混淆矩阵求解(多分类与单分类)
混淆矩阵(confusion matrix)衡量的是一个分类器分类的准确程度。理解其概念本身容易理解,但一些特定术语易被混淆。
为此本文针对多分类或二分类的混淆矩阵给出相应原理解释,并为更好理解,本文也实现如何求解混淆矩阵。
因此,本文内容结构包含,原理介绍、代码实现、结果展示。
一 原理介绍
混淆矩阵适用于包含多个分类器的问题,本文为了让读者理解更加容易,以二元分类的混淆矩阵为例进行讲解。
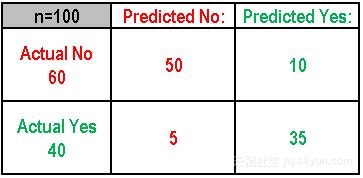
观察混淆矩阵,可得如下结论:
- 示例是一个二元分类问题,产生两种可能的分类:“是”或者“不是”。当预测一个事件是否发生时,“是”意味着该事件已经发生,而“否”则相反,该事件没有发生。
- 该模型对这个事件进行了100次预测。
- 在这100次预测结果中,“是”有45次,“否”有55次。但实际上该事件发生了40次。
重要概念:
- 真阳性(True Positive,TP):样本的真实类别是正例,并且模型预测的结果也是正例
- 真阴性(True Negative,TN):样本的真实类别是负例,并且模型将其预测成为负例
- 假阳性(False Positive,FP):样本的真实类别是负例,但是模型将其预测成为正例
- 假阴性(False Negative,FN):样本的真实类别是正例,但是模型将其预测成为负例
混淆矩阵延伸出的各个评价指标
1.正确率(Accuracy):被正确分类的样本比例或数量
(TP+TN)/Total = (35+50)/100 = 85%
2.错误率(Misclassification/Error Rate):被错误分类的样本比例或数量
(FP+FN)/Total = (5+10)/100 = 15%
3.真阳率(True Positive Rate):分类器预测为正例的样本占实际正例样本数量的比例,也叫敏感度(sensitivity)或召回率(recall),描述了分类器对正例类别的敏感程度。
TP/ actual yes = 35/40 = 87%
4.假阳率(False Positive Rate):分类器预测为正例的样本占实际负例样本数量的比例。
FP/actual no = 10/60 = 17%
5.特异性(Specificity):实例是负例,分类器预测结果的类别也是负例的比例。
TN/actual no = 50/60 = 83%
6. 精度(Precision):在所有判别为正例的结果中,真正正例所占的比例。
TP/predicted yes = 35/45 = 77%
7.流行程度(Prevalence):正例在样本中所占比例。
Actual Yes/Total = 40/100 = 40%
注:以上内容来源 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42475636
二 代码实现
以下代码根据文件夹路径统计,并实现,只需按照文件要求,给出相应路径,便可求得混淆矩阵,为此本文将介绍文件存放方式,并不在介绍实现过程。
文件格式:
如456路径有真实类别为A B C 而456/A文件夹下预测有A B 类别,并分别将结果保存此类文件夹,如456/A/A文件保存了预测图片
将绝对路径.../456文件夹给以下代码,即可生成混淆矩阵。
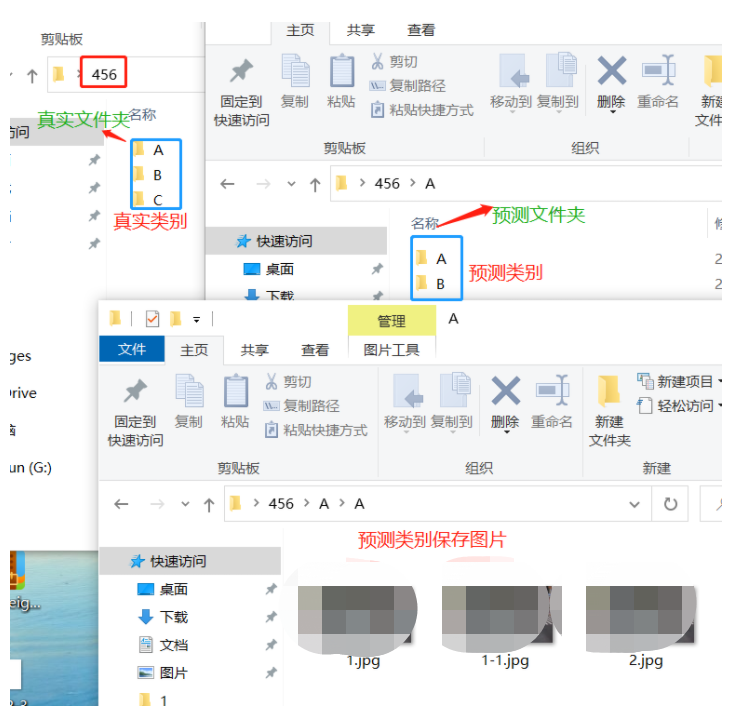
混淆矩阵代码实现

#!/usr/bin/env python # encoding: utf-8 """ @author:tangjun @desc: analysis the model infer result loaded from csv file, which has columns with manual code, predict code, code score. 安装库: pip install scikit-learn -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package pip install pandas -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package pip install numpy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package """ import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix import os import json import pickle class ResultAnalysis_tj(object): def __init__(self, read_path): # self.false_code='FALSE' # self.others_code='Others' self.read_path=read_path self.model_categories=[] def get_codename(self): code_name = [] codes=os.listdir(self.read_path) for code in codes: if not code.endswith('.csv'): code_name.append(code) code_name=sorted(code_name) # if self.false_code not in code_name: # code_name.append(self.false_code) # if self.others_code not in code_name: # code_name.append(self.others_code) return code_name def get_true_pre_category(self): prediction_categories=[] true_categories=[] files=os.listdir(self.read_path) for file in files: if not file.endswith('.csv'): file_path=os.path.join(self.read_path,file) file_names=os.listdir(file_path) for file_name in file_names: temp_path=os.path.join(file_path,file_name) for end_name in os.listdir(temp_path): if not end_name.endswith('.xml'): true_categories.append(file) prediction_categories.append(file_name) return true_categories,prediction_categories def process_confusion_matrix(self): true_categories,prediction_categories = self.get_true_pre_category() model_codes=self.get_codename() names=set(true_categories) for name in names: if name not in model_codes: model_codes.append(name) names=set(prediction_categories) for name in names: if name not in model_codes: model_codes.append(name) # model_codes=sorted(model_codes) self.model_categories=model_codes matrix = confusion_matrix(true_categories, prediction_categories, labels=self.model_categories, sample_weight=None) return matrix def save_confusion_matrix2csv(self): matrix=self.process_confusion_matrix() cm_df = self.cm2df(matrix, self.model_categories) precision_list = [] recall_list = [] for i in range(len(cm_df.columns)): precision = round(cm_df.iloc[i, i] / sum(cm_df[cm_df.columns[i]]), 4) recall = round(cm_df.iloc[i, i] / sum(cm_df.loc[cm_df.columns[i]]), 4) precision_list.append(precision) recall_list.append(recall) cm_df['recall'] = recall_list precision_list.append(None) cm_df.loc['precision'] = precision_list print(cm_df) import time out_name = str(time.strftime("%Y_%m%d_%H_%M", time.localtime())) save_file = os.path.join(self.read_path, 'matrix_'+str(out_name)+'.csv') cm_df.to_csv(save_file) @staticmethod def cm2df(conf_matrix, labels): df = pd.DataFrame() # rows for i, row_label in enumerate(labels): rowdata = {} # columns for j, col_label in enumerate(labels): rowdata[col_label] = conf_matrix[i, j] df = df.append(pd.DataFrame.from_dict({row_label: rowdata}, orient='index')) return df[labels] if __name__ == '__main__': read_path=r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\456' matrix_result=ResultAnalysis_tj(read_path) matrix_result.save_confusion_matrix2csv()
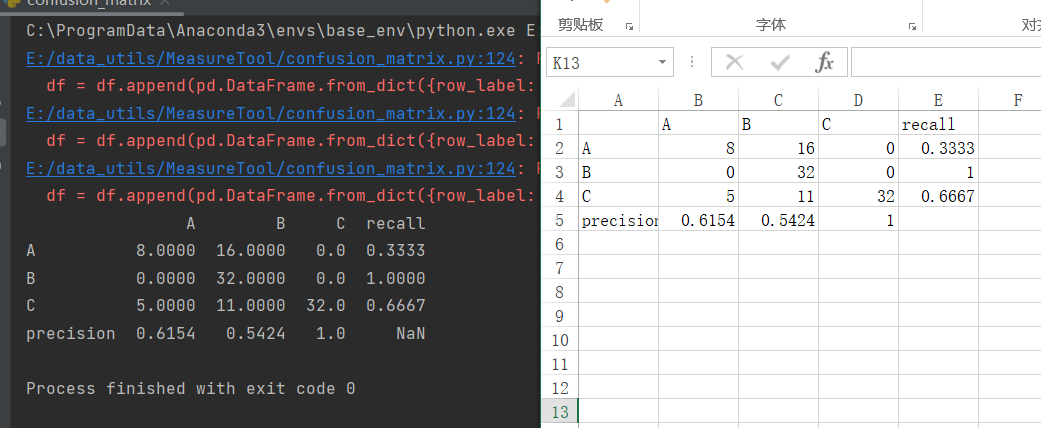
结果展示:
左图为结果输出,右图为将结果保存于csv文件中




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号