JS数据结构第四篇 --- 栈和队列
一、什么是数据结构栈
在数据结构中有一个栈结构,在内存空间中也有一个栈空间,这两个”栈“是两个不同的概念。这篇我们说的是数据结构中的栈。栈是一种特殊的线性表,特殊性体现在只能在栈顶进行操作,往栈顶添加元素,一般叫push, 入栈;从栈顶移除元素,一般叫pop, 出栈,操作如图:

这个特征叫”后进先出“,Last In First On, 简称LIFO。和JS数组中的push和pop函数功能有点像。当然栈的内部设计,就可以用数组,或者也可以用链表。
二、栈结构设计和应用示例
2.1 内部实现:
栈结构对外暴露的方法有入栈(push)、出栈(pop)、获取栈顶元素(top)、获取栈长度(length)、清空栈内元素。如图:

这里贴出内部用数组实现的栈设计构造函数,链表实现见Github

/** * 数据结构栈:先进后出,后进先出,即LIFO,栈的内部实现可以用数组,也可以用链表; * 这里先用数组实现,对外暴露的方法有: * push(element): 放入一个元素,即入栈 * pop() : 移除栈顶元素,即出栈 * top() : 获取栈顶元素 * clear() : 移除所有栈元素 * length() : 获取栈长度 */ const Stack = function(){ let arr = []; //内部数组 //入栈方法 function push(element){ arr.push(element); } //出栈方法 function pop(){ return arr.pop(); } //获取栈顶元素 function top(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[arr.length-1]:null; } //移除所有栈元素 function clear(){ arr = []; } //获取栈长度 function length(){ return arr.length; } this.push = push; this.pop = pop; this.top = top; this.clear = clear; this.length = length; }
2.2 在这个栈构造函数的基础上,做几题目应用实践一下
2.2.1 用栈实现将十进制数字转成二进制,和八进制

/** * 十进制转成二进制或八进制 * @param num 十进制数字 * @param base =2表示转成二进制,=8表示转成八进制 */ function numChange(num, base){ var stack = new Stack(); do { stack.push(num%base); num = Math.floor(num/base); }while(num > 0) let str = ''; while(stack.length()>0){ str += stack.pop(); } return str; } console.log(numChange(8, 2)); console.log(numChange(9, 2)); console.log(numChange(10, 2)); console.log(numChange(8, 8)); console.log(numChange(17, 8)); console.log(numChange(35, 8));

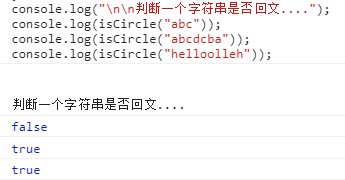
2.2.2 用栈来判断一个字符串是否回文。比如"abc"不是回文,"abcba"是回文,"abccba"是回文

//测试3,判断一个字符串是否回文 function isCircle(s){ let stack = new Stack(); for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++){ stack.push(s[i]); } let newStr = ''; while(stack.length() > 0){ newStr += stack.pop(); } return newStr == s; } console.log("\n\n判断一个字符串是否回文...."); console.log(isCircle("abc")); console.log(isCircle("abcdcba")); console.log(isCircle("helloolleh"));
三、力扣栈结构应用题目
3.1 有效的括号_第20题
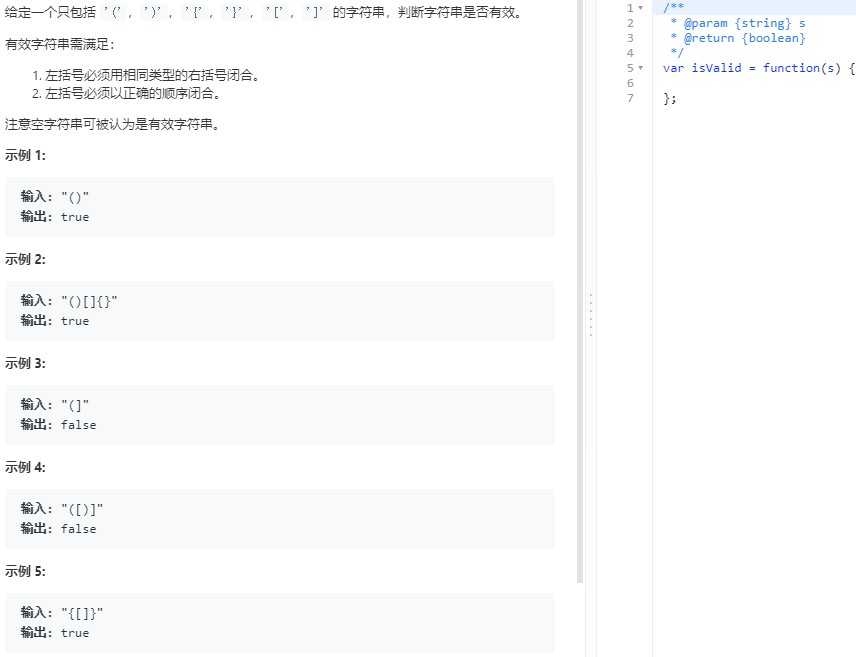

/** * @param {string} s * @return {boolean} */ var isValid = function(s) { /** * 执行用时 :68 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了98.63%的用户 * 内存消耗 :33.7 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了76.56%的用户 */ let arr = [], temp = top = null; for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++){ temp = s[i]; //碰到左括号,入栈 if (temp == '(' || temp == '[' || temp == '{'){ arr.push(temp); } //碰到右括号,出栈 else{ if (arr.length < 1) return false; top = arr[arr.length-1]; if ((temp == ')' && top == '(')|| (temp == ']' && top == '[')|| (temp == '}' && top == '{')){ arr.pop(); } else{ return false; } } } return arr.length > 0 ? false : true; };
3.2 根据括号计算分数_第856题


/** * @param {string} S * @return {number} * 执行用时 :80 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了62.96%的用户 * 内存消耗 :33.7 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了33.33%的用户 */ var scoreOfParentheses = function(S) { let arr = [], temp = null; for (let i = 0; i < S.length; i++){ temp = S[i]; if (temp == '('){ arr.push(temp); } else{ if (arr.length < 1) return 0; //调整栈,找到数组里面配套的左括号,如果目标左括号在栈顶,调整"("为1; // 如果目标左括号不在栈顶,则从栈顶到目标左括号累加,每累加一次,出栈一次; // 一直到目标左括号成为栈顶,这事根据规则(A)=2*A,则目标左括号位置的值为2*累加分 // 比如:()()((()(()())())()()) // [1,1,(,(,1,4,1 findTarget(arr); } } return findTarget(arr); }; //寻找匹配左括号, 倒序找到第一个匹配的"(",然后调整目标位置的值 function findTarget(arr){ let score = 0; for (let i = arr.length-1; i >= 0; i--){ if (arr[i] == '('){ arr[i] = score > 0 ? 2*score : 1; return 0; } else{ score += arr.pop(); } } return score; }
3.3 逆波兰式求值_第150题
我们普通的运算式叫中缀表达式,后缀表达式是把运算符号写在数字后面,前缀表达式是把运算符号写在数字前面。比如
中缀表达式:a+b, 用后缀表达式为:ab+, 用前缀表达式为:+ab ;
中缀表达式:(a + b) * c - d/e, 用后缀表达式为:ab+c*de/-, 前缀表达式为:-*+abc/de
中缀表达式方便人类识别,后缀表达式是为了方便计算机识别,后缀表达式也叫逆波兰式;前缀表达式也叫波兰式
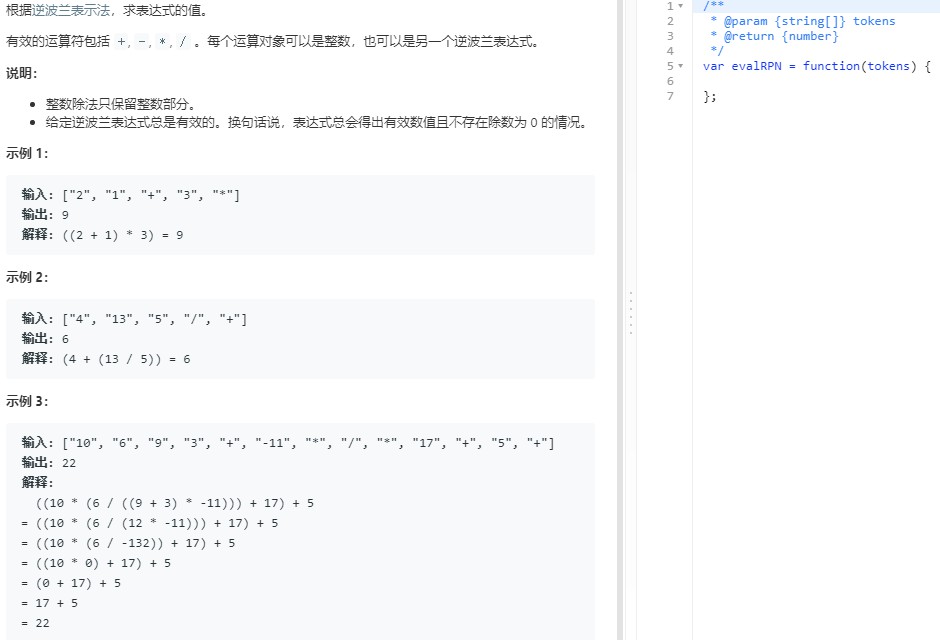

/** * @param {string[]} tokens * @return {number} * 执行用时 :92 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了91.72%的用户 * 内存消耗 :37.2 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了40.48%的用户 */ var evalRPN = function(tokens) { //用栈来实现,碰到数字入栈,碰到运算符号,出栈计算 let arr = [], str = null; for (let i =0; i < tokens.length; i++){ str = tokens[i]; if (str == "+" || str == "-" || str == "*" || str == "/"){ let num2 = parseInt(arr.pop()), num1 = parseInt(arr.pop()), res = 0; if (str == "+"){ res = num1 + num2; } else if(str == "-"){ res = num1 - num2; } else if(str == "*"){ res = num1 * num2; } else if(str == "/"){ res = parseInt(num1 / num2); } arr.push(res); } else{ arr.push(str); } } return arr.length ? arr.pop() : 0; };
3.4 基本计算器_第224题(困难)
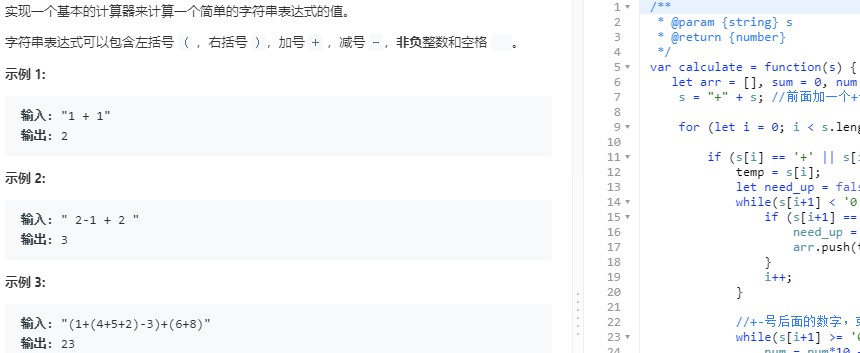

/** * 按顺序计算,存储左括号前面的运算符,碰到“-”号,后面匹配的数字为相反数。相当于去括号计算 * @param s * @return {number} * 执行用时 :112 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了88.14%的用户 * 内存消耗 :36.8 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了94.12%的用户 */ var calculate = function(s){ let arr = [], sum = 0, num = 0, flag = 1; s = "+" + s; //前面加一个+号 for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++){ if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-'){ //+-后面可能为数字/空格/左括号 temp = s[i]; let need_up = false; while(s[i+1] < '0' || s[i+1] > '9'){ if (s[i+1] == '('){ //将左括号前面的符号压入栈。一个左括号匹配一个+-号 need_up = true; arr.push(temp); } i++; } //+-号后面的数字,或者+-号后面口号里面的数字 while(s[i+1] >= '0' && s[i+1] <= '9'){ num = num*10 + (s[i+1] - '0'); //拼接完整数字 i++; } if (temp == '+'){ sum += flag * num; } else{ sum -= flag * num; } num = 0; if (need_up && arr[arr.length-1] == '-'){ flag *= (-1); //如果左括号前是-号,flag需要反转 } } else if(s[i] == ')'){ if (arr[arr.length-1] == '-'){ flag *= (-1); //移除-号时,flag需要反转 } arr.pop(); //碰到右括号移除一个运算符 } } return sum; }
栈链表实现和题目完整Demo见:https://github.com/xiaotanit/Tan_DataStruct
四、数据结构队列
队列和栈差不多,一个特殊的线性表,只是队列只能在头尾两端进行操作,先进先出,FIFO(First In First Out):
队尾(rear):只能从队尾进行添加数据,一般叫enQueue, 入队;
队头(front):只能从队头进行删除数据,一般叫deQueue, 出队;

队列结构实现,内部可以用数组、链表、栈来实现,对外暴露:


/** * 队列:从队尾添加元素,从队头移除元素,就像排队一样,先入先出,FIFO(Fast In Fast Out) * 内部可以用数组/链表/栈实现 * 对外暴露方法有: * enQueue(element) 入队,从队尾添加元素 * deQueue() 出队,从队头移除元素 * front() 获取对头元素 * length() 获取队列长度 * clear() 清空队列 */ //这里内部先用数组实现 const Queue = function(){ let arr = []; //入队 function enQueue(element){ arr.push(element); } //出队, 从队头移除元素 function deQueue(){ return arr.shift(); } //获取队头元素 function front(){ return arr.length ? arr[0] : null; } //清空队列 function clear(){ return arr = []; } function length(){ return arr.length; } this.enQueue = enQueue; this.deQueue = deQueue; this.front = front; this.length = length; this.clear = clear; }
五、双端队列
双端队列是指能在队列的头尾两端进行添加、删除的操作。


/** * 双端队列,特点:可以从队尾插入数据,也能从队尾移除元素;可以从队头插入元素,也能从队头移除元素 * 内部用数组来实现,时间复杂度O(1) , 双端循环队列 * enQueueRear(element) 入队,从队尾添加元素 * enQueueFront(element) 入队,从对头添加元素 * deQueueFront() 出队,从队头移除元素 * deQueueRear() 出队,从队尾移除车元素 * front() 获取队头元素 * rear() 获取队尾元素 * length() 获取队列长度 * clear() 清空队列 */ const Queue_Circle = function(){ let arr = []; //从队尾入队方法 function enQueueRear(element){ arr.push(element); } //从对头入队方法 function enQueueFront(element){ arr.unshift(element); } //从队头出队方法 function deQueueFront(){ return arr.shift() } //从队尾出队方法 function deQueueRear(){ return arr.pop(); } //获取队头元素 function front(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[0] : null; } //获取队尾元素 function rear(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[arr.length-1]: null; } //移除栈所有元素 function clear(){ arr = []; } //获取栈长度 function length(){ return arr.length; } this.enQueueFront = enQueueFront; this.enQueueRear = enQueueRear; this.deQueueFront = deQueueFront; this.deQueueRear = deQueueRear; this.front = front; this.rear = rear; this.length = length; this.clear = clear; }
六、力扣队列题
6.1 用栈来实现队列_第232题

/** * Initialize your data structure here. */ var MyQueue = function() { this.stack = new Stack(); //内部栈对象 this.head = null; //存储队列队头元素 }; /** * Push element x to the back of queue. * @param {number} x * @return {void} */ MyQueue.prototype.push = function(x) { if (this.stack.empty()){ this.head = x; } this.stack.push(x); }; /** * Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. * @return {number} */ MyQueue.prototype.pop = function() { //队头出队 var temp = new Stack(); //新建一个栈, 栈逆序存储 while(!this.stack.empty()){ temp.push(this.stack.pop()) } var ele = temp.pop(); //要移除的队头 this.head = null; //移除后,重新入队 while(!temp.empty()){ if (this.stack.empty()){ this.head = temp.top(); } this.stack.push(temp.pop()); } return ele; }; /** * Get the front element. * @return {number} */ MyQueue.prototype.peek = function() { return this.head; }; /** * Returns whether the queue is empty. * @return {boolean} */ MyQueue.prototype.empty = function() { return this.stack.empty(); }; //自定义栈, 内部用数组实现 var Stack = function(){ var arr = []; //入栈 this.push = function(element){ arr.push(element) } //出栈 this.pop = function(){ return arr.pop(); } //栈顶 this.top = function(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[arr.length-1]:null; } //栈是否为空 this.empty = function(){ return arr.length == 0; } } /** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new MyQueue() * obj.push(x) * var param_2 = obj.pop() * var param_3 = obj.peek() * var param_4 = obj.empty() */
6.2 用队列来实现栈_第225题

/** * 使用队列实现栈的下列操作: push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈 pop() -- 移除栈顶元素 top() -- 获取栈顶元素 empty() -- 返回栈是否为空 注意: 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。 */ /** * Initialize your data structure here. * 执行用时 :76 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了87.56%的用户 * 内存消耗 :33.7 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了41.86%的用户 */ var MyStack = function() { this.queue = new MyQueue(); }; /** * Push element x onto stack. * @param {number} x * @return {void} */ MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) { this.queue.enQueueRear(x); //入栈 }; /** * Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. * @return {number} */ MyStack.prototype.pop = function() { return this.queue.deQueueRear(); //出栈 }; /** * Get the top element. * @return {number} */ MyStack.prototype.top = function() { return this.queue.rear(); //获取栈顶元素 }; /** * Returns whether the stack is empty. * @return {boolean} */ MyStack.prototype.empty = function() { return this.queue.empty(); }; //自定义双端队列 var MyQueue = function(){ let arr = []; //从队尾入队方法 function enQueueRear(element){ arr.push(element); } //从对头入队方法 function enQueueFront(element){ arr.unshift(element); } //从队头出队方法 function deQueueFront(){ return arr.shift() } //从队尾出队方法 function deQueueRear(){ return arr.pop(); } //获取队头元素 function front(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[0] : null; } //获取队尾元素 function rear(){ return arr.length > 0 ? arr[arr.length-1]: null; } //队列是否为空 function empty(){ return arr.length == 0; } this.enQueueFront = enQueueFront; //从队列头部入队 this.enQueueRear = enQueueRear; //从队列尾部入队 this.deQueueFront = deQueueFront; //从队列头部出队 this.deQueueRear = deQueueRear; //从队列尾部出队 this.front = front; //获取队列头部 this.rear = rear; //获取队列尾部 this.empty = empty; } /** * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new MyStack() * obj.push(x) * var param_2 = obj.pop() * var param_3 = obj.top() * var param_4 = obj.empty() */





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?