LSTM结构原理与代码实践
近日学习LSTM结构,已有很多博客对LSTM结构进行说明,但某些细节仍然存在模糊情况,为此本文将进行补充与说明,可分以下内容:
一.RNN原理简介与LSTM原理阐释。
一般来说,RNN的输入和输出都是一个序列,分别记为和
,同时
的取值不仅与
有关还与序列中更早的输入有关(序列中的第t个元素我们叫做序列在time_step=t时的取值)。
注:seqin={x1,x2,...,x3}可假设指代有顺序的句子序列长度,如 I Like code ,其中x1=I,x2=Like,x3=code;以此类推seqout指代我们想输出结果。
更直观的理解可看下图:
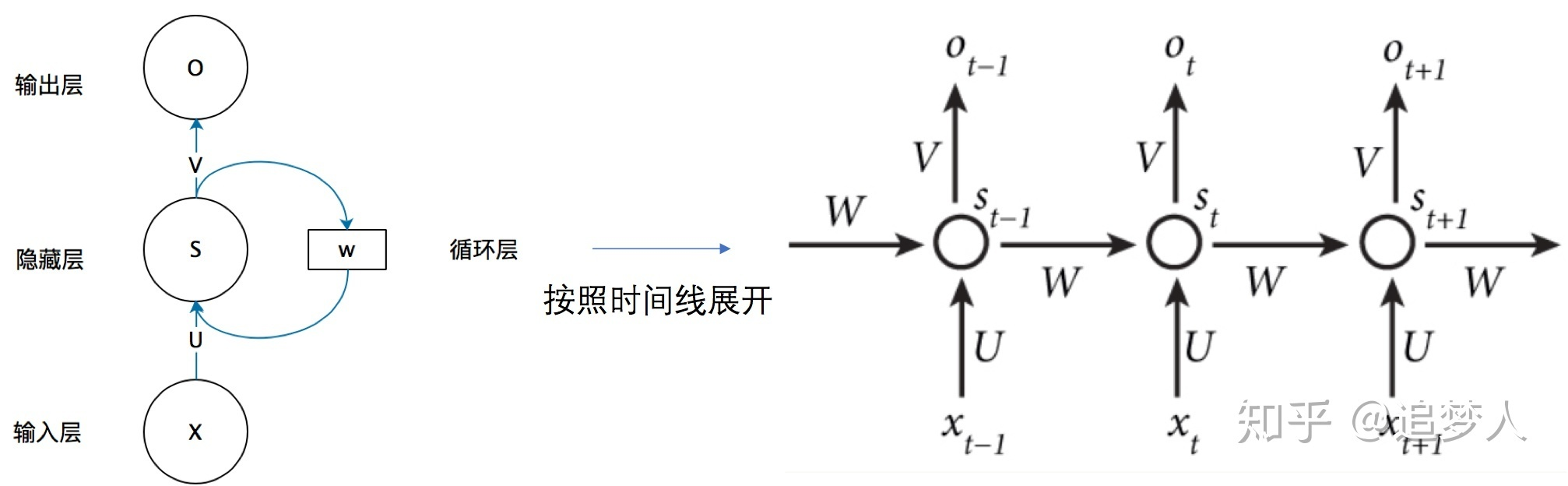
LSTM是一种特殊的RNN,主要通过三个门控逻辑实现(遗忘、输入、输出)。它的提出就是为了解决长序列训练过程中的梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题。
下图是一个LSTM结构示意图,如Xt指代Like单词:
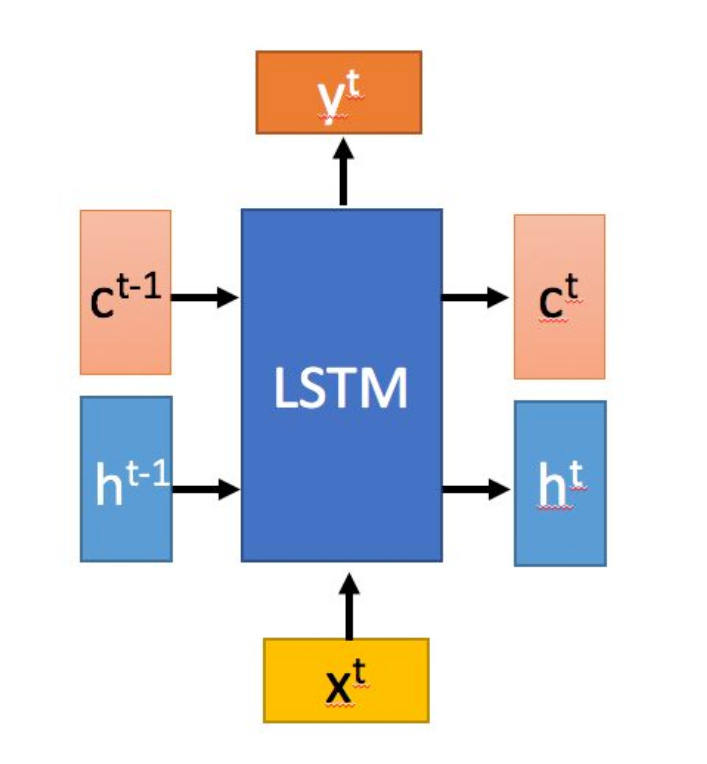
以上可看出输出为yt,ct和ht
![]()
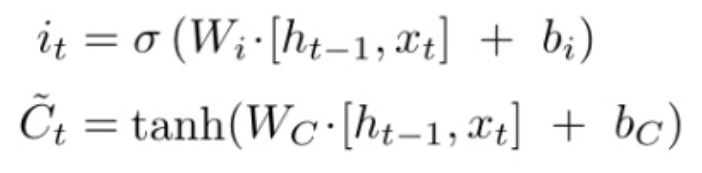
![]() 求解Ct公式
求解Ct公式
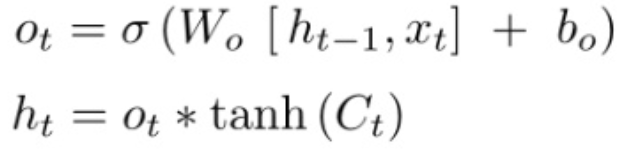 求解ht
求解ht
σ函数表示sigmoid函数
更详细解释如下:
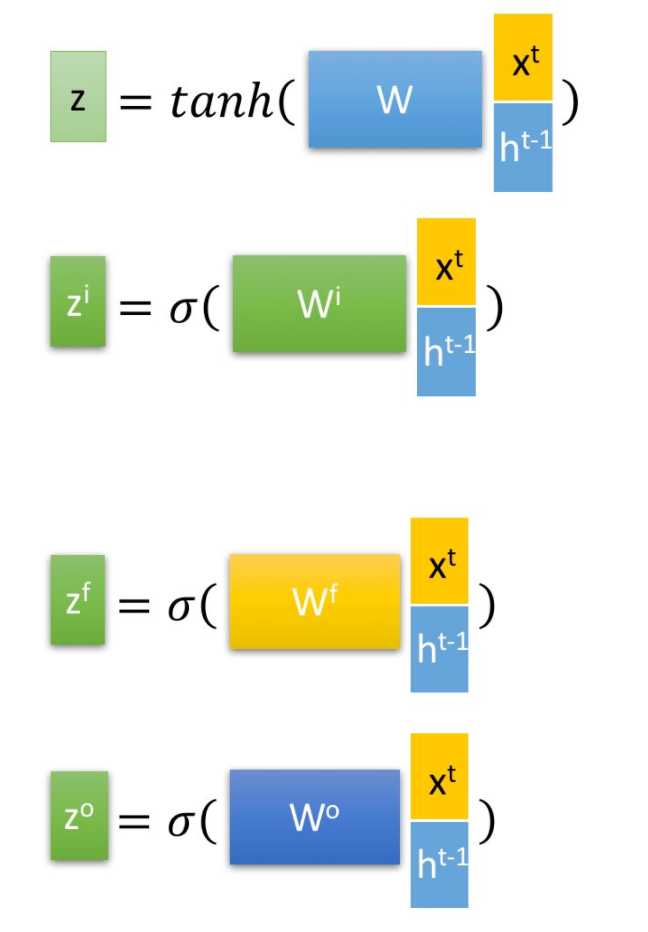
其中, ,
,
是由拼接向量乘以权重矩阵之后,再通过一个
激活函数转换成0到1之间的数值,来作为一种门控状态。而
则是将结果通过一个
激活函数将转换成-1到1之间的值(这里使用
是因为这里是将其做为输入数据,而不是门控信号)。
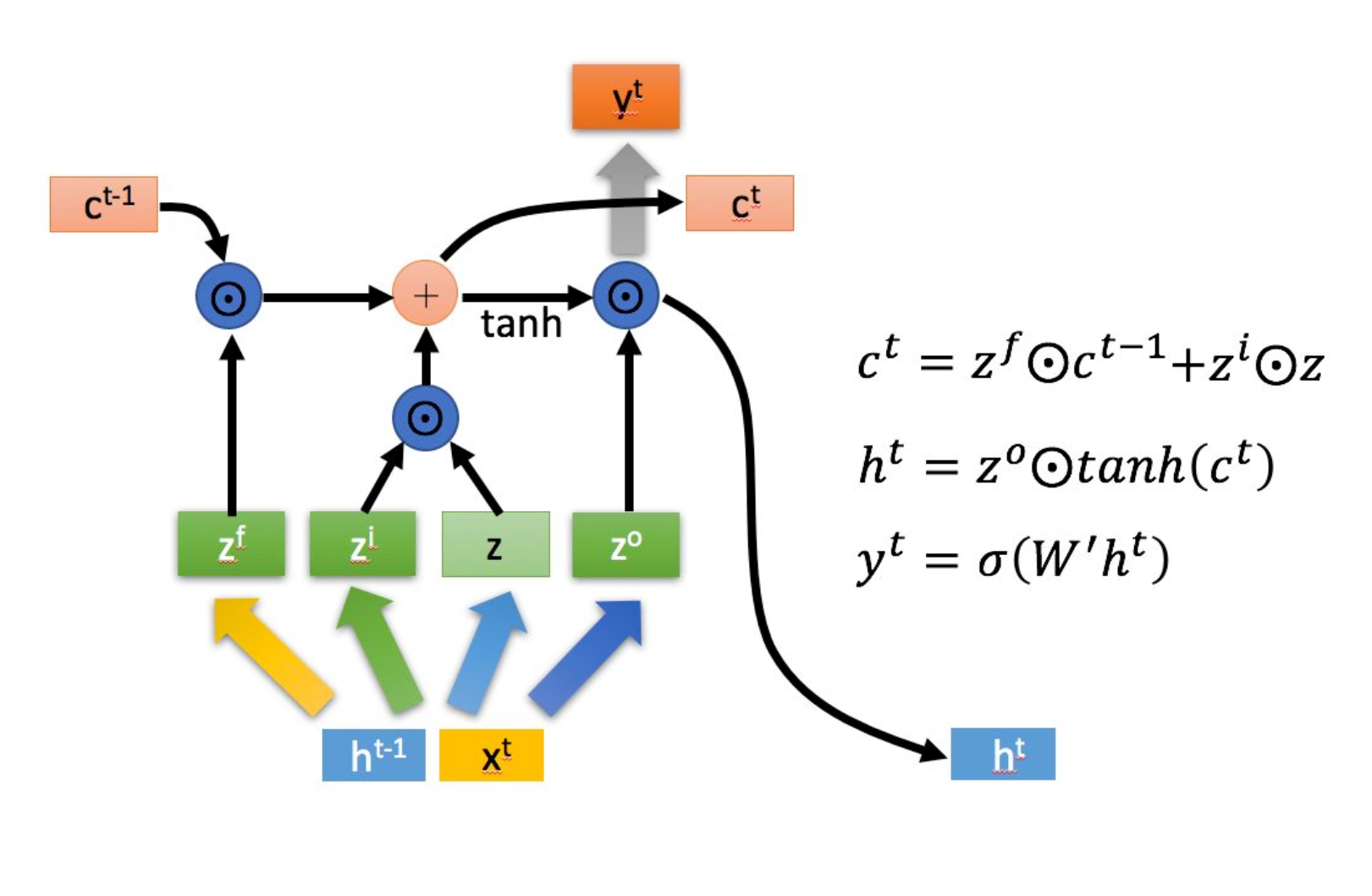
与普通RNN类似,输出 往往最终也是通过
变化得到。
二.LSTM代码如下:
注:主要调用nn.LSTM
''' 本程序实现了对单词词性的判断,输入一句话,输出该句话中每个单词的词性。 ''' import torch import torch.nn.functional as F from torch import nn, optim from tqdm import tqdm training_data = [("The dog ate the apple".split(), ["DET", "NN", "V", "DET", "NN"]), ("Everybody read that book".split(), ["NN", "V", "DET", "NN"])] def build_data(training_data): # 构建数据集 # 数据转换方法 word_to_idx = {} tag_to_idx = {} for context, tag in training_data: for word in context: if word not in word_to_idx: word_to_idx[word] = len(word_to_idx) for label in tag: if label not in tag_to_idx: tag_to_idx[label] = len(tag_to_idx) idx_to_tag = {tag_to_idx[tag]: tag for tag in tag_to_idx} return word_to_idx,tag_to_idx,idx_to_tag class LSTMTagger(nn.Module): def __init__(self, n_word, n_dim, n_hidden, n_tag): super(LSTMTagger, self).__init__() self.word_embedding = nn.Embedding(n_word, n_dim) self.lstm = nn.LSTM(n_dim, n_hidden, batch_first=True) # nn.lstm()接受的数据输入是(序列长度,batch,输入维数), # 这和我们cnn输入的方式不太一致,所以使用batch_first=True,把输入变成(batch,序列长度,输入维度),本程序的序列长度指的是一句话的单词数目 # 同时,batch_first=True会改变输出的维度顺序。<br data-filtered="filtered"> self.linear1 = nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_tag) def forward(self, x): # x是word_list,即单词的索引列表,size为len(x) x = self.word_embedding(x) # embedding之后,x的size为(len(x),n_dim) x = x.unsqueeze(0) # unsqueeze之后,x的size为(1,len(x),n_dim),1在下一行程序的lstm中被当做是batchsize,len(x)被当做序列长度 x, _ = self.lstm(x) # lstm的隐藏层输出,x的size为(1,len(x),n_hidden),因为定义lstm网络时用了batch_first=True,所以1在第一维,如果batch_first=False,则len(x)会在第一维 x = x.squeeze(0) # squeeze之后,x的size为(len(x),n_hidden),在下一行的linear层中,len(x)被当做是batchsize x = self.linear1(x) # linear层之后,x的size为(len(x),n_tag) y = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) # 对第1维先进行softmax计算,然后log一下。y的size为(len(x),n_tag)。 return y word_to_idx, tag_to_idx, idx_to_tag=build_data(training_data) def main(): # 用于训练 model = LSTMTagger(len(word_to_idx), 100, 128, len(tag_to_idx)) # 模型初始化 if torch.cuda.is_available(): model = model.cuda() criterion = nn.NLLLoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2) for epoch in tqdm(range(200)): running_loss = 0 for data in training_data: sentence, tags = data word_list = [word_to_idx[word] for word in sentence] # word_list是word索引列表 word_list = torch.LongTensor(word_list) tag_list = [tag_to_idx[tag] for tag in tags] # tag_list是tag索引列表 tag_list = torch.LongTensor(tag_list) if torch.cuda.is_available(): word_list = word_list.cuda() tag_list = tag_list.cuda() # forward out = model(word_list) loss = criterion(out, tag_list) running_loss += loss.data.cpu().numpy() # backward optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() print('Epoch: {:<3d} | Loss: {:6.4f}'.format(epoch, running_loss / len(data))) # 模型测试 test_sentence = "Everybody ate the apple" print('\n The test sentence is:\n', test_sentence) test_sentence = test_sentence.split() test_list = [word_to_idx[word] for word in test_sentence] test_list = torch.LongTensor(test_list) if torch.cuda.is_available(): test_list = test_list.cuda() out = model(test_list) _, predict_idx = torch.max(out, 1) # 1表示找行的最大值。 predict_idx是词性索引,是一个size为([len(test_sentence)]的张量 predict_tag = [idx_to_tag[idx] for idx in list(predict_idx.cpu().numpy())] print('The predict tags are:', predict_tag) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
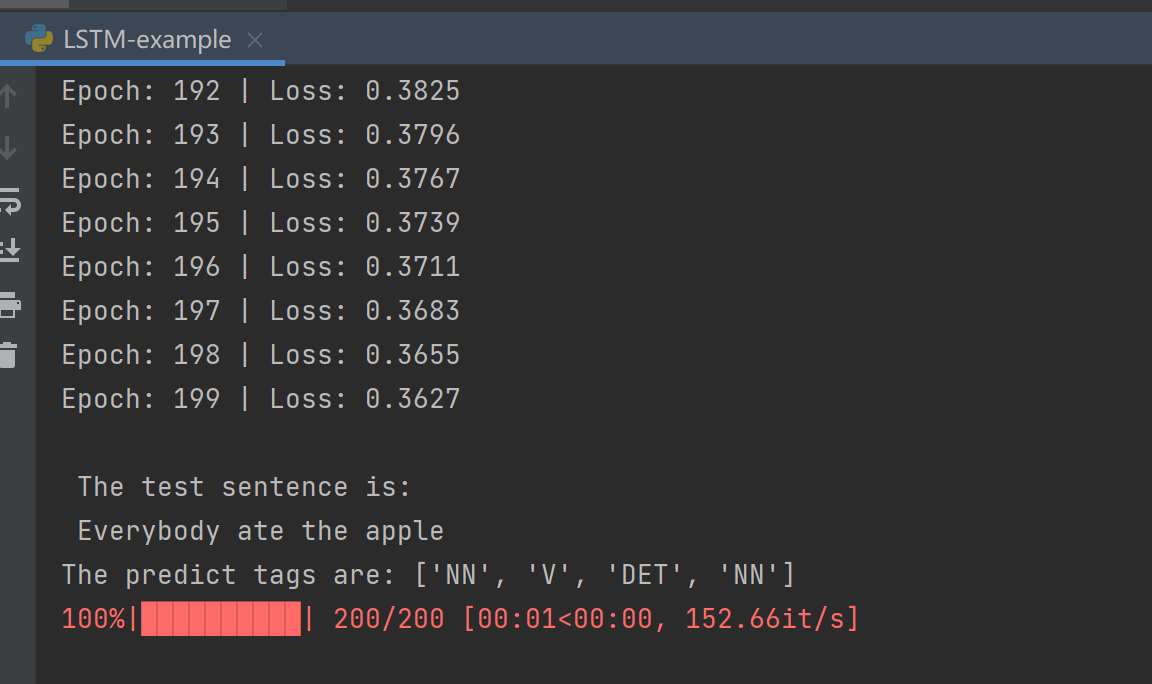
结果如下:
借鉴内容如下:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32085405
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128098497



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号