Mybatis3详解(八)----高级映射之一对一映射
1、前言
在前面SQL映射文件的介绍中,说到resultMap元素中有两个标签是用来做关联查询操作的,也就是一对一,一对多,对应到Mybatis中的标签分别是association和collection标签。它们在实际的项目中,会经常用到关联表的查询,因为实际的项目中不可能是对单表的查询,经常会有一对一,一对多等情况,我们可以使用这两个标签来配合实现。在Java实体对象中,一对一属性使用包装对象来实现,一对多属性使用List或者Set来实现。
association和collection二者标签的内部属性基本是一致的,它们的属性介绍如下(红色标注表示常用):
- property:映射实体类属性名。
- column:映射数据库字段名或者其别名(这个别名是数据库起的,如 select username as name)。
- javaType:映射java类型。
- jdbcType:映射数据库类型。
- ofType:映射集合的类型(注意:javaType是用来指定pojo中属性的类型,而ofType指定的是映射到list集合属性中pojo的类型,也就是尖括号的泛型private List<User> users)。
- select:用于加载复杂类型属性的映射语句的id (全限定名加方法,方法名后面无括号,例如:com.thr.mapper.UserMapper.selectAllUser),它会从 column 属性指定的列中检索数据,作为参数传递给目标 select 语句。 具体请参考下面的第二个例子。
- fetchType:延迟加载,lazy打开延迟加载,eager积极加载。指定属性后,将在映射中忽略全局配置参数 lazyLoadingEnabled,使用属性的值。
- resultMap:不使用嵌套模式,而是将此关联的嵌套结果集映射到一个外部的<resultMap>标签中,然后通过 id 进行引入。
- resultSet:指定用于加载复杂类型的结果集名字。
- autoMapping:自动封装,如果数据库字段和javaBean的字段名一样,可以使用这种方式,但是不建议采取,还是老老实实写比较稳妥,如果非要使用此功能,那就在全局配置中加上mapUnderscoreToCamelCase=TRUE,它会使经典数据库字段命名规则翻译成javaBean的经典命名规则,如:a_column翻译成aColumn。
- columnPrefix:关联多张表查询时,为了使列明不重复,使用此功能可以减少开发量。
- foreignColumn:指定外键对应的列名,指定的列将与父类型中 column 的给出的列进行匹配。
- notNullColumn:不为空的列,如果指定了列,那么只有当字段不为空时,Mybatis才会真正创建对象,才能得到我们想要的值。
- typeHandler:数据库与Java类型匹配处理器(可以参考前面的TypeHandler部分)。
如果你想对这些属性有更加深入了解的话可以自行去参考Mybatis的官方文档,链接:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
2、案例分析
我们以典型的 员工(Employee)和部门(Department)为例:
- 一个员工只能在一个部门;Employee—>Department(一对一)
- 一个部门可以包含多个员工;Department—>Employee(一对多)
下面我们分别创建 员工表:t_employee 和 部门表:t_department:
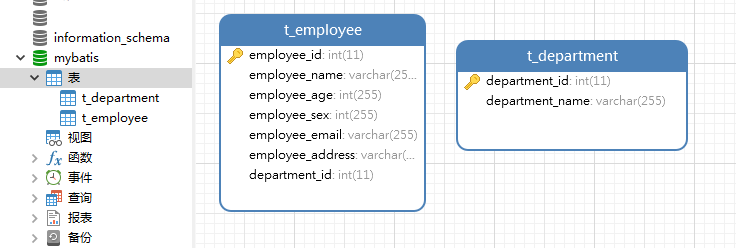
对应mysql的sql脚本如下:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | -- ------------------------------ Table structure for t_department-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_department`;CREATE TABLE `t_department` ( `department_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `department_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`department_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 8 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- ------------------------------ Records of t_department-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (1, '开发部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (2, '人力资源部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (3, '市场营销部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (4, '财务部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (5, '行政部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (6, '监察部');INSERT INTO `t_department` VALUES (7, '客服服务部');-- ------------------------------ Table structure for t_employee-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_employee`;CREATE TABLE `t_employee` ( `employee_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `employee_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `employee_age` int(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `employee_sex` int(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `employee_email` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `employee_address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `department_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 10 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;-- ------------------------------ Records of t_employee-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (1, '唐浩荣', 23, 1, '15477259875@163.com', '中国上海浦东区', 1);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (2, '黄飞鸿', 32, 1, '86547547@qq.com', '大清广东', 2);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (3, '十三姨', 18, 0, '520520520@gmail.com', '大清广东', 3);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (4, '纳兰元述', 28, 1, '545627858@qq.com', '大清京师', 5);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (5, '梁宽', 31, 1, '8795124578@qq.com', '大清广东', 7);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (6, '蔡徐坤', 20, 0, '4257895124@gmail.com', '四川成都', 4);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (7, '杨超越', 21, 0, '8746821252@qq.com', '中国北京', 7);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (8, '马保国', 66, 1, '6666666666@qq.com', '广东深圳', 6);INSERT INTO `t_employee` VALUES (9, '马牛逼', 45, 1, 'asdfg45678@163.com', '湖北武汉', 3); |
注意:在MyBatis中主要有这两种方式实现关联查询:
- 嵌套结果:使用嵌套映射的方式来处理关联结果的子集。
- 分步查询:通过 select 属性来执行另外一个 SQL 映射语句来返回预期的复杂类型。select属性的规则是全限定名加方法名,例如:com.thr.mapper.UserMapper.selectAllUser,方法名后面无括号。
所以下面我们就通过代码来学习这两种方式实现Mybatis的关联查询。
3、嵌套结果
①、分别定义Employee和Department实体类
Employee实体类:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | /** * 员工实体类 */public class Employee { //员工id private Integer empId; //员工名称 private String empName; //员工年龄 private Integer empAge; //员工性别 private Integer empSex; //员工邮箱 private String empEmail; //员工地址 private String empAddress; //员工所属部门,和部门表构成一对一的关系,一个员工只能在一个部门 private Department department; //getter、setter、toString方法和一些构造方法省略...} |
Department实体类:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 | /** * 部门实体类 */public class Department { //部门id private Integer deptId; //部门名称 private String deptName; //getter、setter、toString方法和一些构造方法省略...} |
②、创建EmployeeMapper接口和EmployeeMapper.xml 文件
EmployeeMapper接口:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 | /** * 员工Mapper接口 */public interface EmployeeMapper { //查询所有数据 List<Employee> selectAll(); //根据员工id查询数据 Employee selectEmpByEmpId(@Param("id") Integer empId);} |
EmployeeMapper.xml:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.thr.mapper.EmployeeMapper"> <resultMap id="employeeMap" type="com.thr.pojo.Employee"> <id property="empId" column="employee_id"/> <result property="empName" column="employee_name"/> <result property="empAge" column="employee_age"/> <result property="empSex" column="employee_sex"/> <result property="empEmail" column="employee_email"/> <result property="empAddress" column="employee_address"/> <!-- 一对一关联对象 --> <association property="department" javaType="department"> <id property="deptId" column="department_id"/> <result property="deptName" column="department_name"/> </association> </resultMap> <!-- 查询所有数据--> <select id="selectAll" resultMap="employeeMap"> SELECT * FROM t_employee e, t_department d where e.department_id=d.department_id </select> <!--根据员工id查询数据--> <select id="selectEmpByEmpId" parameterType="int" resultMap="employeeMap"> SELECT * FROM t_employee e, t_department d where e.department_id=d.department_id and e.employee_id= #{id} </select></mapper> |
③、创建数据库连接文件和日志文件
db.properties文件:
01 02 03 04 05 | #数据库连接配置database.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverdatabase.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8database.username=rootdatabase.password=root |
log4j.properties文件:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 | log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, Console#Consolelog4j.appender.Console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppenderlog4j.appender.Console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayoutlog4j.appender.Console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d [%t] %-5p [%c] - %m%nlog4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=INFOlog4j.logger.org.apache=INFOlog4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUGlog4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUGlog4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG |
④、注册 EmployeeMapper.xml 文件
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration> <!--引入properties文件--> <properties resource="db.properties"/> <!--配置别名--> <typeAliases> <!-- 对包进行扫描,可以批量进行别名设置,设置规则是:获取类名称,将其第一个字母变为小写 --> <package name="com.thr.pojo"/> </typeAliases> <!-- 配置环境.--> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${database.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${database.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${database.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${database.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--注册mapper,通过扫描的方式--> <mappers> <package name="com.thr.mapper"/> </mappers></configuration> |
⑤、编写测试代码
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 | package com.thr.test;import com.thr.mapper.EmployeeMapper;import com.thr.pojo.Employee;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import org.junit.After;import org.junit.Before;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.util.List;/** * 测试代码 */public class MybatisTest { //定义 SqlSession private SqlSession sqlSession = null; //定义 EmployeeMapper对象 private EmployeeMapper mapper = null; @Before//在测试方法执行之前执行 public void getSqlSession(){ //1、加载 mybatis 全局配置文件 InputStream is = MybatisTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); //2、创建SqlSessionFactory对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //3、根据 sqlSessionFactory 产生 session sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //4、创建Mapper接口的的代理对象,getMapper方法底层会通过动态代理生成UserMapper的代理实现类 mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); } @After//在测试方法执行完成之后执行 public void destroy() throws IOException { sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } //查询所有数据 @Test public void testSelectAll(){ List<Employee> employees = mapper.selectAll(); for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee); } } //根据员工id查询数据 @Test public void testSelectEmpByEmpId(){ Employee employee = mapper.selectEmpByEmpId(1); System.out.println(employee); }} |
⑥、运行结果
项目整体目录:
查询所有数据:

根据员工id查询数据:

4、分步查询
分步查询的这种方式是通过association标签中的select属性来完成,它需要执行另外一个 SQL 映射语句来返回预期的复杂类型,并且会从 column 属性指定的列中检索数据,作为参数传递给目标 select 语句。所以我们必须在关联的另一个Mapper接口中创建一个根据 id 查询数据的方法,并且表字段和实体属性如果不同还要进行映射。
①、更改EmployeeMapper.xml 文件,其它之前的文件都不变
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.thr.mapper.EmployeeMapper"> <resultMap id="employeeMap" type="com.thr.pojo.Employee"> <id property="empId" column="employee_id"/> <result property="empName" column="employee_name"/> <result property="empAge" column="employee_age"/> <result property="empSex" column="employee_sex"/> <result property="empEmail" column="employee_email"/> <result property="empAddress" column="employee_address"/> <!-- 一对一关联对象,注意:select方式需要加column属性,column属性会从当前查询出的指定列检索数据, 这里为t_employee表中的department_id,然后作为参数传递给目标的select语句--> <association property="department" column="department_id" javaType="department" select="com.thr.mapper.DepartmentMapper.selectDeptByDeptId"/> </resultMap> <!-- 查询所有数据--> <select id="selectAll" resultMap="employeeMap"> SELECT * FROM t_employee </select> <!--根据员工id查询数据--> <select id="selectEmpByEmpId" parameterType="int" resultMap="employeeMap"> SELECT * FROM t_employee where employee_id= #{id} </select></mapper> |
②、创建DepartmentMapper和DepartmentMapper.xml文件
DepartmentMapper接口:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 | /** * 部门Mapper接口 */public interface DepartmentMapper { //根据部门id查询数据 Department selectDeptByDeptId(@Param("id") Integer deptId);} |
DepartmentMapper.xml文件:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.thr.mapper.DepartmentMapper"> <resultMap id="departmentMap" type="com.thr.pojo.Department"> <id property="deptId" column="department_id"/> <result property="deptName" column="department_name"/> </resultMap> <!--根据部门id查询--> <select id="selectDeptByDeptId" parameterType="int" resultMap="departmentMap"> select * from t_department where department_id = #{id} </select></mapper> |
③、运行结果
查询所有数据:

根据员工id查询数据:

可以发现使用这种方式明显多执行了很多SQL语句,所以肯定会导致查询的效率变低,但是这种方式也有好处,那就是可以延迟加载。


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
2019-11-16 IDEA中常用优化设置