目标检测mAP计算方法-简单易懂
本次将整理一份map计算方法,主要分为三部分,第一部分简单了解原理,第二部分理解如何调用coco等相关库得到map,第三部分教会读者如何结合模型(任何可计算map的网络模型)调用而生成map,而本博客希望读者能掌握使用模型预测map,其重点也为第三部分:
第一部分介绍map原理,主要引用部分他人结果,
第二部分说明如何整理真实标签的数据及预测数据,调用pycocotools库实现map的计算,以下便是本博客的整理(附带转换coco json代码)
第三部分说明如何在模型中直接预测map,即结合模型预测+本博客代码样列,便可预测map,样列如下:
以下是根据模型运用Computer_map类主代码,详细,我将在第三部分展示细节代码。
1 def computer_main(data_root, model): 2 ''' 3 data_root:任何文件夹,但必须保证每个图片与对应xml必须放在同一个文件夹中 4 model:模型,用于预测 5 ''' 6 C = Computer_map() 7 img_root_lst = C.get_img_root_lst(data_root) # 获得图片绝对路径与图片产生image_id映射关系 8 9 # 在self.coco_json中保存categories,便于产生coco_json和predetect_json 10 categories = model.CLASSES # 可以给txt路径读取,或直接给列表 #*********************得到classes,需要更改的地方***********## 11 C.get_categories(categories) 12 13 # 产生coco_json格式 14 xml_root_lst = [name[:-3] + 'xml' for name in img_root_lst] 15 for xml_root in xml_root_lst: C.xml2cocojson(xml_root) # 产生coco json 并保存到self.coco_json中 16 17 # 产生预测的json 18 for img_path in img_root_lst: 19 20 parse_result = predict(model, img_path) ####**********************需要更改的地方***********************#### 21 22 23 result, classes = parse_result['result'], parse_result['classes'] 24 # restult 格式为列表[x1,y1,x2,y2,score,label],若无结果为空 25 img_name = C.get_strfile(img_path) 26 C.detect2json(result, img_name) 27 C.computer_map() # 计算map
一.map原理:
定义内容均来自此网址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/70667071
Accuracy:准确率
✔️ 准确率=预测正确的样本数/所有样本数,即预测正确的样本比例(包括预测正确的正样本和预测正确的负样本,不过在目标检测领域,没有预测正确的负样本这一说法,所以目标检测里面没有用Accuracy的)。
Precision:查准率
✔️ recision表示某一类样本预测有多准。
✔️ Precision针对的是某一类样本,如果没有说明类别,那么Precision是毫无意义的(有些地方不说明类别,直接说Precision,是因为二分类问题通常说的Precision都是正样本的Precision)。
Recall:召回率
✔️ Recall和Precision一样,脱离类别是没有意义的。说道Recall,一定指的是某个类别的Recall。Recall表示某一类样本,预测正确的与所有Ground Truth的比例。
✍️ Recall计算的时候,分母是Ground Truth中某一类样本的数量,而Precision计算的时候,是预测出来的某一类样本数。
F1 Score:平衡F分数
F1分数,它被定义为查准率和召回率的调和平均数
更加广泛的会定义 分数,其中
和
分数在统计学在常用,并且,
分数中,召回率的权重大于查准率,而
分数中,则相反。
AP: Average Precision
以Recall为横轴,Precision为纵轴,就可以画出一条PR曲线,PR曲线下的面积就定义为AP,即:
 PR曲线
PR曲线
由于计算积分相对困难,因此引入插值法,计算AP公式如下:
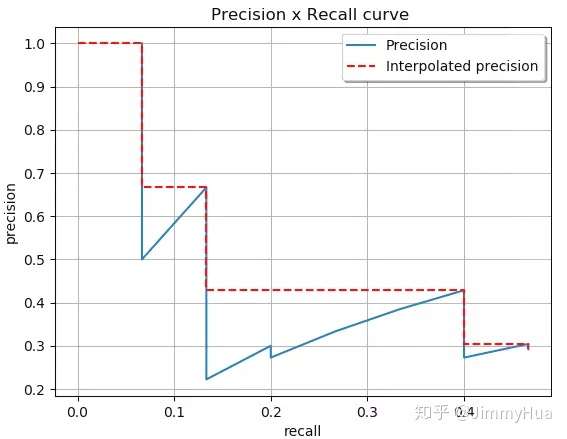
计算面积:

原理:
二.代码-用于实现map:
本部分才是本博客重要内容,我将介绍2部分,第一部分如何使用有标记的真实数据产生coco json格式与如何使用模型预测结果产生预测json格式,第二部分如何使用代码计算map。
①.json格式
真实数据json格式实际是coco json 格式,主要是如下图:
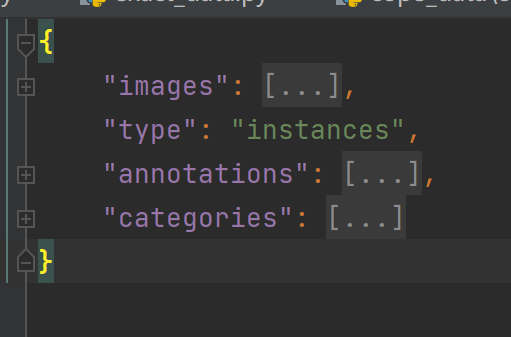
其中images格式如下图:

annotations格式如下:
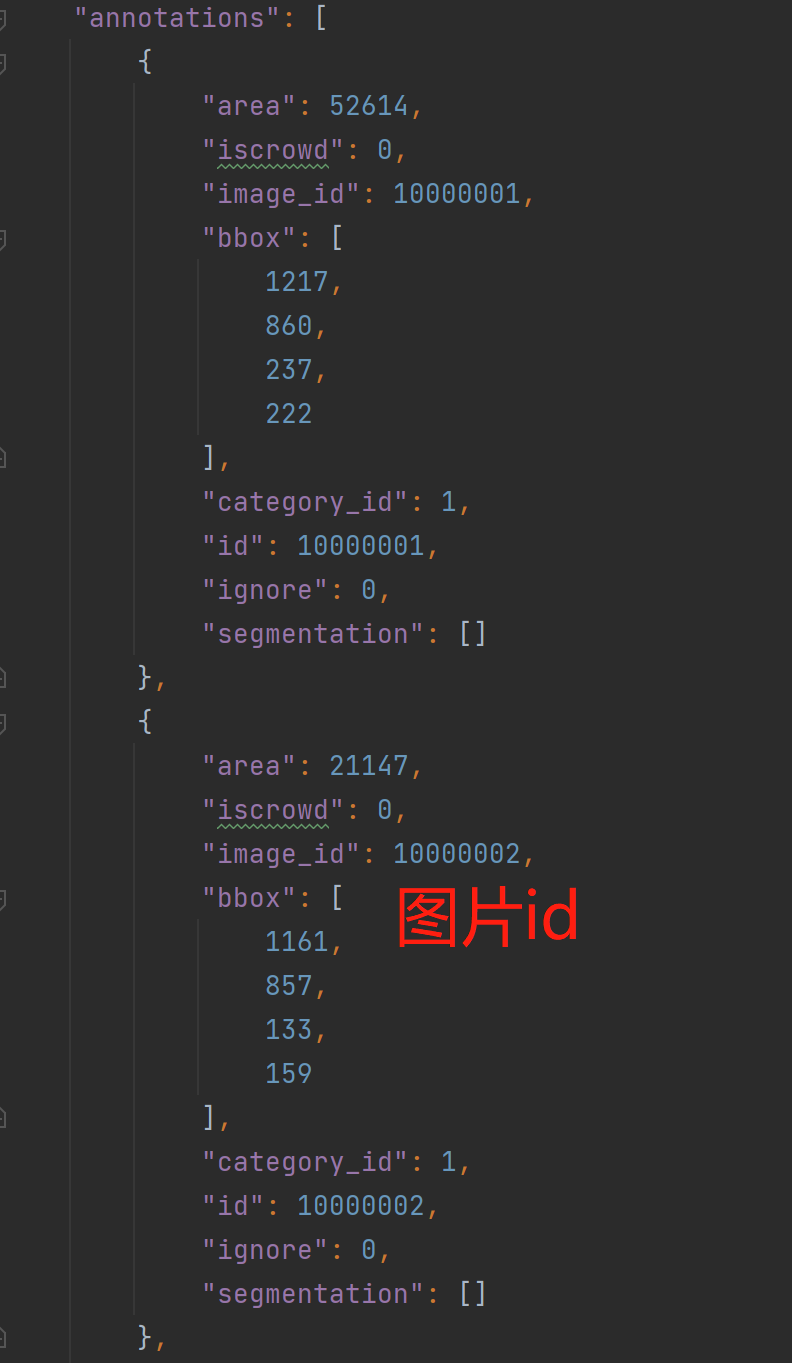
categories格式为:
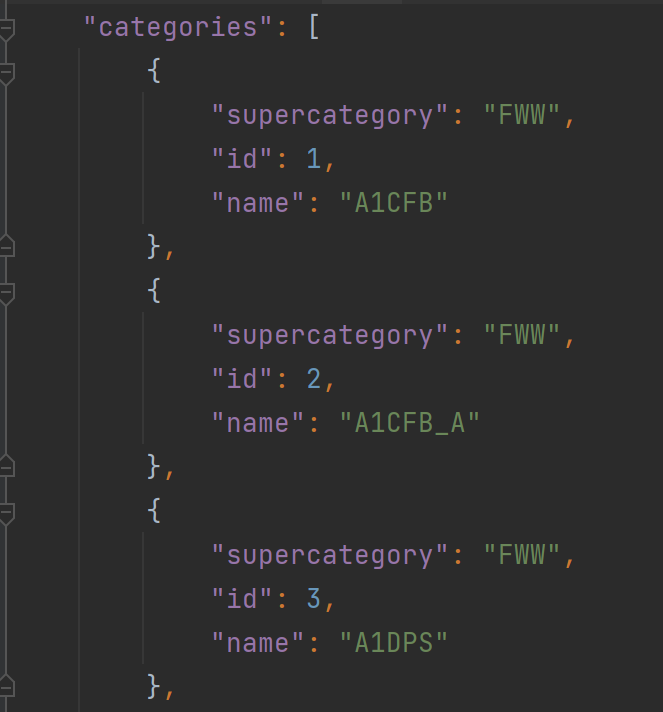
以上为真实数据转换为json的格式。
预测结果数据json格式转换,主要是如下图:
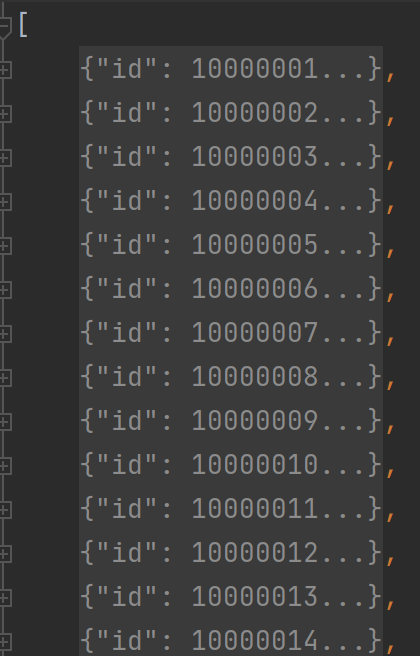
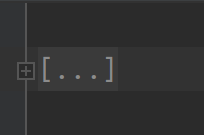
以上右图是整体结构,实际为列表,左图是预测信息,保存为字典,其详细内容如下:

特别注意:image id 对应真实coco json图像的image-id,类别id也是对应真实coco json中的类别id。
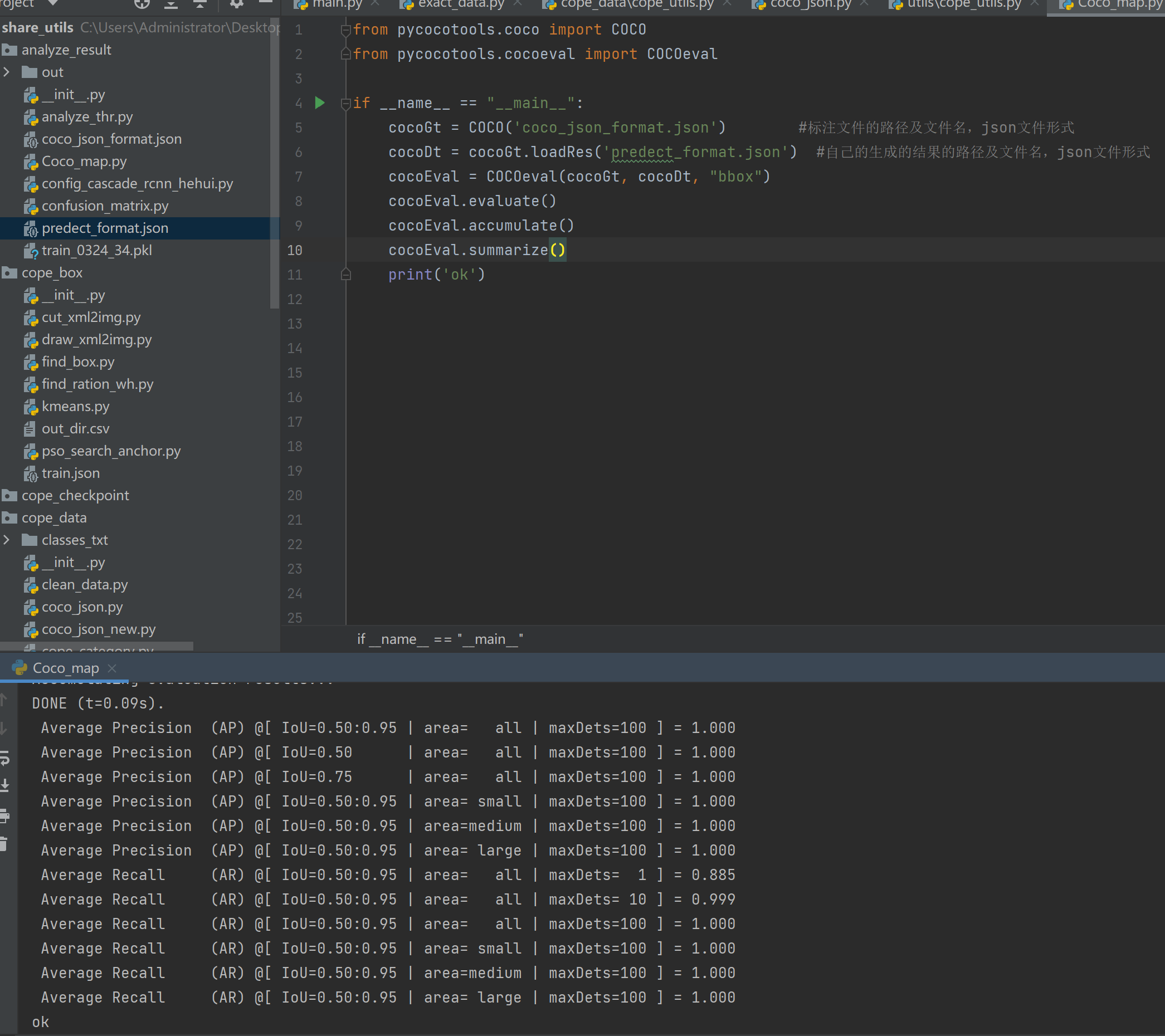
②.实际代码,借助pycocotools 库中评估类别,具体代码如下图:
1 from pycocotools.coco import COCO 2 from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval 3 4 if __name__ == "__main__": 5 cocoGt = COCO('coco_json_format.json') #标注文件的路径及文件名,json文件形式 6 cocoDt = cocoGt.loadRes('predect_format.json') #自己的生成的结果的路径及文件名,json文件形式 7 cocoEval = COCOeval(cocoGt, cocoDt, "bbox") 8 cocoEval.evaluate() 9 cocoEval.accumulate() 10 cocoEval.summarize()
③结果展示:
二.代码-模型预测map:
使用模型实现代码的类:
模型预测map:
1 class Computer_map(): 2 ''' 3 主代码样列 4 def computer_main(data_root, model):#data_root:任何文件夹,但必须保证每个图片与对应xml必须放在同一个文件夹中,model:模型,用于预测 5 C = Computer_map() 6 img_root_lst = C.get_img_root_lst(data_root) # 获得图片绝对路径与图片产生image_id映射关系 7 8 # 在self.coco_json中保存categories,便于产生coco_json和predetect_json 9 categories = model.CLASSES # 可以给txt路径读取,或直接给列表 #*********************得到classes,需要更改的地方***********## 10 C.get_categories(categories) 11 12 # 产生coco_json格式 13 xml_root_lst = [name[:-3] + 'xml' for name in img_root_lst] 14 for xml_root in xml_root_lst: C.xml2cocojson(xml_root) # 产生coco json 并保存到self.coco_json中 15 16 # 产生预测的json 17 for img_path in img_root_lst: 18 19 parse_result = predict(model, img_path) ####**********************需要更改的地方***********************#### 20 21 result, classes = parse_result['result'], parse_result['classes'] 22 # restult 格式为列表[x1,y1,x2,y2,score,label],若无结果为空 23 img_name = C.get_strfile(img_path) 24 C.detect2json(result, img_name) 25 C.computer_map() # 计算map 26 27 ''' 28 29 def __init__(self): 30 self.img_format = ['png', 'jpg', 'JPG', 'PNG', 'bmp', 'jpeg'] 31 self.coco_json = {'images': [], 'type': 'instances', 'annotations': [], 'categories': []} 32 self.predetect_json = [] # 保存字典 33 self.image_id = 10000000 # 图像的id,每增加一张图片便+1 34 self.anation_id = 10000000 35 self.imgname_map_id = {} # 图片名字映射id 36 37 def read_txt(self, file_path): 38 with open(file_path, 'r') as f: 39 content = f.read().splitlines() 40 return content 41 42 def get_categories(self, categories): 43 ''' 44 categories:为字符串,指绝对路径;为列表,指类本身 45 return:将categories存入coco json中 46 ''' 47 if isinstance(categories, str): 48 categories = self.read_txt(categories) 49 elif isinstance(categories, list or tuple): 50 categories = list(categories) 51 52 category_json = [{"supercategory": cat, "id": i + 1, "name": cat} for i, cat in enumerate(categories)] 53 self.coco_json['categories'] = category_json 54 55 def computer_map(self, coco_json_path=None, predetect_json_path=None): 56 from pycocotools.coco import COCO 57 from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval 58 from collections import defaultdict 59 import time 60 import json 61 from pycocotools import mask as maskUtils 62 import numpy as np 63 # 继承修改coco json文件 64 class COCO_modify(COCO): 65 def __init__(self, coco_json_data=None): 66 """ 67 Constructor of Microsoft COCO helper class for reading and visualizing annotations. 68 :param annotation_file (str): location of annotation file 69 :param image_folder (str): location to the folder that hosts images. 70 :return: 71 """ 72 # load dataset 73 self.dataset, self.anns, self.cats, self.imgs = dict(), dict(), dict(), dict() 74 self.imgToAnns, self.catToImgs = defaultdict(list), defaultdict(list) 75 if coco_json_data is not None: 76 print('loading annotations into memory...') 77 tic = time.time() 78 if isinstance(coco_json_data, str): 79 with open(coco_json_data, 'r') as f: 80 dataset = json.load(f) 81 assert type(dataset) == dict, 'annotation file format {} not supported'.format(type(dataset)) 82 print('Done (t={:0.2f}s)'.format(time.time() - tic)) 83 else: 84 dataset = coco_json_data 85 self.dataset = dataset 86 self.createIndex() 87 88 def loadRes(self, predetect_json_data): 89 import copy 90 """ 91 Load result file and return a result api object. 92 :param resFile (str) : file name of result file 93 :return: res (obj) : result api object 94 """ 95 res = COCO_modify() 96 res.dataset['images'] = [img for img in self.dataset['images']] 97 98 print('Loading and preparing results...') 99 tic = time.time() 100 101 if isinstance(predetect_json_data, str): 102 with open(predetect_json_data, 'r') as f: 103 anns = json.load(f) 104 105 print('Done (t={:0.2f}s)'.format(time.time() - tic)) 106 else: 107 anns = predetect_json_data 108 109 assert type(anns) == list, 'results in not an array of objects' 110 annsImgIds = [ann['image_id'] for ann in anns] 111 assert set(annsImgIds) == (set(annsImgIds) & set(self.getImgIds())), \ 112 'Results do not correspond to current coco set' 113 if 'caption' in anns[0]: 114 imgIds = set([img['id'] for img in res.dataset['images']]) & set([ann['image_id'] for ann in anns]) 115 res.dataset['images'] = [img for img in res.dataset['images'] if img['id'] in imgIds] 116 for id, ann in enumerate(anns): 117 ann['id'] = id + 1 118 elif 'bbox' in anns[0] and not anns[0]['bbox'] == []: 119 res.dataset['categories'] = copy.deepcopy(self.dataset['categories']) 120 for id, ann in enumerate(anns): 121 bb = ann['bbox'] 122 x1, x2, y1, y2 = [bb[0], bb[0] + bb[2], bb[1], bb[1] + bb[3]] 123 if not 'segmentation' in ann: 124 ann['segmentation'] = [[x1, y1, x1, y2, x2, y2, x2, y1]] 125 ann['area'] = bb[2] * bb[3] 126 ann['id'] = id + 1 127 ann['iscrowd'] = 0 128 elif 'segmentation' in anns[0]: 129 res.dataset['categories'] = copy.deepcopy(self.dataset['categories']) 130 for id, ann in enumerate(anns): 131 # now only support compressed RLE format as segmentation results 132 ann['area'] = maskUtils.area(ann['segmentation']) 133 if not 'bbox' in ann: 134 ann['bbox'] = maskUtils.toBbox(ann['segmentation']) 135 ann['id'] = id + 1 136 ann['iscrowd'] = 0 137 elif 'keypoints' in anns[0]: 138 res.dataset['categories'] = copy.deepcopy(self.dataset['categories']) 139 for id, ann in enumerate(anns): 140 s = ann['keypoints'] 141 x = s[0::3] 142 y = s[1::3] 143 x0, x1, y0, y1 = np.min(x), np.max(x), np.min(y), np.max(y) 144 ann['area'] = (x1 - x0) * (y1 - y0) 145 ann['id'] = id + 1 146 ann['bbox'] = [x0, y0, x1 - x0, y1 - y0] 147 print('DONE (t={:0.2f}s)'.format(time.time() - tic)) 148 149 res.dataset['annotations'] = anns 150 res.createIndex() 151 return res 152 153 coco_json_data = coco_json_path if coco_json_path is not None else self.coco_json 154 cocoGt = COCO_modify(coco_json_data) # 标注文件的路径及文件名,json文件形式 155 predetect_json_data = predetect_json_path if predetect_json_path is not None else self.predetect_json 156 cocoDt = cocoGt.loadRes(predetect_json_data) # 自己的生成的结果的路径及文件名,json文件形式 157 158 cocoEval = COCOeval(cocoGt, cocoDt, "bbox") 159 cocoEval.evaluate() 160 cocoEval.accumulate() 161 cocoEval.summarize() 162 163 def get_img_root_lst(self, root_data): 164 import os 165 img_root_lst = [] 166 for dir, file, names in os.walk(root_data): 167 img_lst = [os.path.join(dir, name) for name in names if name[-3:] in self.img_format] 168 img_root_lst = img_root_lst + img_lst 169 for na in img_lst: # 图片名字映射image_id 170 self.image_id += 1 171 self.imgname_map_id[self.get_strfile(na)] = self.image_id 172 return img_root_lst # 得到图片绝对路径 173 174 def get_strfile(self, file_str, pos=-1): 175 ''' 176 得到file_str / or \\ 的最后一个名称 177 ''' 178 endstr_f_filestr = file_str.split('\\')[pos] if '\\' in file_str else file_str.split('/')[pos] 179 return endstr_f_filestr 180 181 def read_xml(self, xml_root): 182 ''' 183 :param xml_root: .xml文件 184 :return: dict('cat':['cat1',...],'bboxes':[[x1,y1,x2,y2],...],'whd':[w ,h,d]) 185 ''' 186 187 import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET 188 import os 189 190 dict_info = {'cat': [], 'bboxes': [], 'box_wh': [], 'whd': []} 191 if os.path.splitext(xml_root)[-1] == '.xml': 192 tree = ET.parse(xml_root) # ET是一个xml文件解析库,ET.parse()打开xml文件。parse--"解析" 193 root = tree.getroot() # 获取根节点 194 whd = root.find('size') 195 whd = [int(whd.find('width').text), int(whd.find('height').text), int(whd.find('depth').text)] 196 xml_filename = root.find('filename').text 197 dict_info['whd'] = whd 198 dict_info['xml_filename'] = xml_filename 199 for obj in root.findall('object'): # 找到根节点下所有“object”节点 200 cat = str(obj.find('name').text) # 找到object节点下name子节点的值(字符串) 201 bbox = obj.find('bndbox') 202 x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text), 203 int(bbox.find('ymin').text), 204 int(bbox.find('xmax').text), 205 int(bbox.find('ymax').text)] 206 b_w = x2 - x1 + 1 207 b_h = y2 - y1 + 1 208 209 dict_info['cat'].append(cat) 210 dict_info['bboxes'].append([x1, y1, x2, y2]) 211 dict_info['box_wh'].append([b_w, b_h]) 212 213 else: 214 print('[inexistence]:{} suffix is not xml '.format(xml_root)) 215 return dict_info 216 217 def xml2cocojson(self, xml_root): 218 ''' 219 处理1个xml,将其真实json保存到self.coco_json中 220 ''' 221 assert len(self.coco_json['categories']) > 0, 'self.coco_json[categories] must exist v' 222 categories = [cat_info['name'] for cat_info in self.coco_json['categories']] 223 xml_info = self.read_xml(xml_root) 224 if len(xml_info['cat']) > 0: 225 xml_filename = xml_info['xml_filename'] 226 xml_name = self.get_strfile(xml_root) 227 img_name = xml_name[:-3] + xml_filename[-3:] 228 # 转为coco json时候,若add_file为True则在coco json文件的file_name增加文件夹名称+图片名字 229 230 image_id = self.imgname_map_id[img_name] 231 w, h, d = xml_info['whd'] 232 # 构建json文件字典 233 image_json = {'file_name': img_name, 'height': h, 'width': w, 'id': image_id} 234 ann_json = [] 235 for i, category in enumerate(xml_info['cat']): 236 # 表示有box存在,可以添加images信息 237 238 category_id = categories.index(category) + 1 # 给出box对应标签索引为类 239 self.anation_id = self.anation_id + 1 240 xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = xml_info['bboxes'][i] 241 242 o_width, o_height = xml_info['box_wh'][i] 243 244 if (xmax <= xmin) or (ymax <= ymin): 245 print('code:[{}] will be abandon due to {} min of box w or h more than max '.format(category, 246 xml_root)) # 打印错误的box 247 else: 248 ann = {'area': o_width * o_height, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': image_id, 249 'bbox': [xmin, ymin, o_width, o_height], 250 'category_id': category_id, 'id': self.anation_id, 'ignore': 0, 251 'segmentation': []} 252 ann_json.append(ann) 253 254 if len(ann_json) > 0: # 证明存在 annotation 255 for ann in ann_json: self.coco_json['annotations'].append(ann) 256 self.coco_json['images'].append(image_json) 257 258 def detect2json(self, predetect_result, img_name,score_thr=-1): 259 ''' 260 predetect_result:为列表,每个列表中包含[x1, y1, x2, y2, score, label] 261 img_name: 图片的名字 262 ''' 263 if len(predetect_result) > 0: 264 categories = [cat_info['name'] for cat_info in self.coco_json['categories']] 265 for result in predetect_result: 266 x1, y1, x2, y2, score, label = result 267 if score>score_thr: 268 w, h = int(x2 - x1), int(y2 - y1) 269 x1, y1 = int(x1), int(y1) 270 img_name_new = self.get_strfile(img_name) 271 image_id = self.imgname_map_id[img_name_new] 272 category_id = list(categories).index(label) + 1 273 detect_json = { 274 "area": w * h, 275 "iscrowd": 0, 276 "image_id": image_id, 277 "bbox": [ 278 x1, 279 y1, 280 w, 281 h 282 ], 283 "category_id": category_id, 284 "id": image_id, 285 "ignore": 0, 286 "segmentation": [], 287 "score": score 288 } 289 self.predetect_json.append(detect_json) 290 291 def write_json(self,out_dir): 292 import os 293 import json 294 coco_json_path=os.path.join(out_dir,'coco_json_data.json') 295 with open(coco_json_path, 'w') as f: 296 json.dump(self.coco_json, f, indent=4) # indent表示间隔长度 297 predetect_json_path=os.path.join(out_dir,'predetect_json_data.json') 298 with open(predetect_json_path, 'w') as f: 299 json.dump(self.predetect_json, f, indent=4) # indent表示间隔长度
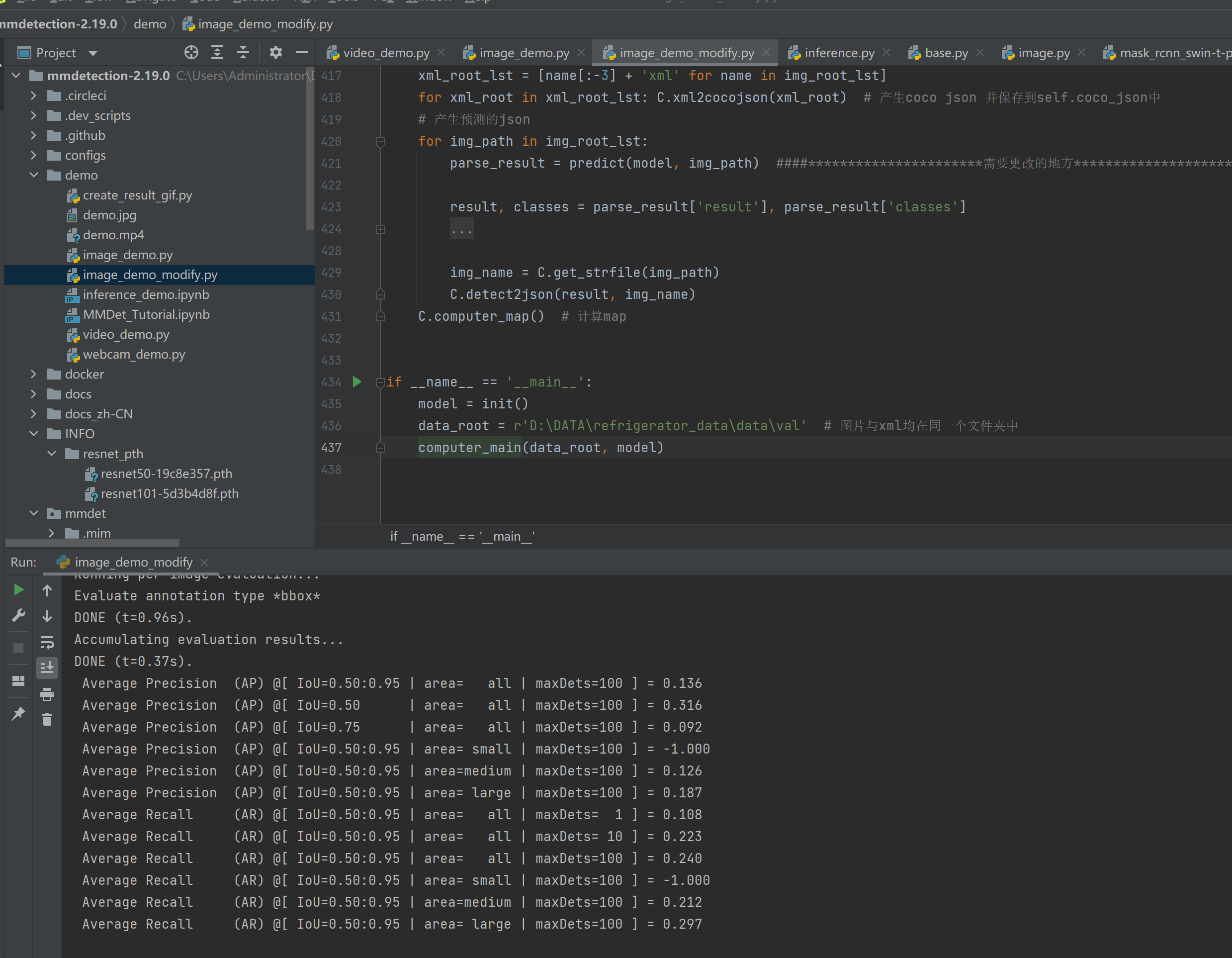
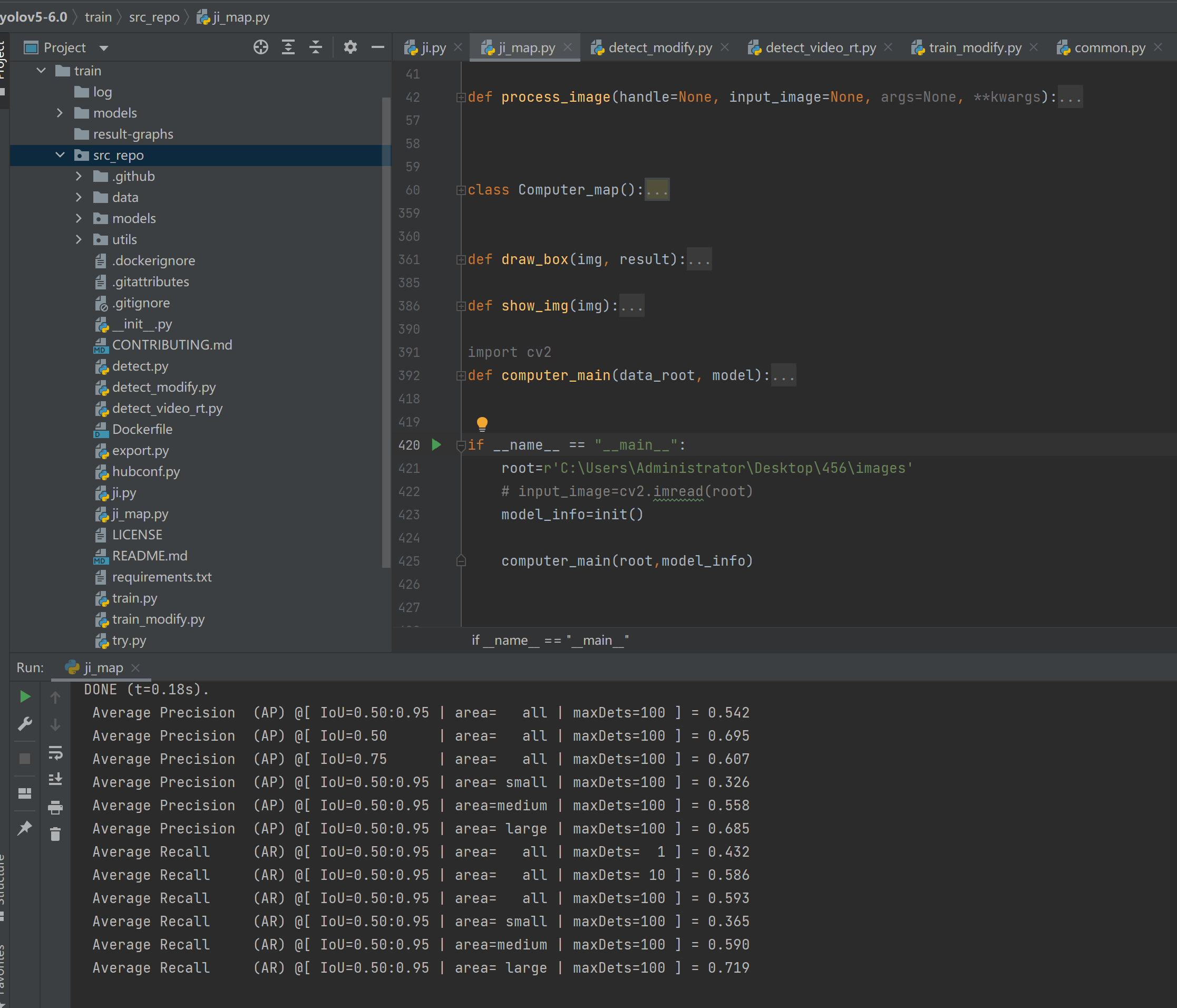
结果展示:左图为mmdet2.19模型结果,右图为yolov5模型结果
附带xml转换coco json代码:

1 import os 2 import json 3 import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET 4 import cv2 # 无xml时候需要读取图片高与宽 5 # from cope_data.cope_utils import * 6 from tqdm import tqdm 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def read_xml(xml_root): 16 ''' 17 :param xml_root: .xml文件 18 :return: dict('cat':['cat1',...],'bboxes':[[x1,y1,x2,y2],...],'whd':[w ,h,d]) 19 ''' 20 dict_info = {'cat': [], 'bboxes': [], 'box_wh': [], 'whd': []} 21 if os.path.splitext(xml_root)[-1] == '.xml': 22 tree = ET.parse(xml_root) # ET是一个xml文件解析库,ET.parse()打开xml文件。parse--"解析" 23 root = tree.getroot() # 获取根节点 24 whd = root.find('size') 25 whd = [int(whd.find('width').text), int(whd.find('height').text), int(whd.find('depth').text)] 26 xml_filename = root.find('filename').text 27 dict_info['whd']=whd 28 dict_info['xml_filename']=xml_filename 29 for obj in root.findall('object'): # 找到根节点下所有“object”节点 30 cat = str(obj.find('name').text) # 找到object节点下name子节点的值(字符串) 31 bbox = obj.find('bndbox') 32 x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text), 33 int(bbox.find('ymin').text), 34 int(bbox.find('xmax').text), 35 int(bbox.find('ymax').text)] 36 b_w = x2 - x1 + 1 37 b_h = y2 - y1 + 1 38 39 dict_info['cat'].append(cat) 40 dict_info['bboxes'].append([x1, y1, x2, y2]) 41 dict_info['box_wh'].append([b_w, b_h]) 42 43 else: 44 print('[inexistence]:{} suffix is not xml '.format(xml_root)) 45 return dict_info 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 # xml转换为训练集 54 def train_multifiles(root_data, json_name='train.json', categories=None, out_dir=None, add_file=False,refuse_category=[],category_path=None): 55 ''' 56 json文件中的file_name包含文件夹/名字 57 :param json_name: 保存json文件名字,最终结果在out_dir+json_name(若out_dir有路径情况),否则在root_data下面 58 :param categories: 类别信息,为None则将self.root文件夹的名字作为类别信息 59 add_file :True表示cocojson中添加文件名,否则不添加 60 refuse_category:拒绝装换为cocojson的类的列表 61 :return: 62 ''' 63 64 65 66 def read_txt(file_path): 67 with open(file_path, 'r') as f: 68 content = f.read().splitlines() 69 return content 70 def write_txt(text_lst, out_dir): 71 ''' 72 每行内容为列表,将其写入text中 73 ''' 74 file_write_obj = open(out_dir, 'w') # 以写的方式打开文件,如果文件不存在,就会自动创建 75 for text in text_lst: 76 file_write_obj.writelines(text) 77 file_write_obj.write('\n') 78 file_write_obj.close() 79 return out_dir 80 81 def get_strfile(file_str, pos=-1): 82 ''' 83 得到file_str / or \\ 的最后一个名称 84 ''' 85 endstr_f_filestr = file_str.split('\\')[pos] if '\\' in file_str else file_str.split('/')[pos] 86 return endstr_f_filestr 87 88 # coco json文件格式 89 json_dict = {"images": [], "type": "instances", "annotations": [], "categories": []} 90 image_id = 10000000 91 anation_id = 10000000 92 xml_root_lst = [] 93 for dir, dir_file, dir_names in os.walk(root_data): 94 name_lst = [os.path.join(dir, name) for name in dir_names if name[-3:] == 'xml'] 95 xml_root_lst = xml_root_lst + name_lst 96 if category_path is None: 97 if categories is None: 98 categories = [] 99 elif isinstance(categories, list): 100 categories = categories 101 else: 102 raise IOError('categories must be list or None') 103 else: 104 categories=read_txt(category_path) 105 106 107 count_categories = {} 108 for xml_root in tqdm(xml_root_lst): 109 try: 110 xml_info=read_xml(xml_root) 111 if len(xml_info['cat'])>0: 112 xml_filename = xml_info['xml_filename'] 113 xml_name = get_strfile(xml_root) 114 img_name = xml_name[:-3] + xml_filename[-3:] 115 # 转为cocojson时候,若add_file为True则在cocojson文件的file_name增加文件夹名称+图片名字 116 file_name = get_strfile(xml_root, pos=-2) + '/' + img_name if add_file else img_name # 只记录图片名字 117 118 image_id = image_id + 1 119 120 w,h,d=xml_info['whd'] 121 # 构建json文件字典 122 image = {'file_name': file_name, 'height': h, 'width': w, 'id': image_id} 123 for i, category in enumerate(xml_info['cat']): 124 125 if category in refuse_category: 126 print('refuse {} code will not convert coojson format '.format(category)) 127 continue 128 # 若categories列表不包含该code则增加该code到列表中 129 if category not in categories and category_path is None: 130 categories.append(category) 131 # 计数每个cat的数量 132 count_categories[category]=1 if category not in count_categories else count_categories[category]+1 133 134 135 # 表示有box存在,可以添加images信息 136 if image not in json_dict['images']: 137 json_dict['images'].append(image) # 将图像信息添加到json中 138 category_id = categories.index(category) + 1 # 给出box对应标签索引为类 139 anation_id = anation_id + 1 140 xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax=xml_info['bboxes'][i] 141 142 o_width,o_height=xml_info['box_wh'][i] 143 144 if (xmax <= xmin) or (ymax <= ymin): 145 print('code:[{}] will be abandon due to {} min of box w or h more than max '.format(category,xml_root)) # 打印错误的box 146 147 else: 148 ann = {'area': o_width * o_height, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': image_id, 149 'bbox': [xmin, ymin, o_width, o_height], 150 'category_id': category_id, 'id': anation_id, 'ignore': 0, 151 'segmentation': []} 152 json_dict['annotations'].append(ann) 153 except: 154 print('xml file: {} not read error!'.format(xml_root)) 155 156 157 for cid, cate in enumerate(categories): 158 cat = {'supercategory': cate, 'id': cid + 1, 'name': cate} 159 json_dict['categories'].append(cat) 160 if out_dir is not None: 161 build_dir(self.out_dir) 162 out_dir = os.path.join(out_dir, json_name) 163 out_dir_txt=os.path.join(out_dir, 'classes.txt') 164 else: 165 out_dir = os.path.join(root_data, json_name) 166 out_dir_txt = os.path.join(root_data, 'classes.txt') 167 with open(out_dir, 'w') as f: 168 json.dump(json_dict, f, indent=4) # indent表示间隔长度 169 170 write_txt(categories,out_dir_txt) 171 172 173 print('categories count : \n',count_categories) 174 175 176 177 178 if __name__ == '__main__': 179 root_path = r'D:\DATA\coco2017_train_val\data_coco_clear_2017\val' 180 category_path=r'D:\DATA\coco2017_train_val\data_coco_clear_2017\classes.txt' 181 train_multifiles(root_path,category_path=category_path)
借鉴博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35916487/article/details/89076570




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号