memcached学习笔记——连接模型
文章链接:http://www.hcoding.com/?p=121
个人站点:JC&hcoding.com
memcached是什么呢?memcached是一个优秀的、高性能的内存缓存工具。
memcached具有以下的特点:
- 协议简单:memcached的服务器客户端通信并不使用复杂的MXL等格式,而是使用简单的基于文本的协议。
- 基于libevent的事件处理:libevent是个程序库,他将Linux 的epoll、BSD类操作系统的kqueue等时间处理功能封装成统一的接口。memcached使用这个libevent库,因此能在Linux、BSD、Solaris等操作系统上发挥其高性能。(libevent是什么)
- 内置内存存储方式:为了提高性能,memcached中保存的数据都存储在memcached内置的内存存储空间中。由于数据仅存在于内存中,因此重启memcached,重启操作系统会导致全部数据消失。另外,内容容量达到指定的值之后memcached回自动删除不适用的缓存。
- Memcached不互通信的分布式:memcached尽管是“分布式”缓存服务器,但服务器端并没有分布式功能。各个memcached不会互相通信以共享信息。他的分布式主要是通过客户端实现的。
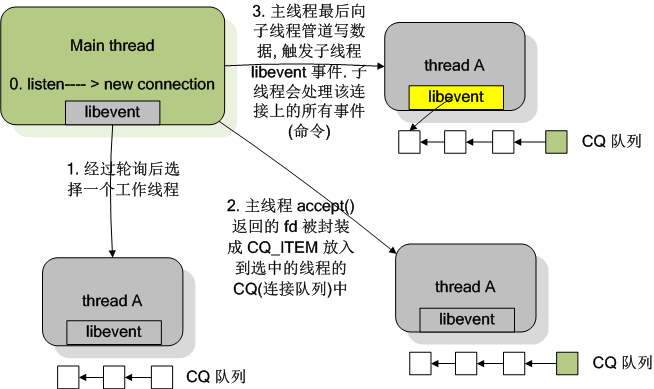
本文主要讲解memcached的连接模型,memcached由一条主线程(连接线程)监听连接,然后把成功的连接交给子线程(工作线程)处理读写操作。N条【启动memcached通过-t命令指定】子线程(工作线程)负责读写数据,一条子线程(工作线程)维护着多个连接。一个conn结构体对象对应着一个连接,主线程(连接线程)成功连接后,会把连接的内容赋值到一个conn结构体对象,并把这个conn结构体对象传递给一条子线程(工作线程)处理。
conn结构体:

1 typedef struct conn conn; 2 struct conn { 3 int sfd; 4 sasl_conn_t *sasl_conn; 5 6 // 连接状态 7 enum conn_states state; 8 enum bin_substates substate; 9 struct event event; 10 short ev_flags; 11 12 // 刚刚出发的事件 13 short which; /** which events were just triggered */ 14 15 // read buffer 16 char *rbuf; /** buffer to read commands into */ 17 18 // 已经解析了一部分的命令, 指向已经解析结束的地方 19 char *rcurr; /** but if we parsed some already, this is where we stopped */ 20 21 // rbuf 已分配的大小 22 int rsize; /** total allocated size of rbuf */ 23 24 // 尚未解析的命令大小 25 int rbytes; /** how much data, starting from rcur, do we have unparsed */ 26 27 // buffer to write 28 char *wbuf; 29 30 // 指向已经返回的地方 31 char *wcurr; 32 33 // 写大小 34 int wsize; 35 36 // 尚未写的数据大小 37 int wbytes; 38 39 /** which state to go into after finishing current write */ 40 // 当写回结束后需要即刻转变的状态 41 enum conn_states write_and_go; 42 43 void *write_and_free; /** free this memory after finishing writing */ 44 45 char *ritem; /** when we read in an item's value, it goes here */ 46 int rlbytes; 47 48 /* data for the nread state */ 49 50 /** 51 * item is used to hold an item structure created after reading the command 52 * line of set/add/replace commands, but before we finished reading the actual 53 * data. The data is read into ITEM_data(item) to avoid extra copying. 54 */ 55 56 // 指向当下需要完成的任务 57 void *item; /* for commands set/add/replace */ 58 59 /* data for the swallow state */ 60 int sbytes; /* how many bytes to swallow */ 61 62 /* data for the mwrite state */ 63 struct iovec *iov; 64 int iovsize; /* number of elements allocated in iov[] */ 65 int iovused; /* number of elements used in iov[] */ 66 67 // msghdr 链表, 一个连接可能有多个 msghdr 68 // 如果是 UDP, 需要为每一个 msghdr 填写一个 UDP 头部 69 struct msghdr *msglist; 70 int msgsize; /* number of elements allocated in msglist[] */ 71 int msgused; /* number of elements used in msglist[] */ 72 int msgcurr; /* element in msglist[] being transmitted now */ 73 int msgbytes; /* number of bytes in current msg */ 74 75 item **ilist; /* list of items to write out */ 76 int isize; 77 item **icurr; 78 79 // 记录任务数量 80 int ileft; 81 82 char **suffixlist; 83 int suffixsize; 84 char **suffixcurr; 85 int suffixleft; 86 87 enum protocol protocol; /* which protocol this connection speaks */ 88 enum network_transport transport; /* what transport is used by this connection */ 89 90 /* data for UDP clients */ 91 int request_id; /* Incoming UDP request ID, if this is a UDP "connection" */ 92 struct sockaddr request_addr; /* Who sent the most recent request */ 93 socklen_t request_addr_size; 94 95 unsigned char *hdrbuf; /* udp packet headers */ 96 int hdrsize; /* number of headers' worth of space is allocated */ 97 98 bool noreply; /* True if the reply should not be sent. */ 99 /* current stats command */ 100 struct { 101 char *buffer; 102 size_t size; 103 size_t offset; 104 } stats; 105 106 /* Binary protocol stuff */ 107 /* This is where the binary header goes */ 108 protocol_binary_request_header binary_header; 109 uint64_t cas; /* the cas to return */ 110 short cmd; /* current command being processed */ 111 112 // ? 不透明 113 int opaque; 114 int keylen; 115 116 // 可见是一个链表 117 conn *next; /* Used for generating a list of conn structures */ 118 119 // 指向服务于此连接的线程 120 LIBEVENT_THREAD *thread; /* Pointer to the thread object serving this connection */ 121 };
1 //memcached.c 2 int main{ 3 4 // ...... 5 6 // 第一步:初始化主线程的事件机制 7 /* initialize main thread libevent instance */ 8 // libevent 事件机制初始化 9 main_base = event_init(); 10 11 // ...... 12 13 // 第二步:初始化 N 个 (初始值200,当连接超过200个的时候会往上递增) conn结构体对象 14 // 空闲连接数组初始化 15 conn_init(); 16 17 // ...... 18 19 20 // 第三步:启动工作线程 21 /* start up worker threads if MT mode */ 22 thread_init(settings.num_threads, main_base); 23 24 // ...... 25 26 // 第四步:初始化socket,绑定监听端口,为主线程的事件机制设置连接监听事件(event_set、event_add) 27 /** 28 memcached 有可配置的两种模式: unix 域套接字和 TCP/UDP, 允许客户端以两种方式向 memcached 发起请求. 客户端和服务器在同一个主机上的情况下可以用 unix 域套接字, 否则可以采用 TCP/UDP 的模式. 两种模式是不兼容的. 29 以下的代码便是根据 settings.socketpath 的值来决定启用哪种方式. 30 */ 31 /** 32 第一种, unix 域套接字. 33 */ 34 /* create unix mode sockets after dropping privileges */ 35 if (settings.socketpath != NULL) { 36 errno = 0; 37 if (server_socket_unix(settings.socketpath,settings.access)) { 38 vperror("failed to listen on UNIX socket: %s", settings.socketpath); 39 exit(EX_OSERR); 40 } 41 } 42 43 /** 44 第二种, TCP/UDP. 45 */ 46 /* create the listening socket, bind it, and init */ 47 if (settings.socketpath == NULL) { 48 const char *portnumber_filename = getenv("MEMCACHED_PORT_FILENAME"); 49 char temp_portnumber_filename[PATH_MAX]; 50 FILE *portnumber_file = NULL; 51 52 // 读取端口号文件 53 if (portnumber_filename != NULL) { 54 snprintf(temp_portnumber_filename, 55 sizeof(temp_portnumber_filename), 56 "%s.lck", portnumber_filename); 57 58 portnumber_file = fopen(temp_portnumber_filename, "a"); 59 if (portnumber_file == NULL) { 60 fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open \"%s\": %s\n", 61 temp_portnumber_filename, strerror(errno)); 62 } 63 } 64 65 // TCP 66 errno = 0; 67 if (settings.port && server_sockets(settings.port, tcp_transport, 68 portnumber_file)) { 69 vperror("failed to listen on TCP port %d", settings.port); 70 exit(EX_OSERR); 71 } 72 73 /* 74 * initialization order: first create the listening sockets 75 * (may need root on low ports), then drop root if needed, 76 * then daemonise if needed, then init libevent (in some cases 77 * descriptors created by libevent wouldn't survive forking). 78 */ 79 80 // UDP 81 /* create the UDP listening socket and bind it */ 82 errno = 0; 83 if (settings.udpport && server_sockets(settings.udpport, udp_transport, 84 portnumber_file)) { 85 vperror("failed to listen on UDP port %d", settings.udpport); 86 exit(EX_OSERR); 87 } 88 89 if (portnumber_file) { 90 fclose(portnumber_file); 91 rename(temp_portnumber_filename, portnumber_filename); 92 } 93 } 94 95 // ...... 96 97 98 // 第五步:主线程进入事件循环 99 /* enter the event loop */ 100 // 进入事件循环 101 if (event_base_loop(main_base, 0) != 0) { 102 retval = EXIT_FAILURE; 103 } 104 105 // ...... 106 107 }
LIBEVENT_THREAD 结构体:

1 // 多个线程, 每个线程一个 event_base 2 typedef struct { 3 pthread_t thread_id; /* unique ID of this thread */ 4 struct event_base *base; /* libevent handle this thread uses */ 5 6 // event 结构体, 用于管道读写事件的监听 7 struct event notify_event; /* listen event for notify pipe */ 8 9 // 读写管道文件描述符 10 int notify_receive_fd; /* receiving end of notify pipe */ 11 int notify_send_fd; /* sending end of notify pipe */ 12 13 // 线程的状态 14 struct thread_stats stats; /* Stats generated by this thread */ 15 16 // 这个线程需要处理的连接队列 17 struct conn_queue *new_conn_queue; /* queue of new connections to handle */ 18 cache_t *suffix_cache; /* suffix cache */ 19 uint8_t item_lock_type; /* use fine-grained or global item lock */ 20 } LIBEVENT_THREAD;
第三步工作线程的详细启动过程:
1 /* 2 * thread.c 3 * 4 * 初始化线程子系统, 创建工作线程 5 * Initializes the thread subsystem, creating various worker threads. 6 * 7 * nthreads Number of worker event handler threads to spawn 8 * 需准备的线程数 9 * main_base Event base for main thread 10 * 分发线程 11 */ 12 void thread_init(int nthreads, struct event_base *main_base) { 13 int i; 14 int power; 15 16 // 互斥量初始化 17 pthread_mutex_init(&cache_lock, NULL); 18 pthread_mutex_init(&stats_lock, NULL); 19 20 pthread_mutex_init(&init_lock, NULL); 21 //条件同步 22 pthread_cond_init(&init_cond, NULL); 23 24 pthread_mutex_init(&cqi_freelist_lock, NULL); 25 cqi_freelist = NULL; 26 27 /* Want a wide lock table, but don't waste memory */ 28 if (nthreads < 3) { 29 power = 10; 30 } else if (nthreads < 4) { 31 power = 11; 32 } else if (nthreads < 5) { 33 power = 12; 34 } else { 35 // 2^13 36 /* 8192 buckets, and central locks don't scale much past 5 threads */ 37 power = 13; 38 } 39 40 // hashsize = 2^n 41 item_lock_count = hashsize(power); 42 43 item_locks = calloc(item_lock_count, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t)); 44 if (! item_locks) { 45 perror("Can't allocate item locks"); 46 exit(1); 47 } 48 // 初始化 49 for (i = 0; i < item_lock_count; i++) { 50 pthread_mutex_init(&item_locks[i], NULL); 51 } 52 //item_lock_type_key设置为线程的私有变量的key 53 pthread_key_create(&item_lock_type_key, NULL); 54 pthread_mutex_init(&item_global_lock, NULL); 55 56 57 // LIBEVENT_THREAD 是结合 libevent 使用的结构体, event_base, 读写管道 58 threads = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(LIBEVENT_THREAD)); 59 if (! threads) { 60 perror("Can't allocate thread descriptors"); 61 exit(1); 62 } 63 64 // main_base 是分发任务的线程, 即主线程 65 dispatcher_thread.base = main_base; 66 dispatcher_thread.thread_id = pthread_self(); 67 68 // 管道, libevent 通知用的 69 // 一个 LIBEVENT_THREAD 结构体对象对应由一条子线程维护 70 // 子线程通过读管道来接收主线程的命令(例如主线程接收到新连接,会往子线程的读管道写入字符'c',子线程接收到命令就会做出相应的处理) 71 for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 72 int fds[2]; 73 if (pipe(fds)) { 74 perror("Can't create notify pipe"); 75 exit(1); 76 } 77 78 // 读管道 79 threads[i].notify_receive_fd = fds[0]; 80 // 写管道 81 threads[i].notify_send_fd = fds[1]; 82 83 // 初始化线程信息数据结构, 其中就将 event 结构体的回调函数设置为 thread_libevent_process(),此时线程还没有创建 84 setup_thread(&threads[i]); 85 /* Reserve three fds for the libevent base, and two for the pipe */ 86 stats.reserved_fds += 5; 87 } 88 89 /* Create threads after we've done all the libevent setup. */ 90 // 创建并初始化线程, 线程的代码都是 work_libevent() 91 for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 92 // 调用 pthread_attr_init() 和 pthread_create() 来创建子线程 93 // 子线程的函数入口 worker_libevent ,负责启动子线程的事件循环 94 create_worker(worker_libevent, &threads[i]); 95 } 96 97 /* Wait for all the threads to set themselves up before returning. */ 98 pthread_mutex_lock(&init_lock); 99 // wait_for_thread_registration() 是 pthread_cond_wait 的调用 100 wait_for_thread_registration(nthreads); 101 pthread_mutex_unlock(&init_lock); 102 } 103 104 105 106 107 /* 108 * Set up a thread's information. 109 */ 110 // 填充 LIBEVENT_THREAD 结构体, 其中包括: 111 // 填充 struct event 112 // 初始化线程工作队列 113 // 初始化互斥量 114 // 等 115 static void setup_thread(LIBEVENT_THREAD *me) { 116 // 子线程的事件机制,每条子线程都有一个事件机制 117 me->base = event_init(); 118 if (! me->base) { 119 fprintf(stderr, "Can't allocate event base\n"); 120 exit(1); 121 } 122 123 /* Listen for notifications from other threads */ 124 // 在线程数据结构初始化的时候, 为 me->notify_receive_fd 读管道注册读事件, 回调函数是 thread_libevent_process() 125 // 为子线程的事件机制添加事件 126 event_set(&me->notify_event, me->notify_receive_fd, 127 EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, thread_libevent_process, me); 128 event_base_set(me->base, &me->notify_event); 129 130 if (event_add(&me->notify_event, 0) == -1) { 131 fprintf(stderr, "Can't monitor libevent notify pipe\n"); 132 exit(1); 133 } 134 135 // ...... 136 } 137 138 139 140 /* 141 * Worker thread: main event loop 142 * 线程函数入口, 启动事件循环 143 */ 144 static void *worker_libevent(void *arg) { 145 LIBEVENT_THREAD *me = arg; 146 147 // ...... 148 149 // 进入事件循环 150 event_base_loop(me->base, 0); 151 return NULL; 152 }
子线程读管道回调函数:

1 /* 2 * Processes an incoming "handle a new connection" item. This is called when 3 * input arrives on the libevent wakeup pipe. 4 * 5 * 当管道有数据可读的时候会触发此函数的调用 6 */ 7 static void thread_libevent_process(int fd, short which, void *arg) { 8 LIBEVENT_THREAD *me = arg; 9 CQ_ITEM *item; 10 char buf[1]; 11 12 if (read(fd, buf, 1) != 1) 13 if (settings.verbose > 0) 14 fprintf(stderr, "Can't read from libevent pipe\n"); 15 16 switch (buf[0]) { 17 case 'c': 18 // 表示主线程把一个新的连接分发给该子线程处理 19 // 取出一个任务 20 item = cq_pop(me->new_conn_queue); 21 22 if (NULL != item) { 23 // 为新的请求建立一个连接结构体. 连接其实已经建立, 这里只是为了填充连接结构体. 最关键的动作是在 libevent 中注册了事件, 回调函数是 event_handler() 24 conn *c = conn_new(item->sfd, item->init_state, item->event_flags, 25 item->read_buffer_size, item->transport, me->base); 26 if (c == NULL) { 27 if (IS_UDP(item->transport)) { 28 fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on UDP socket\n"); 29 exit(1); 30 } else { 31 if (settings.verbose > 0) { 32 fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on fd %d\n", 33 item->sfd); 34 } 35 close(item->sfd); 36 } 37 } else { 38 c->thread = me; 39 } 40 cqi_free(item); 41 } 42 break; 43 44 /* we were told to flip the lock type and report in */ 45 case 'l': 46 me->item_lock_type = ITEM_LOCK_GRANULAR; 47 register_thread_initialized(); 48 break; 49 50 case 'g': 51 me->item_lock_type = ITEM_LOCK_GLOBAL; 52 register_thread_initialized(); 53 break; 54 } 55 }
第四步主要是初始化socket、绑定服务器端口和IP、为主线程事件机制添加监听连接事件:
1 // memcached.c 2 // server_sockets()->server_socket() 3 4 static int server_socket(const char *interface, 5 int port, 6 enum network_transport transport, 7 FILE *portnumber_file) { 8 9 // ...... 10 11 // getaddrinfo函数能够处理名字到地址以及服务到端口这两种转换,返回的是一个addrinfo的结构(列表)指针而不是一个地址清单。 12 error= getaddrinfo(interface, port_buf, &hints, &ai); 13 14 if (error != 0) { 15 if (error != EAI_SYSTEM) 16 fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo(): %s\n", gai_strerror(error)); 17 else 18 perror("getaddrinfo()"); 19 return 1; 20 } 21 22 for (next= ai; next; next= next->ai_next) { 23 conn *listen_conn_add; 24 25 // new_socket() 申请了一个 UNIX 域套接字,通过调用socket()方法创建套接字,并设置把套接字为非阻塞 26 if ((sfd = new_socket(next)) == -1) { 27 28 // ...... 29 30 }// if 31 32 33 // ...... 34 35 36 // bind() 绑定源IP的端口 37 if (bind(sfd, next->ai_addr, next->ai_addrlen) == -1) { 38 39 // ...... 40 41 } else { 42 success++; 43 // bind()调用成功后,调用listen() 44 if (!IS_UDP(transport) && listen(sfd, settings.backlog) == -1) { 45 46 // ...... 47 48 } 49 50 // ...... 51 52 } 53 54 // UDP 和 TCP 区分对待, UDP 没有连接概念, 只要绑定服务器之后, 直接读取 socket 就好了, 所以与它对应 conn 的初始状态应该为 conn_read; 而 TCP 对应的 conn 初始状态应该为 conn_listening 55 if (IS_UDP(transport)) { 56 // UDP 57 int c; 58 59 for (c = 0; c < settings.num_threads_per_udp; c++) { 60 /* this is guaranteed to hit all threads because we round-robin */ 61 // 分发新的连接到线程池中的一个线程中 62 dispatch_conn_new(sfd, conn_read, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 63 UDP_READ_BUFFER_SIZE, transport); 64 } 65 } else { 66 // TCP 要建立连接 67 if (!(listen_conn_add = conn_new(sfd, conn_listening, 68 EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 1, 69 transport, main_base))) { 70 fprintf(stderr, "failed to create listening connection\n"); 71 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 72 } 73 74 // 放在头部, listen_conn 是头指针 75 listen_conn_add->next = listen_conn; 76 listen_conn = listen_conn_add; 77 } 78 } 79 80 freeaddrinfo(ai); 81 82 /* Return zero iff we detected no errors in starting up connections */ 83 return success == 0; 84 } 85 86 87 88 89 // 填写 struct conn 结构体, 包括 struct conn 中的 event 结构, 并返回 90 conn *conn_new(const int sfd, enum conn_states init_state, 91 const int event_flags, 92 const int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport, 93 struct event_base *base) { 94 // c 指向一个新的 conn 空间 95 // 可能是出于性能的考虑, memcached 预分配了若干个 struct conn 空间 96 { 97 /* data */ 98 }; 99 conn *c = conn_from_freelist(); 100 101 if (NULL == c) { 102 // 可能分配失败了, 因为默认数量有限. 进行新的扩展,conn_init()中初始数量是200 103 if (!(c = (conn *)calloc(1, sizeof(conn)))) { 104 fprintf(stderr, "calloc()\n"); 105 return NULL; 106 } 107 108 // ...... 109 // 填充conn结构体 110 111 }// if 112 113 114 // ...... 115 116 117 // libevent 操作: 设置事件, 设置回调函数 event_handler() 118 event_set(&c->event, sfd, event_flags, event_handler, (void *)c); 119 120 // libevent 操作:设置 c->event 的 event_base 121 event_base_set(base, &c->event); 122 123 c->ev_flags = event_flags; 124 125 // libevent 操作: 添加事件 126 if (event_add(&c->event, 0) == -1) { 127 128 // ...... 129 130 } 131 132 133 // ...... 134 135 136 return c; 137 }





