条件、循环和其它语句学习2
1、while循环,当条件为真时,一直执行while里的语句块
### 要求客户输入用户名,直到客户输入名字结束
name =''
while not name:
name = input('please entre your name:')
print('hello,%s'%name)
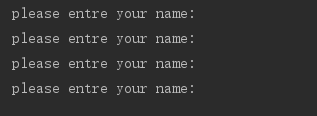
但是有个问题 如果客户输入空格,程序也会把这个空格当成name处理,空格也是字符串,可以用string.strip()去除name的两端空格
name =''
while not name.strip():
name = input('please entre your name:')
print('hello,%s'%name)

2、for循环,遍历序列sequence和字典(字典非可迭代),其他可迭代对象
遍历list
>>> a = [1,2,3,4]
>>> for i in a:
print(i)
1
2
3
4
遍历tuple
>>> b = (1,2,3,4)
>>> for i in b:
print(i)
1
2
3
4
遍历字典
>>> d = {1:'one',2:'two',3:'three'}
>>> for item in d.items(): ###遍历项
print(item)
(1, 'one')
(2, 'two')
(3, 'three')
>>> for k in d.keys(): ###遍历key值
print(k)
1
2
3
>>> for v in d.values(): ###遍历值
print(v)
one
two
three
>>> for k,v in d.items():###遍历items,返回k,v
print(k,v)
1 one
2 two
3 three
3、一些迭代工具
并行迭代
>>> name = ['anne','beth','george','damon']
>>> age = [18,19,20,31]
>>> for i in range(len(name)):###range()返回迭代器
print(name[i],age[i])
anne 18
beth 19
george 20
damon 31
zip函数,将多个序列合并成一个序列,返回一个zip对象,可迭代
>>> name = ['anne','beth','george','damon']
>>> age = [18,19,20,31]
>>> home = ['Beijing','Nanjing','Hangzhou','Kunming']
>>> zip(name,age,home)
<zip object at 0x0000020219B9E048>
>>> for item in zip(name,age,home):
print(item)
('anne', 18, 'Beijing')
('beth', 19, 'Nanjing')
('george', 20, 'Hangzhou')
('damon', 31, 'Kunming')
>>> for n,a,h in zip(name,age,home):
print(n,a,h)
anne 18 Beijing
beth 19 Nanjing
george 20 Hangzhou
damon 31 Kunming
zip可以压缩不同长度的序列,当短的序列压缩完成后,则停止
>>> name = ['anne','beth','george','damon']
>>> age = [18,19]
>>> zip(name,age)
<zip object at 0x0000020219B9E188>
>>> for item in zip(name,age):
print(item)
('anne', 18)
('beth', 19)
4、enumerate(iterable,start=0) 枚举函数,第一参数为可迭代的对象,第二个参数指定下标开始的数字,返回一个enumerate对象;
>>> name = ['anne','beth','george','damon']
>>> for index,n in enumerate(name,0):###指定index从0开始
print(index,n)
index n
0 anne
1 beth
2 george
3 damon
>>> for index,n in enumerate(range(3),1): ###指定index从1开始
print(index,n)
1 0
2 1
3 2
5、翻转和排序迭代,sorted()排序、reversed()翻转,作用于任何序列或可迭代对象上,sorted()返回排序后的新列表;reversed()返回一个可迭代对象
>>> sorted([1,4,2,3,9,6])
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9]
>>> reversed([1,3,2])
<list_reverseiterator object at 0x0000020219A079B0>
>>> list(reversed([1,3,2]))
[2, 3, 1]
>>> list(reversed('hello,world!'))
['!', 'd', 'l', 'r', 'o', 'w', ',', 'o', 'l', 'l', 'e', 'h']
>>> ''.join(reversed('hello,world!'))
'!dlrow,olleh'
6、break跳出循环体,执行下面的语句块,continue跳出当前循环,执行下一个循环(尽量使用break)
例子:求取100以内最大的平方值;那程序可以从100向下迭代
>>> from math import sqrt
>>> for n in range(99,0,-1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print(n)
break
81
for x in seq:
if condition1: continue
if condition2:continue
do_something()
do_something_else()
etc()
可以用下面的语句替换
for x in seq:
if not(condition1 or condition2 or condition3):
do_something()
do_something_else()
etc()
7、while True/Break语句
例子:### 要求客户输入用户名,直到客户输入名字结束
>>> while True:
name = input('please enter your name:')
if name:
print('hello,%s'%name)
break
else:
continue
8、for循环中的else,仅在break未执行时,执行else语句块
from math import sqrt
for n in range(99,81,-1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print(n)
break
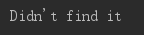
else:
print("Didn't find it")
9、列表推倒式,根据已经有的列表和条件,新建一个列表
###求取1-9的平方
>>> lis = []
>>> for i in range(10):
lis.append(i*i)
>>> lis
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
上面的新建lis列表的方式可以改写成列表推倒式[i*i for i in range(10)]
>>> [i*i for i in range(10)]
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
>>> [i*i for i in range(10) if i%3==0] 添加新列表生成的条件
[0, 9, 36, 81]
多个for语句
>>> [(x,y) for x in range(3) for y in range(3)]
[(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2)]
功能等同于
>>> result = []
>>> for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
result.append((i,j))
>>> result
[(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2)]
10、实例,将boys和girls列表中各名字首字母一样的名字组合在一起
>>> girls = ['alice','bernice','clarice']
>>> boys = ['chris','arnold','bob']
>>> [b+'+'+g for b in boys for g in girls if b[0]==g[0]]
['chris+clarice', 'arnold+alice', 'bob+bernice']
更优方案:上面的方案会每一个组合都对比,效率不高
>>> girls = ['alice','bernice','clarice']
>>> boys = ['chris','arnold','bob']
>>> lettergirls = {}
>>> for girl in girls:
lettergirls.setdefault(girl[0],[]).append(girl) ###将girls列表转换成{首字母:[名字]}的字典,后面用列表是因为遍历读取时,名字可以作为一个元素整个读取,否则默认string会分解成一个一个的letter,例如‘a’‘l’‘i’‘c’‘e’
>>> print(lettergirls)
{'a': ['alice'], 'b': ['bernice'], 'c': ['clarice']}
>>> [b+"+"+g for b in boys for g in lettergirls[b[0]]] ###根据遍历得到的b,直接从字典根据key取value值
['chris+clarice', 'arnold+alice', 'bob+bernice']



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号