).cpu().numpy() f.write("{} {}".format(k, len(vr))) for vv in vr: f.write(" ") f.write(struct.pack(">f", float(vv)).hex()) f.write("\n") def get_onnx(model_path='./resnet18.pth',save_onnx_path="./resnet18.onnx"): # 定义静态onnx,若推理input_data格式不一致,将导致保存 input_data = torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224).cuda() model = torch.load(model_path).cuda() input_names = ["data"] + ["called_%d" % i for i in range(2)] output_names = ["prob"] torch.onnx.export( model, input_data, save_onnx_path, verbose=True, input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names ) if __name__ == '__main__': # build_model() # get_wts(model_path='./resnet18.pth',save_wts_path="./resnet18.wts") get_onnx(model_path='./resnet18.pth', save_onnx_path="./resnet18.onnx")
二.Resnet分类采用C++ API 转换tensorrt 编译语言:C++/tensorrt
①.此代码为resnet分类转换为tensorrt代码,已可使用visualstudi编译器
resnet18.cpp文件

#include "NvInfer.h" #include "cuda_runtime_api.h" //#include "logging.h" #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <chrono> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace std; #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = 224; static const int INPUT_W = 224; static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1000; const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "data"; const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "prob"; using namespace nvinfer1; //static Logger gLogger; //构建Logger class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } } gLogger; // Load weights from files shared with TensorRT samples. // TensorRT weight files have a simple space delimited format: // [type] [size] <data x size in hex> std::map<std::string, Weights> loadWeights(const std::string file) { std::cout << "Loading weights: " << file << std::endl; std::map<std::string, Weights> weightMap; // Open weights file std::ifstream input(file); assert(input.is_open() && "Unable to load weight file."); // Read number of weight blobs int32_t count; input >> count; assert(count > 0 && "Invalid weight map file."); while (count--) { Weights wt{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0 }; uint32_t size; // Read name and type of blob std::string name; input >> name >> std::dec >> size; wt.type = DataType::kFLOAT; // Load blob uint32_t* val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size)); for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; ++x) { input >> std::hex >> val[x]; } wt.values = val; wt.count = size; weightMap[name] = wt; } return weightMap; } IScaleLayer* addBatchNorm2d(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input, std::string lname, float eps) { float* gamma = (float*)weightMap[lname + ".weight"].values; float* beta = (float*)weightMap[lname + ".bias"].values; float* mean = (float*)weightMap[lname + ".running_mean"].values; float* var = (float*)weightMap[lname + ".running_var"].values; int len = weightMap[lname + ".running_var"].count; std::cout << "len " << len << std::endl; float* scval = reinterpret_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float) * len)); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { scval[i] = gamma[i] / sqrt(var[i] + eps); } Weights scale{ DataType::kFLOAT, scval, len }; float* shval = reinterpret_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float) * len)); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { shval[i] = beta[i] - mean[i] * gamma[i] / sqrt(var[i] + eps); } Weights shift{ DataType::kFLOAT, shval, len }; float* pval = reinterpret_cast<float*>(malloc(sizeof(float) * len)); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { pval[i] = 1.0; } Weights power{ DataType::kFLOAT, pval, len }; weightMap[lname + ".scale"] = scale; weightMap[lname + ".shift"] = shift; weightMap[lname + ".power"] = power; IScaleLayer* scale_1 = network->addScale(input, ScaleMode::kCHANNEL, shift, scale, power); assert(scale_1); return scale_1; } IActivationLayer* basicBlock(INetworkDefinition* network, std::map<std::string, Weights>& weightMap, ITensor& input, int inch, int outch, int stride, std::string lname) { Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0 }; IConvolutionLayer* conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{ 3, 3 }, weightMap[lname + "conv1.weight"], emptywts); assert(conv1); conv1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ stride, stride }); conv1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{ 1, 1 }); IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), lname + "bn1", 1e-5); IActivationLayer* relu1 = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU); assert(relu1); IConvolutionLayer* conv2 = network->addConvolutionNd(*relu1->getOutput(0), outch, DimsHW{ 3, 3 }, weightMap[lname + "conv2.weight"], emptywts); assert(conv2); conv2->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{ 1, 1 }); IScaleLayer* bn2 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv2->getOutput(0), lname + "bn2", 1e-5); IElementWiseLayer* ew1; if (inch != outch) { IConvolutionLayer* conv3 = network->addConvolutionNd(input, outch, DimsHW{ 1, 1 }, weightMap[lname + "downsample.0.weight"], emptywts); assert(conv3); conv3->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ stride, stride }); IScaleLayer* bn3 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv3->getOutput(0), lname + "downsample.1", 1e-5); ew1 = network->addElementWise(*bn3->getOutput(0), *bn2->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM); } else { ew1 = network->addElementWise(input, *bn2->getOutput(0), ElementWiseOperation::kSUM); } IActivationLayer* relu2 = network->addActivation(*ew1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU); assert(relu2); return relu2; } // Creat the engine using only the API and not any parser. ICudaEngine* createEngine(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config, DataType dt, string wts_path = "../resnet18.wts") { INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(0U); // Create input tensor of shape { 3, INPUT_H, INPUT_W } with name INPUT_BLOB_NAME ITensor* data = network->addInput(INPUT_BLOB_NAME, dt, Dims3{ 3, INPUT_H, INPUT_W }); assert(data); std::map<std::string, Weights> weightMap = loadWeights(wts_path); Weights emptywts{ DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0 }; IConvolutionLayer* conv1 = network->addConvolutionNd(*data, 64, DimsHW{ 7, 7 }, weightMap["conv1.weight"], emptywts); assert(conv1); conv1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ 2, 2 }); conv1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{ 3, 3 }); IScaleLayer* bn1 = addBatchNorm2d(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), "bn1", 1e-5); IActivationLayer* relu1 = network->addActivation(*bn1->getOutput(0), ActivationType::kRELU); assert(relu1); IPoolingLayer* pool1 = network->addPoolingNd(*relu1->getOutput(0), PoolingType::kMAX, DimsHW{ 3, 3 }); assert(pool1); pool1->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ 2, 2 }); pool1->setPaddingNd(DimsHW{ 1, 1 }); IActivationLayer* relu2 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *pool1->getOutput(0), 64, 64, 1, "layer1.0."); IActivationLayer* relu3 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu2->getOutput(0), 64, 64, 1, "layer1.1."); IActivationLayer* relu4 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu3->getOutput(0), 64, 128, 2, "layer2.0."); IActivationLayer* relu5 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu4->getOutput(0), 128, 128, 1, "layer2.1."); IActivationLayer* relu6 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu5->getOutput(0), 128, 256, 2, "layer3.0."); IActivationLayer* relu7 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu6->getOutput(0), 256, 256, 1, "layer3.1."); IActivationLayer* relu8 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu7->getOutput(0), 256, 512, 2, "layer4.0."); IActivationLayer* relu9 = basicBlock(network, weightMap, *relu8->getOutput(0), 512, 512, 1, "layer4.1."); IPoolingLayer* pool2 = network->addPoolingNd(*relu9->getOutput(0), PoolingType::kAVERAGE, DimsHW{ 7, 7 }); assert(pool2); pool2->setStrideNd(DimsHW{ 1, 1 }); IFullyConnectedLayer* fc1 = network->addFullyConnected(*pool2->getOutput(0), 1000, weightMap["fc.weight"], weightMap["fc.bias"]); assert(fc1); fc1->getOutput(0)->setName(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); std::cout << "set name out" << std::endl; network->markOutput(*fc1->getOutput(0)); // Build engine builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); std::cout << "build out" << std::endl; // Don't need the network any more network->destroy(); // Release host memory for (auto& mem : weightMap) { free((void*)(mem.second.values)); } return engine; } void APIToModel(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IHostMemory** modelStream) { string wts_path = "./resnet18.wts"; // Create builder IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network, then set the outputs and create an engine ICudaEngine* engine = createEngine(maxBatchSize, builder, config, DataType::kFLOAT, wts_path = wts_path); assert(engine != nullptr); // Serialize the engine (*modelStream) = engine->serialize(); // Close everything down engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); } void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) { const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); // Create GPU buffers on device CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float))); CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float))); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); } //加工图片变成拥有batch的输入, tensorrt输入需要的格式,为一个维度 void ProcessImage(cv::Mat image, float input_data[]) { //只处理一张图片,总之结果为一维[batch*3*INPUT_W*INPUT_H] //以下代码为投机取巧了 cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); std::vector<cv::Mat> InputImage; InputImage.push_back(image); int ImgCount = InputImage.size(); //float input_data[BatchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; for (int b = 0; b < ImgCount; b++) { cv::Mat img = InputImage.at(b); int w = img.cols; int h = img.rows; int i = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h; ++row) { uchar* uc_pixel = img.data + row * img.step; for (int col = 0; col < INPUT_W; ++col) { input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i] = (float)uc_pixel[2] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[1] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + 2 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[0] / 255.0; uc_pixel += 3; ++i; } } } } int get_trtengine() { IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; APIToModel(1, &modelStream); assert(modelStream != nullptr); std::ofstream p("./resnet18.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); modelStream->destroy(); return 0; } int infer() { //加载engine引擎 char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("./resnet18.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } //反序列为engine,创建context IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); delete[] trtModelStream; //*********************推理*********************// // 循环推理 float time_read_img = 0.0; float time_infer = 0.0; static float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // 处理图片为固定输出 auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 std::string path = "./1.jpg"; std::cout << "img_path=" << path << endl; static float data[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(path); ProcessImage(img, data); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_read_img = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_read_img; //Run inference start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 doInference(*context, data, prob, 1); end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_infer = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_infer; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; //输出后处理 //std::cout <<"prob="<<prob << std::endl; float cls_float = prob[0]; int cls_id = 0; for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++) { if (cls_float < prob[i]) { cls_float = prob[i]; cls_id = i; } } std::cout << "i=" << i << "\tcls_id=" << cls_id << "\t cls_float=" << cls_float << std::endl; } std::cout << "C++2engine" << "mean read img time =" << time_read_img / 1000 << "ms\t" << "mean infer img time =" << time_infer / 1000 << "ms" << std::endl; // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { //string mode = argv[1]; string mode = "-d"; //适用windows编译,固定指定参数 //if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-s") { if (mode == "-s") { get_trtengine(); } //else if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-d") { else if (mode == "-d") { infer(); } else { return -1; } return 0; }
②.若需要linux系统运行可编译的CMakeLists.txt文件为:

cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6) project(resnet) add_definitions(-std=c++11) option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug) include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) # include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different # cuda include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include) link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64) # tensorrt include_directories(/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/) link_directories(/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/) add_executable(resnet18 ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/resnet18.cpp) target_link_libraries(resnet18 nvinfer) target_link_libraries(resnet18 cudart) add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
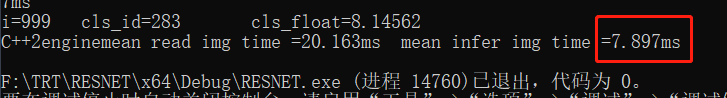
③.visual studio预测结果:
总之测试2张图基本在一个大类中,应该没啥错误。
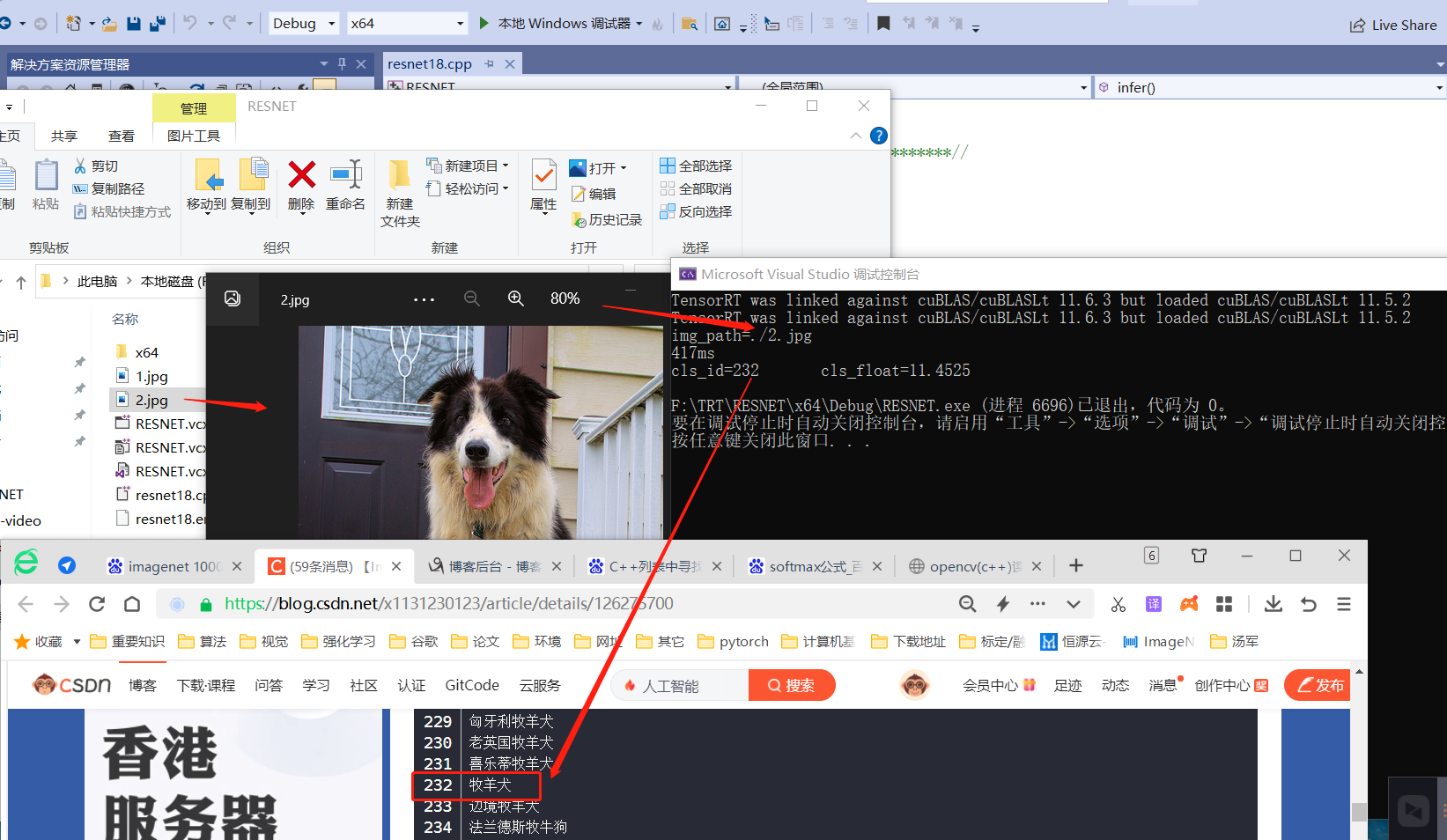
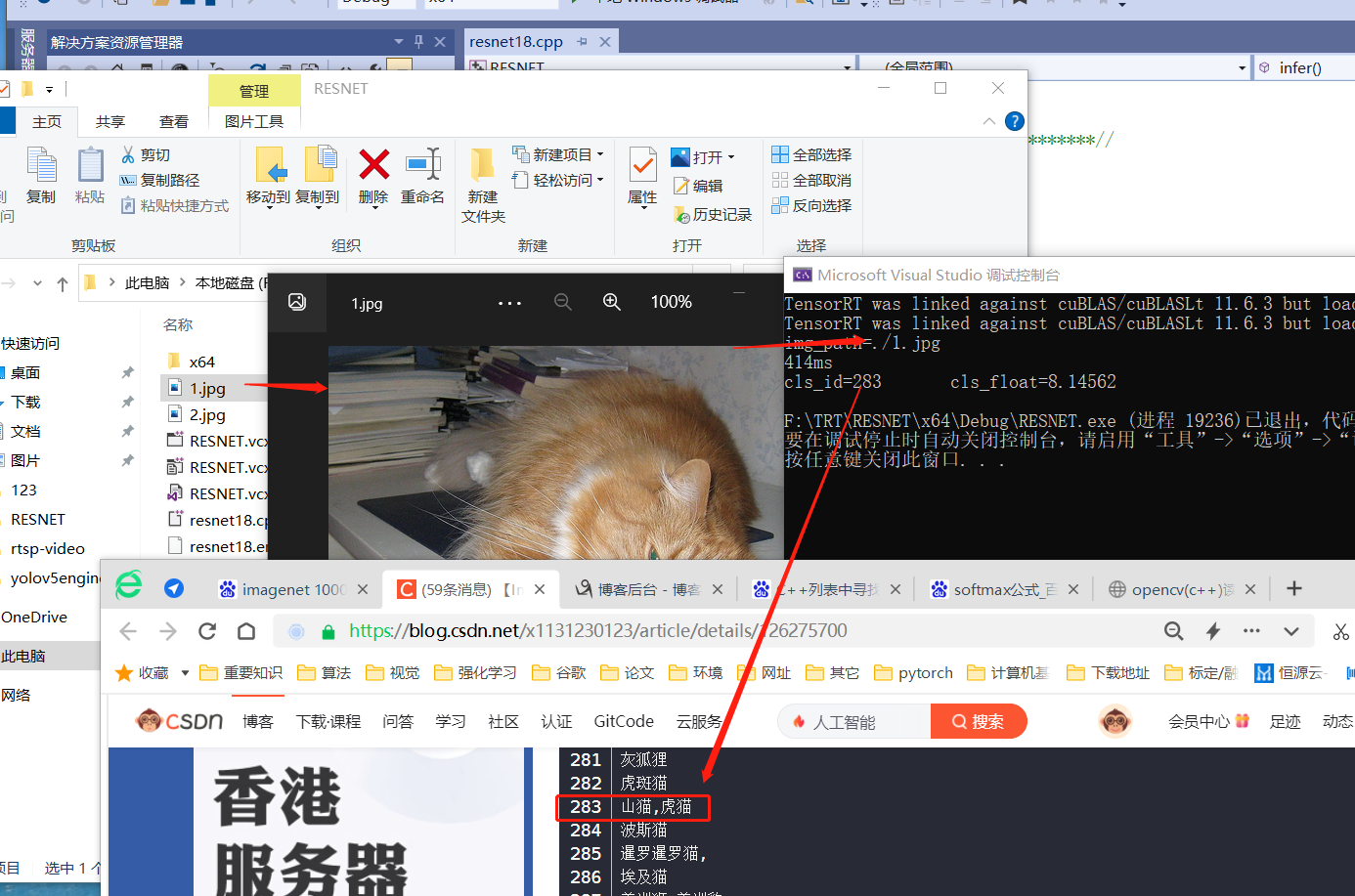
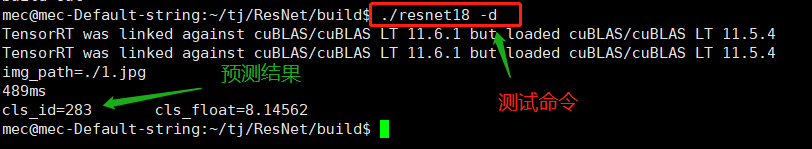
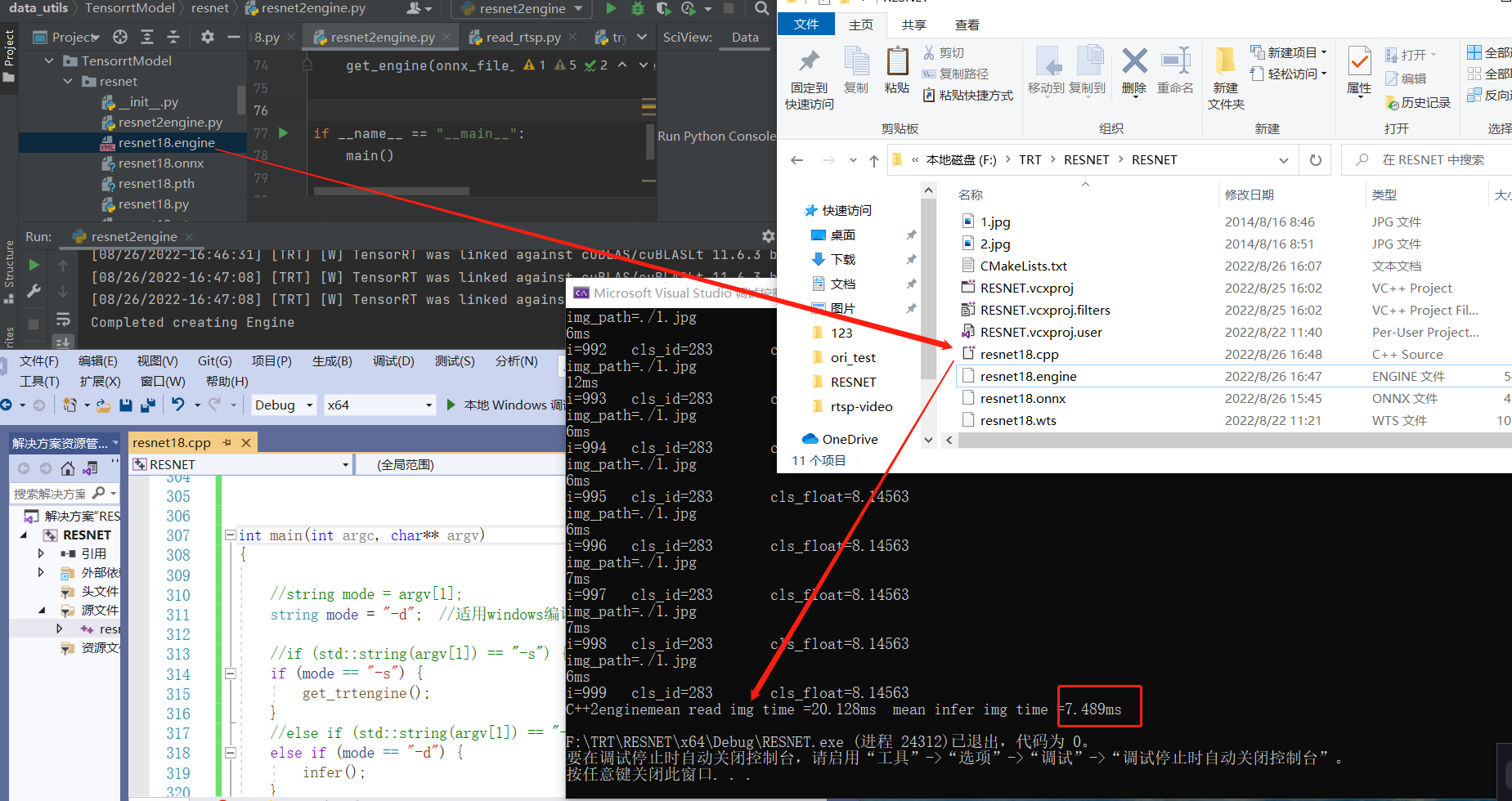
④.linux预测结果显示:
三.Resnet分类采用C++ API 使用onnx 转换tensorrt 编译语言:C++/tensorrt
①.此代码为resnet分类采用onnx转换为tensorrt代码,已可使用visualstudi编译器
resnet18.cpp文件

#include "NvInfer.h" #include "cuda_runtime_api.h" #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <chrono> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> // onnx转换头文件 #include "NvOnnxParser.h" using namespace nvonnxparser; using namespace std; #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = 224; static const int INPUT_W = 224; static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1000; const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "data"; const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "prob"; using namespace nvinfer1; //static Logger gLogger; //构建Logger class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } } gLogger; // Creat the engine using only the API and not any parser. ICudaEngine* createEngine(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config) { const char* onnx_path = "./resnet18.onnx"; INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(1U); //此处重点1U为OU就有问题 IParser* parser = createParser(*network, gLogger); parser->parseFromFile(onnx_path, static_cast<int32_t>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING)); for (int32_t i = 0; i < parser->getNbErrors(); ++i) { std::cout << parser->getError(i)->desc() << std::endl; } std::cout << "successfully load the onnx model" << std::endl; // Build engine builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16); // 设置精度计算 //config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kINT8); ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); std::cout << "successfully create engine " << std::endl; //销毁 network->destroy(); parser->destroy(); return engine; } void APIToModel(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IHostMemory** modelStream) { // Create builder IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger); IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create model to populate the network, then set the outputs and create an engine ICudaEngine* engine = createEngine(maxBatchSize, builder, config); assert(engine != nullptr); // Serialize the engine (*modelStream) = engine->serialize(); // Close everything down engine->destroy(); builder->destroy(); config->destroy(); } void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) { const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); // Create GPU buffers on device CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float))); CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float))); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); } //加工图片变成拥有batch的输入, tensorrt输入需要的格式,为一个维度 void ProcessImage(cv::Mat image, float input_data[]) { //只处理一张图片,总之结果为一维[batch*3*INPUT_W*INPUT_H] //以下代码为投机取巧了 cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); std::vector<cv::Mat> InputImage; InputImage.push_back(image); int ImgCount = InputImage.size(); //float input_data[BatchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; for (int b = 0; b < ImgCount; b++) { cv::Mat img = InputImage.at(b); int w = img.cols; int h = img.rows; int i = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h; ++row) { uchar* uc_pixel = img.data + row * img.step; for (int col = 0; col < INPUT_W; ++col) { input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i] = (float)uc_pixel[2] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[1] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + 2 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[0] / 255.0; uc_pixel += 3; ++i; } } } } int get_trtengine() { IHostMemory* modelStream{ nullptr }; APIToModel(1, &modelStream); assert(modelStream != nullptr); std::ofstream p("./resnet18.engine", std::ios::binary); if (!p) { std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl; return -1; } p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size()); modelStream->destroy(); return 0; } int infer() { //加载engine引擎 char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("./resnet18.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } //反序列为engine,创建context IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); delete[] trtModelStream; //*********************推理*********************// // 循环推理 float time_read_img = 0.0; float time_infer = 0.0; static float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // 处理图片为固定输出 auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 std::string path = "./1.jpg"; std::cout << "img_path=" << path << endl; static float data[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(path); ProcessImage(img, data); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_read_img = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_read_img; //Run inference start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 doInference(*context, data, prob, 1); end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_infer = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_infer; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; //输出后处理 //std::cout <<"prob="<<prob << std::endl; float cls_float = prob[0]; int cls_id = 0; for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++) { if (cls_float < prob[i]) { cls_float = prob[i]; cls_id = i; } } std::cout << "i=" << i << "\tcls_id=" << cls_id << "\t cls_float=" << cls_float << std::endl; } std::cout << "C++2engine" << "mean read img time =" << time_read_img / 1000 << "ms\t" << "mean infer img time =" << time_infer / 1000 << "ms" << std::endl; // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { //string mode = argv[1]; string mode = "-d"; //适用windows编译,固定指定参数 //if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-s") { if (mode == "-s") { get_trtengine(); } //else if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-d") { else if (mode == "-d") { infer(); } else { return -1; } return 0; }
windows visual studio tensorrt8.4版本 onnx转engine展示
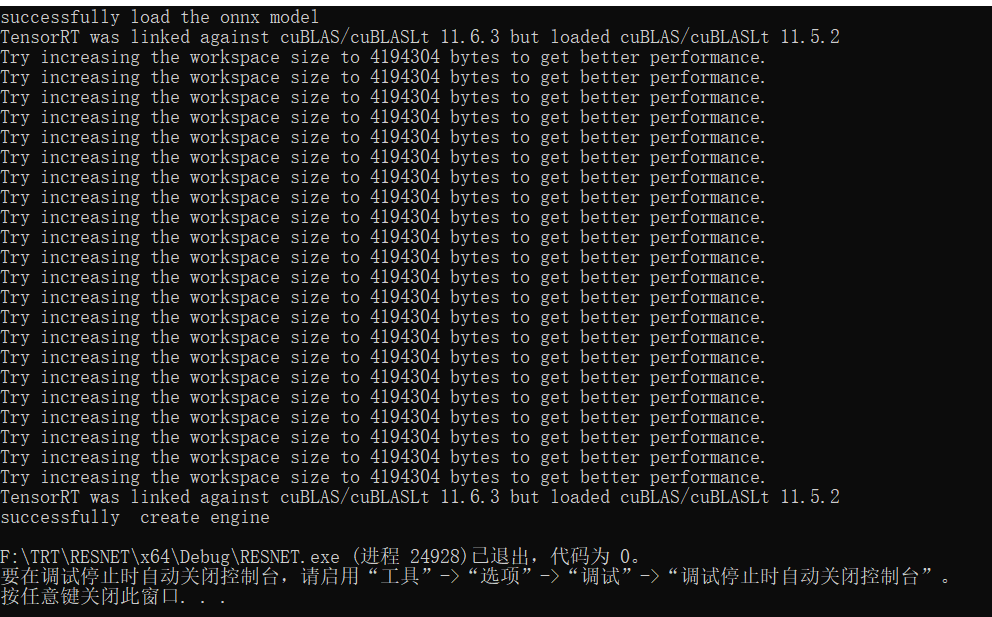
②.使用onnx-simpiler 进行优化onnx,但已是最简化,但若能简化,猜想预测会更快一些。

四.性能测试
性能测试结果(测试平台:windows10 cuda11.4 tensorrt8.4 RTX 2060):

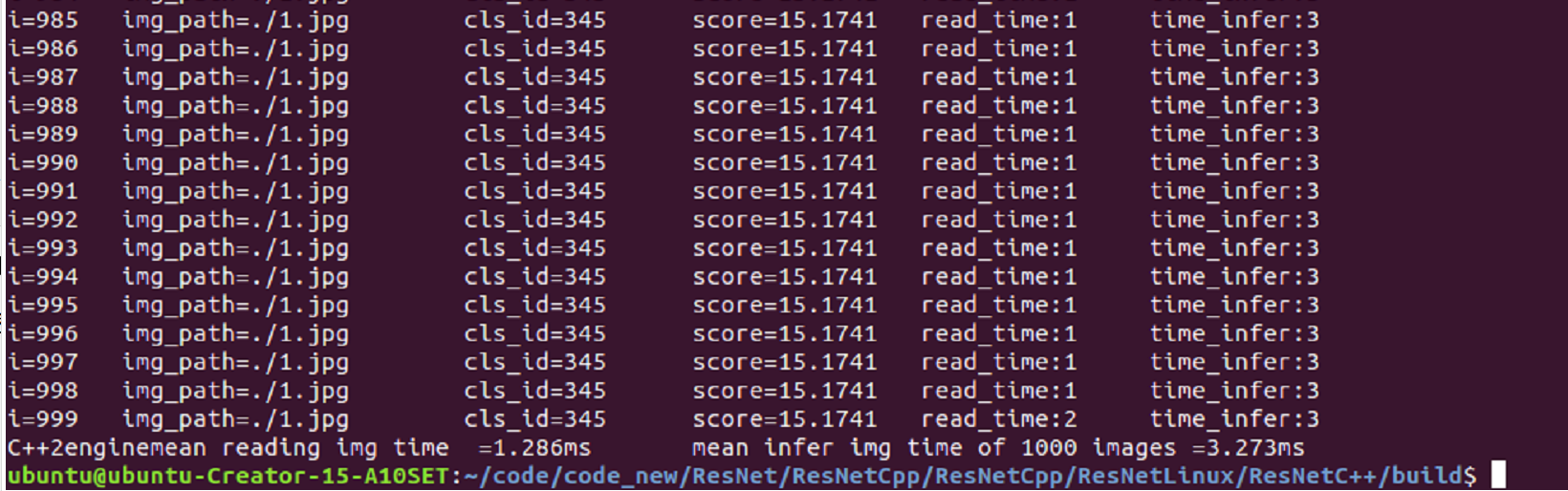
性能测试结果(测试平台:Linux ubuntu18.4 cuda11.3 tensorrt8.2 RTX 2060)(添加:20220914):

注:检测1000张的平均时间
说明 window10与ubuntu是2个独立设备(电脑),读图主要是CPU处理代码,后期可改成CUDA处理提速。
五.验证
①.使用python将onnx转为engine引擎,使用C++调用验证。
结论:windows系统 可行! 很令人兴奋,意味着使用python转换为engine,将可以使用C++调用,无需再使用C++创建engine。
注:推理时间变长了快2倍。
python代码将其转为engine库,注:使用同样的tensorrt版本
 onnx2engine.py
onnx2engine.py
C++推理代码(使用二或三中推理也可以),此代码已简化:

#include "NvInfer.h" #include "cuda_runtime_api.h" #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <chrono> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace std; #define CHECK(status) \ do\ {\ auto ret = (status);\ if (ret != 0)\ {\ std::cerr << "Cuda failure: " << ret << std::endl;\ abort();\ }\ } while (0) // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = 224; static const int INPUT_W = 224; static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1000; const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "data"; const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "prob"; using namespace nvinfer1; //static Logger gLogger; //构建Logger class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } } gLogger; void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) { const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine. // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers. assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2); void* buffers[2]; // In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors. // Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings() const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME); const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); // Create GPU buffers on device CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float))); CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float))); // Create stream cudaStream_t stream; CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); // DMA input batch data to device, infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)); context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); } //加工图片变成拥有batch的输入, tensorrt输入需要的格式,为一个维度 void ProcessImage(cv::Mat image, float input_data[]) { //只处理一张图片,总之结果为一维[batch*3*INPUT_W*INPUT_H] //以下代码为投机取巧了 cv::resize(image, image, cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR); std::vector<cv::Mat> InputImage; InputImage.push_back(image); int ImgCount = InputImage.size(); //float input_data[BatchSize * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; for (int b = 0; b < ImgCount; b++) { cv::Mat img = InputImage.at(b); int w = img.cols; int h = img.rows; int i = 0; for (int row = 0; row < h; ++row) { uchar* uc_pixel = img.data + row * img.step; for (int col = 0; col < INPUT_W; ++col) { input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i] = (float)uc_pixel[2] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[1] / 255.0; input_data[b * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W + i + 2 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W] = (float)uc_pixel[0] / 255.0; uc_pixel += 3; ++i; } } } } int infer() { //加载engine引擎 char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; size_t size{ 0 }; std::ifstream file("./resnet18.engine", std::ios::binary); if (file.good()) { file.seekg(0, file.end); size = file.tellg(); file.seekg(0, file.beg); trtModelStream = new char[size]; assert(trtModelStream); file.read(trtModelStream, size); file.close(); } //反序列为engine,创建context IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr); assert(engine != nullptr); IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); delete[] trtModelStream; //*********************推理*********************// // 循环推理 float time_read_img = 0.0; float time_infer = 0.0; static float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { // 处理图片为固定输出 auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 std::string path = "./1.jpg"; std::cout << "img_path=" << path << endl; static float data[3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W]; cv::Mat img = cv::imread(path); ProcessImage(img, data); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_read_img = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_read_img; //Run inference start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //时间函数 doInference(*context, data, prob, 1); end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); time_infer = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() + time_infer; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; //输出后处理 //std::cout <<"prob="<<prob << std::endl; float cls_float = prob[0]; int cls_id = 0; for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++) { if (cls_float < prob[i]) { cls_float = prob[i]; cls_id = i; } } std::cout << "i=" << i << "\tcls_id=" << cls_id << "\t cls_float=" << cls_float << std::endl; } std::cout << "C++2engine" << "mean read img time =" << time_read_img / 1000 << "ms\t" << "mean infer img time =" << time_infer / 1000 << "ms" << std::endl; // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); return 0; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { infer(); return 0; }
注:最终因环未在服务器验证ONNX转engine方法,但CMakeList可借鉴wts转engine。
六.Linux环境下编译engine(添加:20220914)
本节介绍如何使用编译命令在ubuntu(linux)环境中运行,我将使用C++ API构建的网络称为Cengine,将Onnx转换构建的网络称为Oengine,那么本节将介绍主要介绍CMakeLists.txt文件的构建:
Cengine的CMakeLists.txt构建:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6) project(resnet) add_definitions(-std=c++11) option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug) include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) # include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different # cuda include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include) link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64) # tensorrt include_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/include/) link_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/) #include_directories(/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/) #link_directories(/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/) # opencv find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED) include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(resnet18 ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cpp) target_link_libraries(resnet18 nvinfer) target_link_libraries(resnet18 cudart) target_link_libraries(resnet18 ${OpenCV_LIBS}) add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
Oengine的CMakeLists.txt构建:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6) project(resnet) add_definitions(-std=c++11) option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug) include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include) # include and link dirs of cuda and tensorrt, you need adapt them if yours are different # cuda include_directories(/usr/local/cuda/include) link_directories(/usr/local/cuda/lib64) # tensorrt include_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/include/) link_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/) include_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/samples/common/) #link_directories(/home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/stubs/) # opencv find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED) include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}) add_executable(resnet18 ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/main.cpp) target_link_libraries(resnet18 nvinfer) target_link_libraries(resnet18 cudart) target_link_libraries(resnet18 ${OpenCV_LIBS}) target_link_libraries(resnet18 /home/ubuntu/soft/TensorRT-8.2.5.1/lib/stubs/libnvonnxparser.so ) add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
以上为ONNX及C++构建engine的cmakelists的语句,主要在于库的链接或头文件之类,相关可看其它博客或网上资料。
附带说明:以上Onnx的CmakeLists.txt语句已经在yolov5、yolov7中验证,可以编译运行。
ResNet代码在上面已有说明,我将不放在本博客中,其中细节代码在我发布的链接中可下载使用。
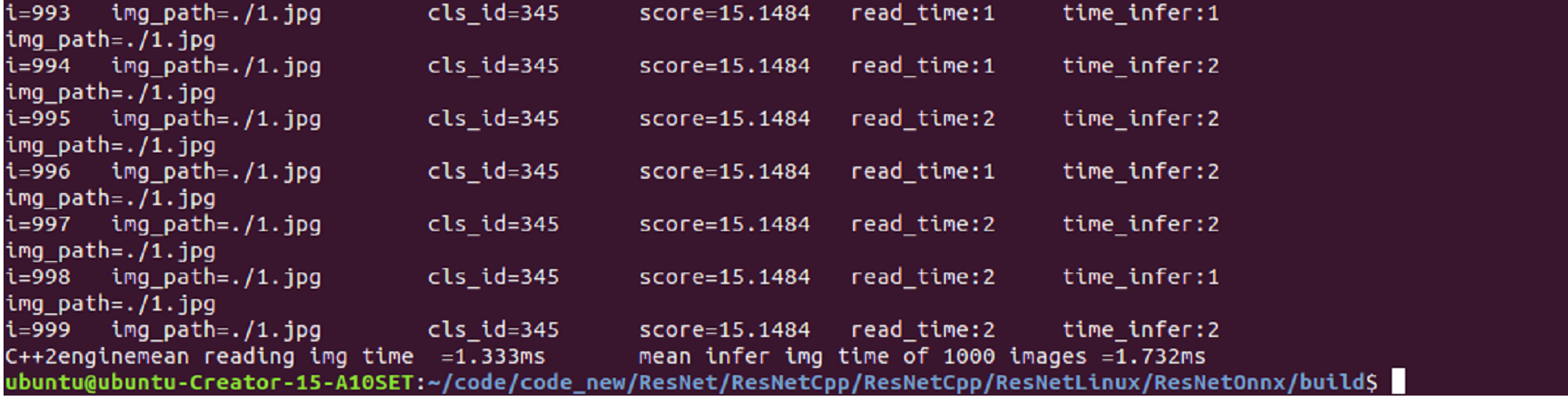
测试结果展示:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号