2 Typical Methods of bridging IT Network and Control Network
While implementing MES projects, I always spent lots of time discussing how to bridge IT Network and Control Network.
Practically, Network team will isolated Control Network from IT Network, such as using VLAN to separate them.
MES works in IT Network, and PLC works in Control Network, and they need to exchange data, so we need to bridge these 2 networks.
Here I list out 2 typical methods based on my practice.
Method 1: Using Communication Panel
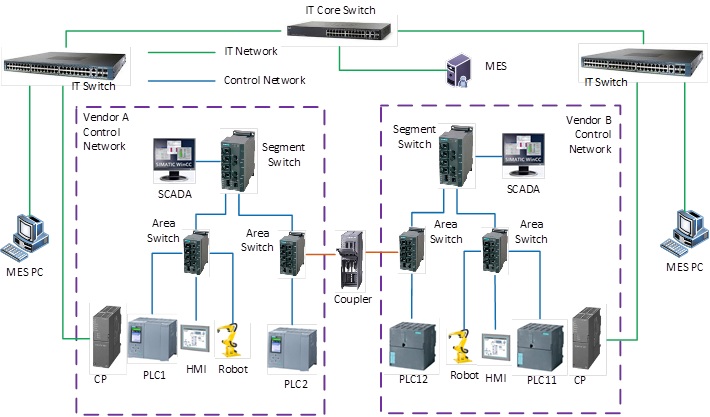
From above diagram, we can see that each PLC works inside Vendor’s private Control Network via CPU port.
The additional CP(Communication Panel) provides an IP address working inside IT Network.
With this method, we add CP for each PLC which needs to talk to IT applications.
Actually some advanced PLC(such as Siemens 317/319/1516/1518) has 2+ PN/IE ports, which means we can use 1 port for Control Network and 1 port for IT Network.
But in practice, we might still use Communication Panels, because CP provides better PLC functions and better communication capacity.
Method 2: NAT
NAT = Network Address Translation

From above diagram, we can see that an NAT Router is added between Control Network Switch and IT Core Switch, so each device’s IP address which matches Route Table will be translated into IT IP address.
Normally route table is defined for a range of IP address, so not only PLC, but also HMI and Robot and other devices will be translated into IT Network.
Comparison:
|
Method |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
CP |
Data secure Network isolated |
More hardware investment More Cabling work |
|
NAT |
Cheap Less cabling work |
Less data secure Network crossed |



