HashMap 核心源码分析(一)
你需要知道
HashMap内部使用一个数组来存储数据,数组的元素是一个叫Entry的静态内部类,该类不过也只是implements了定义在Map中的Entry接口。
Entry的属性:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
// key 的 hash 值
int hash;
...
}
HashMap的存储结构图
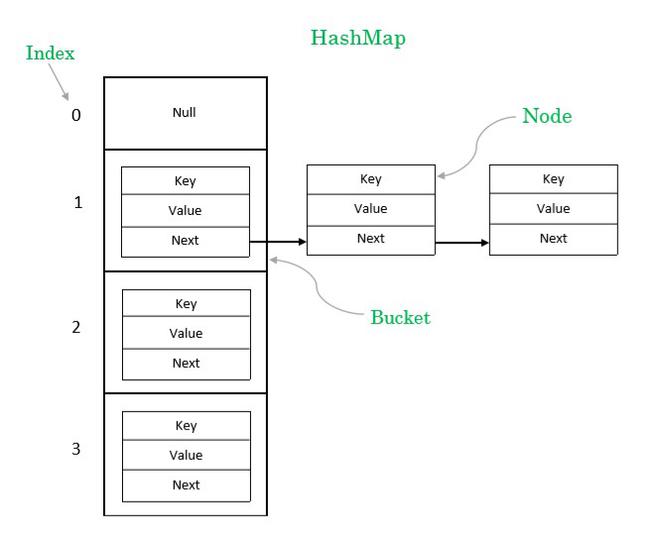
几个问题:
当put的时候内部是怎么知道存放在数组哪个位置?
先计算出 key 的 hash 值,将根据 hash 值和数组的 length 计算出该存放的索引值。从这里也可以看出
HashMap是无序的。
为什么会有链表的存在?
因为 hash 冲突。key 不同,但是根据 key 算出的 hash 可能相同,既然 hash 相同,那么计算出的索引值那就相同,也就是数组的同一个位置需要存放多个值,但是数组一个位置只能存在一个 entry,于是通过 next 属性指向另一个 entry,这样就形成了链表。
put大致逻辑如下:
- 计算 key 的 hash 值
- 根据 hash 和数组 length 计算索引
- 获取数组该索引上的 entry
- 如果 entry == null,则直接在该索引位置处新增 Entry
- 如果 entry != null,则遍历该索引处的链表,看是不是存在过该 key 的 Entry
- 如果存在,则直接把链表上的这个 entry 的 value 替换成新的 value
- 如果不存在,则在数组该索引处新增 entry,这个 entry 的 next 指向原来存在该索引位置上的 entry,也就是新增的 entry 总是存储在数组的该索引处。
属性
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
* 默认的初始容量,必须为2的n次幂
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* 最大容量
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 默认负载因子
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* Entry 数组
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table;
构造方法
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
// hashmap实际的容量大小为小于initialCapacity最大的2的n次幂
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
// 初始化 Entry 数组
table = new Entry[capacity];
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}
put(K key, V value)
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 如果 key == null,单独处理,实际上是放在 table[0] 上
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 计算 key 的 hash 值
int hash = hash(key);
// 根据 hash 和 table.length 计算存放在 table 中的索引值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 获取 table[i] 位置上的 entry
// 1. 如果为 null,则直接在该位置创建 entry,即跳过 for 循环往下继续执行 addEntry();
// 2. 如果该位置已经存在 entry
// 遍历该位置上的 entry 链表
// 1. 链表上已存在相同 key 的 entry,则替换原来 entry 的 value 为传入的 value,并返回原来的 value
// 2. 链表上不存在该 key 的 entry,则继续执行 addEntry();
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 这里判断是否存在该 key 的 entry
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
// 更新 value
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
// 返回旧的 value
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 添加新的 entry
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
// 添加新的 entry 时,返回 null
return null;
}
addEntry()
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// size 达到阈值
// 1. bucketIndex 位置上没有 entry,则新增,最好的情况就是 size == capacity 才扩容
// 2. bucketIndex 位置上存在 entry,则扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 扩容,容量为原来的2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
// 扩容完成,重新计算 hash
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
// 创建 entry
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
createEntry()
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 获取原来数组 bucketIndex 上的 entry
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 在数组 bucketIndex 创建新的 entry,next 指向原来该位置上的 entry,即 e
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
get(K key)
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
// 如果 key == null,则直接在数组 index=0 位置上遍历获取 key == null 的 entry
return getForNullKey();
// 获取 entry
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
getEntry(Object key)
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// 计算 key 的 hash 值
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 根据 hash 获取索引值,获取数组该索引上的 entry
// 如果 entry == null,直接返回 null
// 不为 null,则遍历该索引处的链表,找到就返回,否则返回 null
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号