java基础-Map
简介
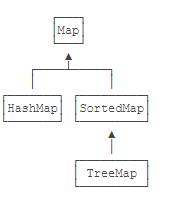
Map是一种接口,实现类有 hashMap
SortedMap是继承自Map的接口,实现类为TreeMap,在内部会对Key进行排序
遍历Map
-
使用
for each循环遍历Map实例的keySet()方法返回的Set集合,它包含不重复的key的集合:import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("apple", 123); map.put("pear", 456); map.put("banana", 789); for (String key : map.keySet()) { Integer value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key + " = " + value); } } } -
同时遍历
key和value可以使用for each循环遍历Map对象的entrySet()集合,它包含每一个key-value映射:import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("apple", 123); map.put("pear", 456); map.put("banana", 789); for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { String key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + " = " + value); } } }
遍历Map时,不可假设输出的key是有序的!
TreeMap
TreeMap不使用equals()和hashCode(),不用对这两个方法进行覆写
TreeMap的key要求
使用TreeMap时,放入的Key必须实现Comparable接口。
String、Integer这些类已经实现了Comparable接口,因此可以直接作为Key使用。作为Value的对象则没有任何要求。
如果作为Key的class没有实现Comparable接口,那么,必须在创建TreeMap时同时指定一个自定义排序算法:
TreeMap在比较两个Key是否相等时,依赖Key的
-
compareTo()方法(key这个类需要实现Comparable接口,覆写compareTo方法)参考 或者 -
Comparator.compare()方法。
将自定义的class作为key
例1:创建的时候传入 Comparator.compare()方法:
注意到Comparator接口要求实现一个比较方法,它负责比较传入的两个元素a和b,
-
如果a<b,则返回负数,通常是-1,
-
如果a==b,则返回0,
-
如果a>b,则返回正数,通常是1。
TreeMap内部根据比较结果对Key进行排序。
例3:在key这个类里面实现Comparable接口,覆写compareTo方法
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(new Student("Tom", 77), 1);
map.put(new Student("Bob", 66), 2);
map.put(new Student("Lily", 99), 3);
for (Student key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
System.out.println(map.get(new Student("Bob", 66))); // null?
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
public String name;
public int score;
Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
Student p = (Student) o;
if (this.score == p.score) {
return 0;
}
return this.score < p.score ? -1 : 1;
}
public String toString() {
return String.format("{%s: score=%d}", name, score);
}
}
小结
SortedMap在遍历时严格按照Key的顺序遍历,最常用的实现类是TreeMap;- 作为
SortedMap的Key必须实现Comparable接口,或者传入Comparator; - 要严格按照
compare()规范实现比较逻辑,否则,TreeMap将不能正常工作。


