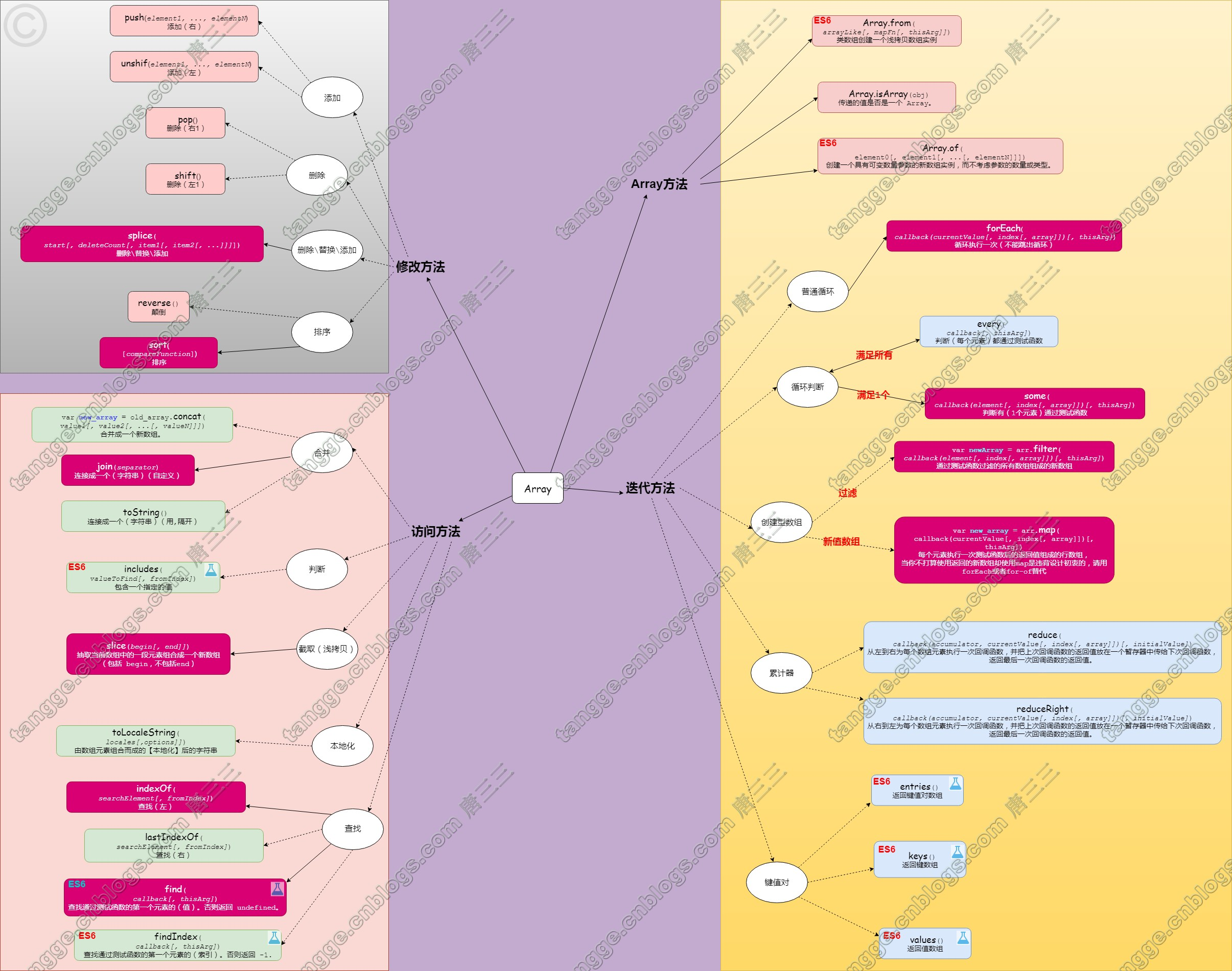
//1.Aarry方法
// 1.1 Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
// @arrayLike 想要转换成数组的伪数组对象或可迭代对象。
// @mapFn 如果指定了该参数,新数组中的每个元素会执行该回调函数。
// @thisArg 可选参数,执行回调函数 mapFn 时 this 对象。
// 浅拷贝:从一个类似数组或可迭代对象创建一个新的,浅拷贝的数组实例。
console.log(Array.from('foo'));
// expected output: Array ["f", "o", "o"]
console.log(Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x));
// expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]
// Array.isArray(obj)
// 于确定传递的值是否是一个 Array
// Array.of(element0[, element1[, ...[, elementN]]])
// 创建一个具有可变数量参数的新数组实例,而不考虑参数的数量或类型。
Array.of(7); // [7] Array.of(7) 创建一个具有单个元素 7 的数组
Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
Array(7); // [ , , , , , , ]
Array(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
// 2.常用方法(修改)
// 2.1 添加
{
// 2.1.1 添加(右)
// push(element1, ..., elementN)
// 2.1.2 添加(左)
// unshift(element1, ..., elementN)
}
// 2.2 删除
{
// 2.2.1 删除(右1):删除最后一个元素,并返回该元素的值。(此方法更改数组的长度)
// pop()
// 2.2.2 删除(左1):第一个元素
// shift()
}
// 2.3 删除\替换\添加
// splice(start[, deleteCount[, item1[, item2[, ...]]]])
// @start 指定修改的开始位置(从0计数)。如果超出了数组的长度,则从数组末尾开始添加内容.
// @deleteCount 整数,表示要移除的数组元素的个数。
// @item1, item2, ... 添加进数组的元素,从start 位置开始。如果不指定,则 splice() 将只删除数组元素
// @return 由被删除的元素组成的一个数组。如果只删除了一个元素,则返回只包含一个元素的数组。如果没有删除元素,则返回空数组
// 实例1:添加,从第 2 位开始删除 0 个元素,插入“drum”
var myFish = ["1ab", "2cd", "3ef", "4gh"];
var removed = myFish.splice(2, 0, "5ij");
// 运算后的 myFish: ["1ab", "2cd", "5ij", "3ef", "4gh"]
// 被删除的元素 removed: [], 没有元素被删除
console.log(myFish);
console.log(removed);
// 实例2:替换,从第 2 位开始删除 1 个元素,插入“trumpet”
var myFish = ["1ab", "2cd", "3ef", "4gh"];
var removed = myFish.splice(2, 1, "5ij");
console.log(myFish);
console.log(removed);
// 运算后的 myFish: ["1ab", "2cd", "5ij", "4gh"]
// 被删除的元素 removed: ["3ef"], 没有元素被删除
// 2.4.排序
{
// 2.4.1 颠倒
// reverse()
// 2.4.2 排序
// sort([compareFunction])
// @compareFunction 一个比较函数
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort
// 比较数字
var numbers = [4, 2, 5, 1, 3];
numbers.sort(function (a, b) {
return a - b;
});
// 可以写成 numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(numbers); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
// 3.常用方法(访问)
// 3.1 合并
{
// 3.1.1 合并成(数组)
// var new_array = old_array.concat(value1[, value2[, ...[, valueN]]])
// 3.1.2 连接成一个(字符串)(自定义)
// join([separator])
var elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water'];
console.log(elements.join()); //"Fire,Air,Water"
console.log(elements.join('')); //"FireAirWater"
console.log(elements.join('-')); //"Fire-Air-Water"
// 3.1.3 连接成一个(字符串)(用,隔开)
// toString()
}
// 3.2 判断
{
// 3.2.1 包含一个指定的值
// includes(valueToFind[, fromIndex])
var array1 = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(array1.includes(2)); //true
}
// 3.3 截取当前数组中的一段元素组合成一个新数组(浅拷贝)
// slice([begin[, end]])
// 由 begin 和 end 决定的原数组的浅拷贝(包括 begin,不包括end)
var animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];
console.log(animals.slice(2)); // Array ["camel", "duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(2, 4)); // Array ["camel", "duck"]
console.log(animals.slice(1, 5)); // Array ["bison", "camel", "duck", "elephant"]
// 3.4 由数组元素组合而成的【本地化】后的字符串
// toLocaleString([locales[,options]])
// @locales 带有BCP 47语言标记的字符串或字符串数组,关于locales参数的形式与解释,请看Intl页面。
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Intl
// @options 一个可配置属性的对象,对于数字 Number.prototype.toLocaleString(),对于日期 Date.prototype.toLocaleString().
var array1 = [1, 'a', new Date('21 Dec 1997 14:12:00 UTC')];
var localeString = array1.toLocaleString('en', { timeZone: "UTC" });
console.log(localeString);
// expected output: "1,a,12/21/1997, 2:12:00 PM",
// This assumes "en" locale and UTC timezone - your results may vary
// 3.5 查找
{
// 3.5.1 查找(左)
// indexOf(searchElement[, fromIndex])
var array = ["1ab", "2cd", "3ef", "4gh"];
var idx1 = array.indexOf('3ef'); //2
var idx2 = array.indexOf('ab'); //-1
// 3.5.2 查找(右)
// lastIndexOf(searchElement[, fromIndex])
var animals = ['Dodo', 'Tiger', 'Penguin', 'Dodo'];
console.log(animals.lastIndexOf('Dodo')); //3
console.log(animals.lastIndexOf('Tiger')); //1
// 3.5.3 查找通过测试函数的第一个元素的(值)。否则返回 undefined。
// find(callback[, thisArg])
var array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
var found = array1.find(function (element) {
return element > 10;
});
console.log(found); // 12
// 3.5.4 查找通过测试函数的第一个元素的(索引)。否则返回 -1.
// findIndex(callback[, thisArg])
var found2 = array1.findIndex(function (element) {
return element > 10;
});
console.log(found2); // 1
}
// 4.常用方法(迭代)
// 4.1 普通循环
// 4.1.1 循环执行一次(不能跳出循环)
// forEach(callback(currentValue[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]);
// @callback(currentValue[, index[, array]]) 为数组中每个元素执行的函数,该函数接收三个参数:
// @currentValue 数组中正在处理的当前元素。
// @index(可选) 数组中正在处理的当前元素的索引。
// @array(可选) forEach() 方法正在操作的数组。
// @thisArg 可选参数。当执行回调函数时用作 this 的值(参考对象) 。
function logArrayElements(element, index, array) {
console.log('a[' + index + '] = ' + element);
}
// 注意索引 2 被跳过了,因为在数组的这个位置没有项
[2, 5, , 9].forEach(logArrayElements);
// logs:
// a[0] = 2
// a[1] = 5
// a[3] = 9
// 4.2 循环判断
{
// 4.2.1 判断(每个元素)都通过测试函数
// every(callback[, thisArg])
function isBelowThreshold(currentValue) {
return currentValue < 40;
}
var array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(array1.every(isBelowThreshold)); //true
// 4.2.2 判断有(1个元素)通过测试函数
// some(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg])
// 例1:是否有能除尽2的值
var array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var even = function (element) {
// checks whether an element is even
return element % 2 === 0;
};
console.log(array.some(even)); //true
console.log("---------");
// 例2:判断数组元素中是否存在某个值
var serr = ["EN-US", "zh-cn", "fr-fr"];
var bool = serr.some(function name(element) {
return element.toLowerCase() === "en-us";
})
console.log(bool); //true
}
// 4.3 创建新数组
{
// 4.3.1 通过测试函数过滤的所有数组组成的新数组
// var newArray = arr.filter(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg])
var words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result);
// expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
// 4.3.2 每个元素执行一次测试函数后的返回值组成的行数组,
// 当你不打算使用返回的新数组却使用map是违背设计初衷的,请用forEach或者for-of替代
// var new_array = arr.map(function callback(currentValue[, index[, array]])[, thisArg])
var array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
const map1 = array1.map(x => x * 2);
console.log(map1);
// expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
}
// 4.4 累计器
{
// 4.4.1 从左到右为每个数组元素执行一次回调函数,并把上次回调函数的返回值放在一个暂存器中传给下次回调函数,
// 并返回最后一次回调函数的返回值。
// reduce(callback(accumulator, currentValue[, index[, array]])[, initialValue])
// @callback 执行数组中每个值 (如果没有提供 initialValue则第一个值除外)的函数,包含四个参数:
// @accumulator 累计器累计回调的返回值; 它是上一次调用回调时返回的累积值,或initialValue(见于下方)。
// @currentValue 数组中正在处理的元素。
// @index (可选) 数组中正在处理的当前元素的索引。 如果提供了initialValue,则起始索引号为0,否则从索引1起始。
// @array (可选) 调用reduce()的数组
// @initialValue (可选) 作为第一次调用 callback函数时的第一个参数的值。 如果没有提供初始值,则将使用数组中的第一个元素。
// 在没有初始值的空数组上调用 reduce 将报错。
// @return 函数累计处理的结果
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const reducer = function (accumulator, currentValue) {
return accumulator + currentValue;
}
// 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer));
// 5 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer, 5));
// 4.4.2 从右到左为每个数组元素执行一次回调函数,并把上次回调函数的返回值放在一个暂存器中传给下次回调函数,
// 并返回最后一次回调函数的返回值。
// reduceRight(callback(accumulator, currentValue[, index[, array]])[, initialValue])
}
// *(实验性API) 4.5 键值对
{
// 4.5.1 entries()
// 返回键值对数组
var array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
var iterator1 = array1.entries();
console.log(iterator1.next().value);
// expected output: Array [0, "a"]
console.log(iterator1.next().value);
// expected output: Array [1, "b"]
// 4.5.2 keys()
// 返回键数组
// 4.5.3 values()
//返回值数组
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号