SAML-based SSO Flow
概念
SAML: Security Assertion Markup Language
SSO: single sign-on
SP: Service Provider
IdP: Identity provider
UA:User Agent (Browser)
SP-Initiated SSO Flow
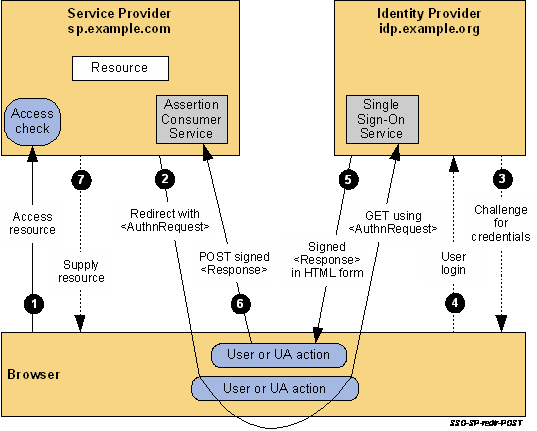
The processing is as follows:
1
The user attempts to access a resource on sp.example.com. The user does not have a valid logon session (i.e. security context) on this site. The SP saves the requested resource URL in local state information that can be saved across the web SSO exchange.
2
The SP sends an HTTP redirect response to the browser (HTTP status 302 or 303). The Location HTTP header contains the destination URI of the Sign-On Service at the identity provider together with an
<samlp:AuthnRequestxmlns:samlp="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion"ID="identifier_1"Version="2.0"IssueInstant="2004-12-05T09:21:59Z"AssertionConsumerServiceIndex="1"> <saml:Issuer>https://sp.example.com/SAML2</saml:Issuer> <samlp:NameIDPolicyAllowCreate="true"Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient"/> </samlp:AuthnRequest>
The query string is encoded using the DEFLATE encoding. The browser processes the redirect response and issues an HTTP GET request to the IdP's Single Sign-On Service with the SAMLRequest query parameter. The local state information (or a reference to it) is also included in the HTTP response encoded in a RelayState query string parameter.
https://idp.example.org/SAML2/SSO/Redirect?SAMLRequest=request&RelayState=token
3
The Single Sign-On Service determines whether the user has an existing logon security context at the identity provider that meets the default or requested (in the
4
The user provides valid credentials and a local logon security context is created for the user at the IdP.
5
The IdP Single Sign-On Service builds a SAML assertion representing the user's logon security context. Since a POST binding is going to be used, the assertion is digitally signed and then placed within a SAML
<form method="post" action="https://sp.example.com/SAML2/SSO/POST" ...> <input type="hidden" name="SAMLResponse" value="response" /> <input type="hidden" name="RelayState" value="token" /> ... <input type="submit" value="Submit" /> </form>
The value of the SAMLResponse parameter is the base64 encoding of the following samlp:Response element:
<samlp:Responsexmlns:samlp="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion"ID="identifier_2"InResponseTo="identifier_1"Version="2.0"IssueInstant="2004-12-05T09:22:05Z"Destination="https://sp.example.com/SAML2/SSO/POST"> <saml:Issuer>https://idp.example.org/SAML2</saml:Issuer> <samlp:Status> <samlp:StatusCodeValue="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:Success"/> </samlp:Status> <saml:Assertionxmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion"ID="identifier_3"Version="2.0"IssueInstant="2004-12-05T09:22:05Z"> <saml:Issuer>https://idp.example.org/SAML2</saml:Issuer><!-- a POSTed assertion MUST be signed --> <ds:Signaturexmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#">... </ds:Signature> <saml:Subject> <saml:NameIDFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient">3f7b3dcf-1674-4ecd-92c8-1544f346baf8 </saml:NameID> <saml:SubjectConfirmationMethod="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:bearer"> <saml:SubjectConfirmationDataInResponseTo="identifier_1"Recipient="https://sp.example.com/SAML2/SSO/POST"NotOnOrAfter="2004-12-05T09:27:05Z"/> </saml:SubjectConfirmation> </saml:Subject> <saml:ConditionsNotBefore="2004-12-05T09:17:05Z"NotOnOrAfter="2004-12-05T09:27:05Z"> <saml:AudienceRestriction> <saml:Audience>https://sp.example.com/SAML2</saml:Audience> </saml:AudienceRestriction> </saml:Conditions> <saml:AuthnStatementAuthnInstant="2004-12-05T09:22:00Z"SessionIndex="identifier_3"> <saml:AuthnContext> <saml:AuthnContextClassRef>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport</saml:AuthnContextClassRef> </saml:AuthnContext> </saml:AuthnStatement> </saml:Assertion> </samlp:Response>
6
The browser, due either to a user action or execution of an “auto-submit” script, issues an HTTP POST request to send the form to the SP's Assertion Consumer Service.
POST /SAML2/SSO/POST HTTP/1.1 Host: sp.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: nnn SAMLResponse=response&RelayState=token
where the values of the SAMLResponse and RelayState parameters are taken from the HTML form of Step 5.
The service provider's Assertion Consumer Service obtains the
7
An access check is made to establish whether the user has the correct authorization to access the resource. If the access check passes, the resource is then returned to the browser.
Ref
http://docs.oasis-open.org/security/saml/Post2.0/sstc-saml-tech-overview-2.0.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/shuidao/p/3463947.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
2022-09-08 PowerShell中异步方法的使用