IdentityServer4.FreeSql 持久化实现
前言
故事是这样开始的:
然后突然又来了句...
扪心自问自从不知道怎么当了 FreeSql 开发群 (QQ群号:4336577) 的管理以来, 几乎没有给 FreeSql 做过什么贡献...惭愧惭愧.
借此机会, 似乎可以做点什么.
整起来
根据官方文档描述, 如要实现自定义存储, 需要实现这3个接口, 它们分别是 IClientStore, IPersistedGrantStore, IResourceStore
新建一个项目 IdentityServer4.FreeSql.
然后新建一个目录 Stores, 用来放置几个接口的实现类.
新建实现类, 它们分别是 ClientStore.cs, PersistedGrantStore.cs, ResourceStore.cs
各自的实现代码如下:
// ClientStore.cs
using FreeSql;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Mappers;
using IdentityServer4.Models;
using IdentityServer4.Stores;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Stores
{
public class ClientStore : IClientStore
{
/// <summary>
/// 数据库上下文
/// </summary>
protected readonly IConfigurationDbContext Context;
/// <summary>
/// 日志
/// </summary>
protected readonly ILogger<ClientStore> Logger;
/// <summary>
/// 初始化一个 <参阅 cref="ClientStore"/> 类的新实例.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context">数据库上下文</param>
/// <param name="logger">日志</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">context</exception>
public ClientStore(IConfigurationDbContext context, ILogger<ClientStore> logger)
{
Context = context ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(paramName: nameof(context));
Logger = logger;
}
/// <summary>
/// 通过客户端标识查找客户端
/// </summary>
/// <param name="clientId">客户端标识</param>
/// <returns>客户端</returns>
public virtual async Task<Client> FindClientByIdAsync(string clientId)
{
ISelect<Entities.Client> baseQuery = Context.Clients
.Where(x => x.ClientId == clientId)
.Take(1);
var client = await baseQuery.ToOneAsync();
if (client == null) return null;
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.AllowedCorsOrigins).IncludeMany(c => c.AllowedCorsOrigins).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.AllowedGrantTypes).IncludeMany(c => c.AllowedGrantTypes).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.AllowedScopes).IncludeMany(c => c.AllowedScopes).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.Claims).IncludeMany(c => c.Claims).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.ClientSecrets).IncludeMany(c => c.ClientSecrets).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.IdentityProviderRestrictions).IncludeMany(c => c.IdentityProviderRestrictions).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.PostLogoutRedirectUris).IncludeMany(c => c.PostLogoutRedirectUris).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.Properties).IncludeMany(c => c.Properties).ToListAsync();
await baseQuery.Include(x => x.RedirectUris).IncludeMany(c => c.RedirectUris).ToListAsync();
var model = client.ToModel();
Logger.LogDebug("{clientId} found in database: {clientIdFound}", clientId, model != null);
return model;
}
}
}
// PersistedGrantStore.cs
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Mappers;
using IdentityServer4.Models;
using IdentityServer4.Stores;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using FreeSql;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Stores
{
/// <summary>
/// Implementation of IPersistedGrantStore thats uses FreeSql.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.Stores.IPersistedGrantStore" />
public class PersistedGrantStore : IPersistedGrantStore
{
/// <summary>
/// The DbContext.
/// </summary>
protected readonly IPersistedGrantDbContext Context;
/// <summary>
/// The logger.
/// </summary>
protected readonly ILogger Logger;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="PersistedGrantStore"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context">The context.</param>
/// <param name="logger">The logger.</param>
public PersistedGrantStore(IPersistedGrantDbContext context, ILogger<PersistedGrantStore> logger)
{
Context = context;
Logger = logger;
}
/// <summary>
/// Stores the asynchronous.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="token">The token.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task StoreAsync(PersistedGrant token)
{
var existing = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x => x.Key == token.Key).ToOneAsync();
if (existing == null)
{
Logger.LogDebug("{persistedGrantKey} not found in database", token.Key);
var persistedGrant = token.ToEntity();
Context.PersistedGrants.Add(persistedGrant);
}
else
{
Logger.LogDebug("{persistedGrantKey} found in database", token.Key);
token.UpdateEntity(existing);
}
try
{
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogWarning("exception updating {persistedGrantKey} persisted grant in database: {error}", token.Key, ex.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the grant.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The key.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<PersistedGrant> GetAsync(string key)
{
var persistedGrant = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x => x.Key == key).ToOneAsync();
var model = persistedGrant?.ToModel();
Logger.LogDebug("{persistedGrantKey} found in database: {persistedGrantKeyFound}", key, model != null);
return model;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets all grants for a given subject id.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="subjectId">The subject identifier.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<IEnumerable<PersistedGrant>> GetAllAsync(string subjectId)
{
var persistedGrants = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x => x.SubjectId == subjectId).ToListAsync();
var model = persistedGrants.Select(x => x.ToModel());
Logger.LogDebug("{persistedGrantCount} persisted grants found for {subjectId}", persistedGrants.Count, subjectId);
return model;
}
/// <summary>
/// Removes the grant by key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The key.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task RemoveAsync(string key)
{
var persistedGrant = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x => x.Key == key).ToOneAsync();
if (persistedGrant != null)
{
Logger.LogDebug("removing {persistedGrantKey} persisted grant from database", key);
Context.PersistedGrants.Remove(persistedGrant);
try
{
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogInformation("exception removing {persistedGrantKey} persisted grant from database: {error}", key, ex.Message);
}
}
else
{
Logger.LogDebug("no {persistedGrantKey} persisted grant found in database", key);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Removes all grants for a given subject id and client id combination.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="subjectId">The subject identifier.</param>
/// <param name="clientId">The client identifier.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task RemoveAllAsync(string subjectId, string clientId)
{
var persistedGrants = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x => x.SubjectId == subjectId && x.ClientId == clientId).ToListAsync();
Logger.LogDebug("removing {persistedGrantCount} persisted grants from database for subject {subjectId}, clientId {clientId}", persistedGrants.Count, subjectId, clientId);
Context.PersistedGrants.RemoveRange(persistedGrants);
try
{
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogInformation("removing {persistedGrantCount} persisted grants from database for subject {subjectId}, clientId {clientId}: {error}", persistedGrants.Count, subjectId, clientId, ex.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Removes all grants of a give type for a given subject id and client id combination.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="subjectId">The subject identifier.</param>
/// <param name="clientId">The client identifier.</param>
/// <param name="type">The type.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task RemoveAllAsync(string subjectId, string clientId, string type)
{
var persistedGrants = await Context.PersistedGrants.Where(x =>
x.SubjectId == subjectId &&
x.ClientId == clientId &&
x.Type == type).ToListAsync();
Logger.LogDebug("removing {persistedGrantCount} persisted grants from database for subject {subjectId}, clientId {clientId}, grantType {persistedGrantType}", persistedGrants.Count, subjectId, clientId, type);
Context.PersistedGrants.RemoveRange(persistedGrants);
try
{
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogInformation("exception removing {persistedGrantCount} persisted grants from database for subject {subjectId}, clientId {clientId}, grantType {persistedGrantType}: {error}", persistedGrants.Count, subjectId, clientId, type, ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
// ResourceStore.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Mappers;
using IdentityServer4.Models;
using IdentityServer4.Stores;
using FreeSql;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Stores
{
/// <summary>
/// Implementation of IResourceStore thats uses FreeSql.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.Stores.IResourceStore" />
public class ResourceStore : IResourceStore
{
/// <summary>
/// The DbContext.
/// </summary>
protected readonly IConfigurationDbContext Context;
/// <summary>
/// The logger.
/// </summary>
protected readonly ILogger<ResourceStore> Logger;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ResourceStore"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context">The context.</param>
/// <param name="logger">The logger.</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">context</exception>
public ResourceStore(IConfigurationDbContext context, ILogger<ResourceStore> logger)
{
Context = context ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
Logger = logger;
}
/// <summary>
/// Finds the API resource by name.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name">The name.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<ApiResource> FindApiResourceAsync(string name)
{
var query =
from apiResource in Context.ApiResources
where apiResource.Name == name
select apiResource;
var apis = query
.IncludeMany(x => x.Secrets)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Scopes, then => then.IncludeMany(s => s.UserClaims))
.IncludeMany(x => x.UserClaims)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Properties);
var api = await apis.ToOneAsync();
if (api != null)
{
Logger.LogDebug("Found {api} API resource in database", name);
}
else
{
Logger.LogDebug("Did not find {api} API resource in database", name);
}
return api.ToModel();
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets API resources by scope name.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="scopeNames"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<IEnumerable<ApiResource>> FindApiResourcesByScopeAsync(IEnumerable<string> scopeNames)
{
var names = scopeNames.ToArray();
var query =
from api in Context.ApiResources
where api.Scopes.Where(x => names.Contains(x.Name)).Any()
select api;
var apis = query
.IncludeMany(x => x.Secrets)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Scopes, then => then.IncludeMany(s => s.UserClaims))
.IncludeMany(x => x.UserClaims)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Properties);
var results = await apis.ToListAsync();
var models = results.Select(x => x.ToModel()).ToArray();
Logger.LogDebug("Found {scopes} API scopes in database", models.SelectMany(x => x.Scopes).Select(x => x.Name));
return models;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets identity resources by scope name.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="scopeNames"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<IEnumerable<IdentityResource>> FindIdentityResourcesByScopeAsync(IEnumerable<string> scopeNames)
{
var scopes = scopeNames.ToArray();
var query =
from identityResource in Context.IdentityResources
where scopes.Contains(identityResource.Name)
select identityResource;
/*
var resources = query
.Include(x => x.UserClaims)
.Include(x => x.Properties)
.AsNoTracking();
*/
var resources = query
.IncludeMany(x => x.UserClaims)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Properties);
var results = await resources.ToListAsync();
Logger.LogDebug("Found {scopes} identity scopes in database", results.Select(x => x.Name));
return results.Select(x => x.ToModel()).ToArray();
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets all resources.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual async Task<Resources> GetAllResourcesAsync()
{
/*
var identity = Context.IdentityResources
.Include(x => x.UserClaims)
.Include(x => x.Properties);
*/
var identity = Context.IdentityResources.Select
.IncludeMany(x => x.UserClaims)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Properties);
/*
var apis = Context.ApiResources
.Include(x => x.Secrets)
.Include(x => x.Scopes)
.ThenInclude(s => s.UserClaims)
.Include(x => x.UserClaims)
.Include(x => x.Properties)
.AsNoTracking();
*/
var apis = Context.ApiResources.Select
.IncludeMany(x => x.Secrets)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Scopes, then => then.IncludeMany(s => s.UserClaims))
.IncludeMany(x => x.UserClaims)
.IncludeMany(x => x.Properties);
var result = new Resources(
(await identity.ToListAsync()).Select(x => x.ToModel()),
(await apis.ToListAsync()).Select(x => x.ToModel())
);
Logger.LogDebug("Found {scopes} as all scopes in database", result.IdentityResources.Select(x => x.Name).Union(result.ApiResources.SelectMany(x => x.Scopes).Select(x => x.Name)));
return result;
}
}
}
这里没有直接用 FreeSql 的 DbContext 对象, 而是抽象了一层 IConfigurationDbContext 和 IPersistedGrantDbContext 以便用接口约束需要的方法集.
// IConfigurationDbContext.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using FreeSql;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Entities;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces
{
/// <summary>
/// 配置上下文的抽象
/// </summary>
/// <可参阅 cref="System.IDisposable">
public interface IConfigurationDbContext : IDisposable
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the clients.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The clients.
/// </value>
DbSet<Client> Clients { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the identity resources.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The identity resources.
/// </value>
DbSet<IdentityResource> IdentityResources { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the API resources.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The API resources.
/// </value>
DbSet<ApiResource> ApiResources { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
int SaveChanges();
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
Task<int> SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
// IPersistedGrantDbContext.cs
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Entities;
using FreeSql;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces
{
/// <summary>
/// Abstraction for the operational data context.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="System.IDisposable" />
public interface IPersistedGrantDbContext : IDisposable
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the persisted grants.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The persisted grants.
/// </value>
DbSet<PersistedGrant> PersistedGrants { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the device flow codes.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The device flow codes.
/// </value>
DbSet<DeviceFlowCodes> DeviceFlowCodes { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
int SaveChanges();
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
Task<int> SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
当然了不要忘了我们的日志 ILogger<ConfigurationDbContext> 和 ILogger<PersistedGrantStore>, 方便后续我们跟踪调试.
数据库上下文
新建一个目录 DbContexts, 用来放置我们需要实现的数据库上下文类 ConfigurationDbContext 和 PersistedGrantDbContext.
非常幸运的是, FreeSql 有对应 EntityFramework DbContext 类似的实现, 叫 FreeSql.DbContext, 又省了不少事.
实现如下:
// ConfigurationDbContext.cs
using FreeSql;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Entities;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Options;
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.DbContexts
{
/// <summary>
/// DbContext for the IdentityServer configuration data.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="FreeSql.DbContext" />
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces.IConfigurationDbContext" />
public class ConfigurationDbContext : ConfigurationDbContext<ConfigurationDbContext>
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ConfigurationDbContext"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="options">The options.</param>
/// <param name="storeOptions">The store options.</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">storeOptions</exception>
public ConfigurationDbContext(IFreeSql<ConfigurationDbContext> freeSql, ConfigurationStoreOptions storeOptions)
: base(freeSql, storeOptions)
{
}
}
/// <summary>
/// DbContext for the IdentityServer configuration data.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="Free.DbContext" />
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.Free.Interfaces.IConfigurationDbContext" />
public class ConfigurationDbContext<TContext> : DbContext, IConfigurationDbContext
where TContext : DbContext, IConfigurationDbContext
{
private readonly IFreeSql<ConfigurationDbContext> freeSql;
//private readonly DbContextOptions options;
private readonly ConfigurationStoreOptions storeOptions;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ConfigurationDbContext"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="options">The options.</param>
/// <param name="storeOptions">The store options.</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">storeOptions</exception>
public ConfigurationDbContext(IFreeSql<ConfigurationDbContext> freeSql, ConfigurationStoreOptions storeOptions)
: base(freeSql, null)
{
this.freeSql = freeSql;
this.storeOptions = storeOptions ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(storeOptions));
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the clients.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The clients.
/// </value>
public DbSet<Client> Clients { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the identity resources.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The identity resources.
/// </value>
public DbSet<IdentityResource> IdentityResources { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the API resources.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The API resources.
/// </value>
public DbSet<ApiResource> ApiResources { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override async Task<int> SaveChangesAsync()
{
return await base.SaveChangesAsync();
}
/// <summary>
/// Override this method to further configure the model that was discovered by convention from the entity types
/// exposed in <see cref="T:FreeSql.DbSet`1" /> properties on your derived context. The resulting model may be cached
/// and re-used for subsequent instances of your derived context.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="modelBuilder">The builder being used to construct the model for this context. Databases (and other extensions) typically
/// define extension methods on this object that allow you to configure aspects of the model that are specific
/// to a given database.</param>
/// <remarks>
/// If a model is explicitly set on the options for this context (via <see cref="M:FreeSql.DbContextOptionsBuilder.UseModel(FreeSql.Metadata.IModel)" />)
/// then this method will not be run.
/// </remarks>
//protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
//{
// modelBuilder.ConfigureClientContext(storeOptions);
// modelBuilder.ConfigureResourcesContext(storeOptions);
// base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
//}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder builder)
{
builder.UseFreeSql(orm: freeSql);
//builder.UseOptions(options: options);
base.OnConfiguring(builder);
}
}
}
// PersistedGrantDbContext.cs
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Entities;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Options;
using FreeSql;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.DbContexts
{
/// <summary>
/// DbContext for the IdentityServer operational data.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="FreeSql.DbContext" />
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces.IPersistedGrantDbContext" />
public class PersistedGrantDbContext : PersistedGrantDbContext<PersistedGrantDbContext>
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="PersistedGrantDbContext"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="options">The options.</param>
/// <param name="storeOptions">The store options.</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">storeOptions</exception>
public PersistedGrantDbContext(IFreeSql<PersistedGrantDbContext> freeSql, OperationalStoreOptions storeOptions)
: base(freeSql, storeOptions)
{
}
}
/// <summary>
/// DbContext for the IdentityServer operational data.
/// </summary>
/// <seealso cref="FreeSql.DbContext" />
/// <seealso cref="IdentityServer4.FreeSql.Interfaces.IPersistedGrantDbContext" />
public class PersistedGrantDbContext<TContext> : DbContext, IPersistedGrantDbContext
where TContext : DbContext, IPersistedGrantDbContext
{
private readonly IFreeSql<PersistedGrantDbContext> freeSql;
private readonly OperationalStoreOptions storeOptions;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="PersistedGrantDbContext"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="options">The options.</param>
/// <param name="storeOptions">The store options.</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">storeOptions</exception>
public PersistedGrantDbContext(IFreeSql<PersistedGrantDbContext> freeSql, OperationalStoreOptions storeOptions)
:base(freeSql, null)
{
this.freeSql = freeSql;
if (storeOptions == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(storeOptions));
this.storeOptions = storeOptions;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the persisted grants.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The persisted grants.
/// </value>
public DbSet<PersistedGrant> PersistedGrants { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the device codes.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The device codes.
/// </value>
public DbSet<DeviceFlowCodes> DeviceFlowCodes { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Saves the changes.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override async Task<int> SaveChangesAsync()
{
return await base.SaveChangesAsync();
}
/// <summary>
/// Override this method to further configure the model that was discovered by convention from the entity types
/// exposed in <see cref="T:Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbSet`1" /> properties on your derived context. The resulting model may be cached
/// and re-used for subsequent instances of your derived context.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="modelBuilder">The builder being used to construct the model for this context. Databases (and other extensions) typically
/// define extension methods on this object that allow you to configure aspects of the model that are specific
/// to a given database.</param>
/// <remarks>
/// If a model is explicitly set on the options for this context (via <see cref="M:Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContextOptionsBuilder.UseModel(Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.IModel)" />)
/// then this method will not be run.
/// </remarks>
//protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
//{
// modelBuilder.ConfigurePersistedGrantContext(storeOptions);
// base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
//}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder builder)
{
builder.UseFreeSql(orm: freeSql);
//builder.UseOptions(options);
base.OnConfiguring(builder);
}
}
}
实体模型
IdentityServer4 的实体及属性有辣么多...
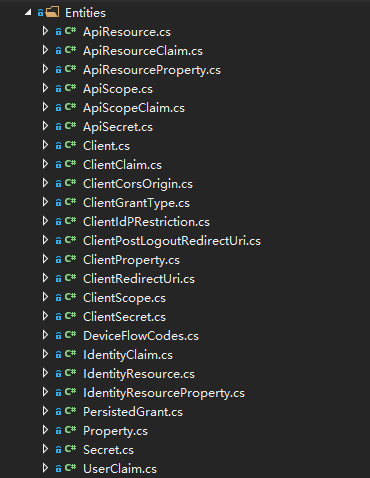
这里为了方便, 直接整个 Entities 目录从 IdentityServer4.EntityFramework 里拷贝过来.
扩展方法和配置选项
我们需要提供选项功能, 以便你在注入和使用有可调整的控制能力.
有以下几项必须实现
- FreeSql 实例的构造注入, 这点跟 EntityFramework 只有一个 DbContext 不同, FreeSql 和 FreeSql.DbContext 是 2 个分开的对象
- IdentityServer4.EntityFramework 中已经提供的最佳实践配置项, 毕竟过来人.
- 提供注入服时必需的扩展方法, 不然你还得手动 new ...
- ...
集成测试
这里用的是传说中的用户测试大法(我自己)...先用 SQLite 试试水
这里用 FreeSql 的 CodeFirst 模式, 自动生成数据结构.
- 新建一个 ASP.NET Core 应用程序;
- 添加依赖
IdentityServer4.FreeSql - 添加依赖
FreeSql和驱动提供器FreeSql.Provider.Sqlite - 在
Startup.cs里实例化 FreeSql, 注入服务 - ...
看下集成测试的项目文件:
// IdentityServer4.FreeSql.IntegrationTest.csproj
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp3.1</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="FreeSql" Version="1.2.0" />
<PackageReference Include="FreeSql.Provider.Sqlite" Version="1.2.0" />
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<ProjectReference Include="..\..\src\IdentityServer4.FreeSql\IdentityServer4.FreeSql.csproj" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
再来看看 Startup.cs 中的 FreeSql 实例化以及 IdentityServer4.FreeSql 的服务配置注入.
// Startup.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using FreeSql;
using IdentityServer4.FreeSql.DbContexts;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
//using IdentityServer4.FreeSql;
namespace IdentityServer4.FreeSql.IntegrationTest
{
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
var freeSqlC = new FreeSqlBuilder()
.UseConnectionString(DataType.Sqlite, @"Data Source=|DataDirectory|\idsr_freesql_config.db;Pooling=true;Max Pool Size=10")
.UseAutoSyncStructure(true)
.UseNoneCommandParameter(true)
.UseMonitorCommand(cmd => Trace.WriteLine(cmd.CommandText))
.Build<ConfigurationDbContext>();
var freeSqlO = new FreeSqlBuilder()
.UseConnectionString(DataType.Sqlite, @"Data Source=|DataDirectory|\idsr_freesql_op.db;Pooling=true;Max Pool Size=10")
.UseAutoSyncStructure(true)
.UseNoneCommandParameter(true)
.UseMonitorCommand(cmd => Trace.WriteLine(cmd.CommandText))
.Build<PersistedGrantDbContext>();
services.AddSingleton<IFreeSql<ConfigurationDbContext>>(freeSqlC);
services.AddSingleton<IFreeSql<PersistedGrantDbContext>>(freeSqlO);
services.AddIdentityServer()
.AddConfigurationStore(options =>
{
options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseFreeSql(orm: freeSqlC);
})
.AddOperationalStore(options =>
{
options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseFreeSql(orm: freeSqlO);
// this enables automatic token cleanup. this is optional.
options.EnableTokenCleanup = true;
options.TokenCleanupInterval = 3600; // interval in seconds (default is 3600)
});
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseRouting();
app.UseIdentityServer();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGet("/", async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
});
}
}
}
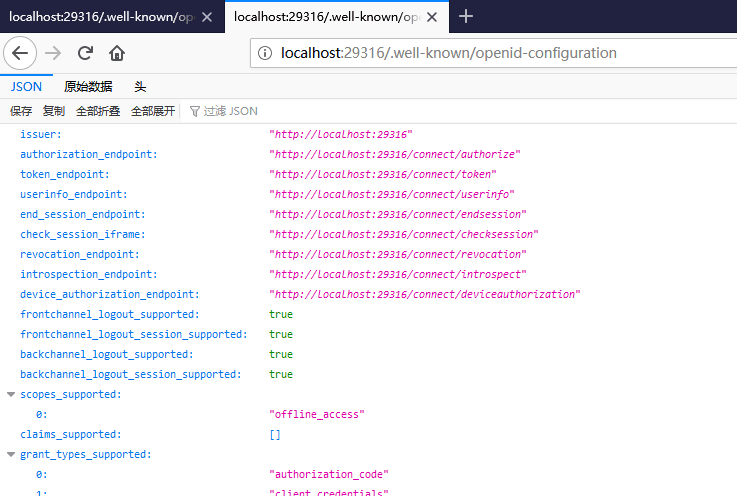
先来几个效果图:
CodeFirst 生成的 2 个 SQLite 数据库:

可以有效访问的发现端点以及对应的查询 SQL 日志:

更多内容
留待下回分解...~其实是其他的还没测试~
源码后续能见人了...也会放出来给大家溜溜
源码在这 IdentityServer4.FreeSql 不要问我为什么用 gitee, 仅仅是因为对于大多数人而言国内访问更快
参考
- IdentityServer4 源码 - 内含 IdentityServer4.EntityFramework 的源码, 极具参考意义.
- IdentityServer4.Dapper - 顾名思义
- 使用Dapper持久化IdentityServer4
- 【.NET Core项目实战-统一认证平台】第九章 授权篇-使用Dapper持久化IdentityServer4
- FreeSql
- Using EntityFramework Core for configuration and operational data
- Entity Framework Support



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步