关于urllib在python2和python3中的验签差异
在python2中
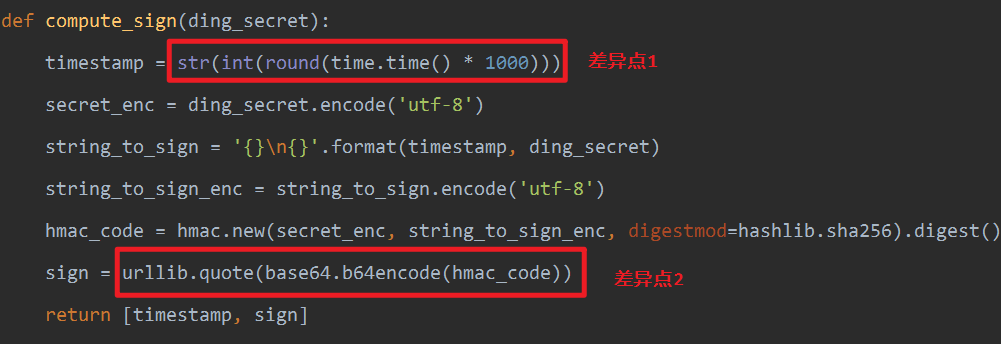
import urllib def compute_sign(ding_secret): timestamp = str(int(round(time.time() * 1000))) secret_enc = ding_secret.encode('utf-8') string_to_sign = '{}\n{}'.format(timestamp, ding_secret) string_to_sign_enc = string_to_sign.encode('utf-8') hmac_code = hmac.new(secret_enc, string_to_sign_enc, digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest() sign = urllib.quote(base64.b64encode(hmac_code)) return [timestamp, sign]
在python3中
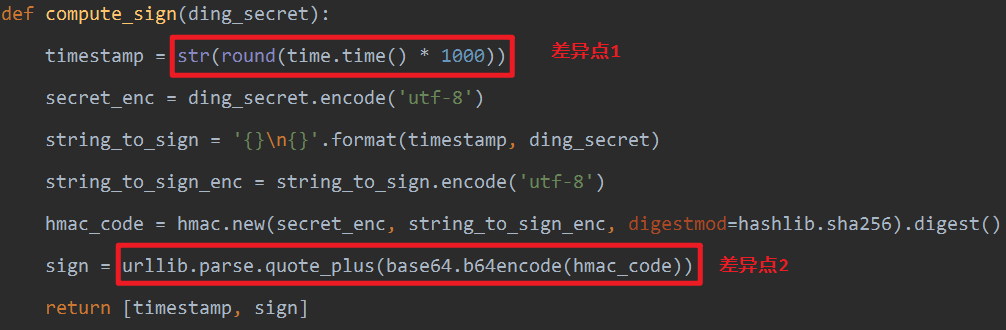
import urllib.parse def compute_sign(ding_secret): timestamp = str(round(time.time() * 1000)) secret_enc = ding_secret.encode('utf-8') string_to_sign = '{}\n{}'.format(timestamp, ding_secret) string_to_sign_enc = string_to_sign.encode('utf-8') hmac_code = hmac.new(secret_enc, string_to_sign_enc, digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest() sign = urllib.parse.quote_plus(base64.b64encode(hmac_code)) return [timestamp, sign]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号