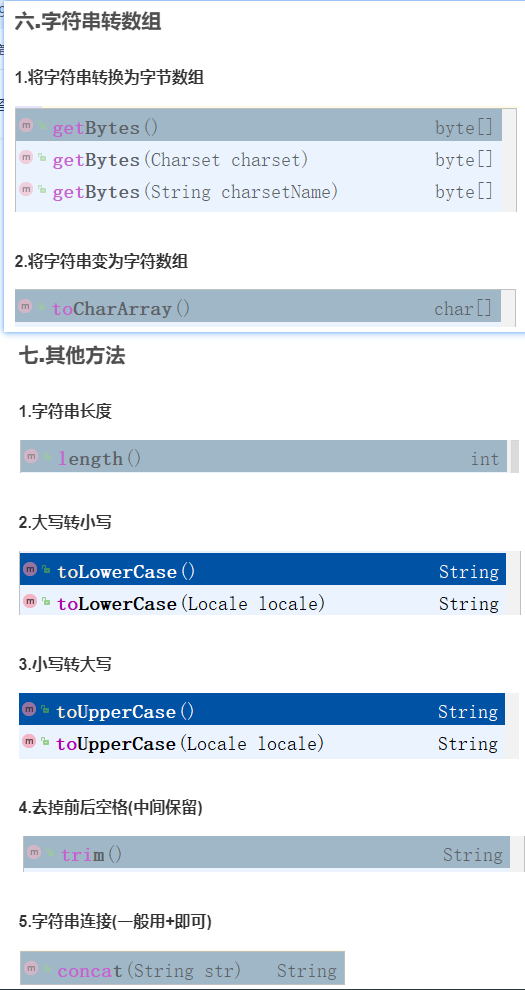
String常用方法
前言
- 记录String的常用方法
1、常用方法汇总
一.字符串的替换
1.replace方法

String string1="Hello Word";
String result1=string1.replace("Hello","你好");
String result2=string1.replace("abc","你好");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//你好 Word(替换的目标存在)
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//Hello Word(替换的目标不存在)
2.replaceAll方法

String string1="Hello Word";
String result3=string1.replaceAll("o","A");
String result4=string1.replaceAll("111","A");
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//HellA WArd(替换的目标存在)
Log.d("TAG","result4----:"+result4);//Hello Word(替换的目标不存在)
3.replaceFirst方法

String string1="Hello Word";
String result5=string1.replaceFirst("H","A");
String result6=string1.replaceFirst("o","A");
String result7=string1.replaceFirst("111","A");
Log.d("TAG","result5----:"+result5);//Aello Word(替换的目标存在)
Log.d("TAG","result6----:"+result6);//HellA Word(替换的目标存在)
Log.d("TAG","result7----:"+result7);//Hello Word(替换的目标不存在)
二.字符串的拆分
1.split(String str)方法

String string1 = "abc1def1ghi1asd12345";
String result1[] = string1.split("1");
for (String s1 : result1) {
Log.d("TAG", "s1----:" + s1);
}
String result2[] = string1.split("L");
for (String s2 : result2) {
Log.d("TAG", "s2----:" + s2);
}
s1----:abc
s1----:def
s1----:ghi
s1----:asd
s1----:2345
s2----:abc1def1ghi1asd12345
2.split(String str,int limit)方法

limit 参数控制模式应用的次数,因此影响结果数组的长度。如果该限制 n 大于 0,则模式将被最多应用 n - 1 次,数组的长度将不会大于 n,而且数组的最后项将包含超出最后匹配的定界符的所有输入。 如果 n 为非正,则模式将被应用尽可能多的次数,而且数组可以是任意长度。如果 n 为零,则模式将被应用尽可能多的次数,数组可有任何长度,并且结尾空字符串将被丢弃。
String line = "aa,bb,cc,dd,,,,";
String result1[] = line.split(",");
for (String s1 : result1) {
Log.d("TAG", "s1----:" + s1);
}
String result2[] = line.split(",", line.length());
for (String s2 : result2) {
Log.d("TAG", "s2----:" + s2);
}
s1----:aa
s1----:bb
s1----:cc
s1----:dd
s2----:aa
s2----:bb
s2----:cc
s2----:dd
s2----:
s2----:
三.字符串截取
1.substring(int startIndex)方法

String string1="1234567";
String result1=string1.substring(2);//[2,最后]
String result2=string1.substring(555);//报错
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//34567
2.substring(int startIndex,int endIndex)方法

String string1="1234567";
String result3=string1.substring(2,4);//[2,4)
String result4=string1.substring(2,555);//报错
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//34
四.字符串的查找
1.contains方法

String string="abcd";
boolean result1=string.contains("a");
boolean result2=string.contains("LLL");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//true
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//false
2.endsWith方法

String string="abcd";
boolean result1=string.endsWith("d");
boolean result2=string.endsWith("LLL");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//true
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//false
3.startsWith(String str)方法

String string="abcd";
boolean result1=string.startsWith("a");
boolean result2=string.startsWith("LLL");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//true
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//false
4.startsWith(String str,int offIndex)方法

String string="abcd";
boolean result3=string.startsWith("a",0);
boolean result4=string.startsWith("a",222222);
boolean result5=string.startsWith("LLL",2);
boolean result6=string.startsWith("LLL",222222);
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//true
Log.d("TAG","result4----:"+result4);//false
Log.d("TAG","result5----:"+result5);//false
Log.d("TAG","result6----:"+result6);//false
5.indexOf(String str)

String string="abcdadvccccaaa";
int result1=string.indexOf("a");
int result2=string.indexOf("c");
int result3=string.indexOf("NN");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//0
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//2
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//-1:没找到
6.indexOf(String str,int formIndex)方法

String string="abcdadvccccaaa";
int result4=string.indexOf("a",2);
int result5=string.indexOf("a",222222);
int result6=string.indexOf("NN",2);
int result7=string.indexOf("NN",222222);
Log.d("TAG","result4----:"+result4);//4
Log.d("TAG","result5----:"+result5);//-1:没找到
Log.d("TAG","result6----:"+result6);//-1
Log.d("TAG","result7----:"+result7);//-1
7.lastIndexOf(String str)方法

String string="abcdadvccccaaa";
int result1=string.lastIndexOf("a");
int result2=string.lastIndexOf("c");
int result3=string.lastIndexOf("NN");
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//13
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//10
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//-1:没找到
8.lastIndexOf(String str,int formIndex)方法

String string="abcdadvccccaaa";
int result4=string.lastIndexOf("a",5);
int result5=string.lastIndexOf("a",222222);
int result6=string.lastIndexOf("NN",2);
int result7=string.lastIndexOf("NN",222222);
int result8=string.lastIndexOf("d",2);
Log.d("TAG","result4----:"+result4);//4
Log.d("TAG","result5----:"+result5);//13
Log.d("TAG","result6----:"+result6);//-1:没找到
Log.d("TAG","result7----:"+result7);//-1
Log.d("TAG","result8----:"+result8);//-1
9.charAt(int index)方法

String string="abcdefasssbbcca";
char result1=string.charAt(0);
char result2=string.charAt(4);
char result3=string.charAt(11111111);//报错
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//a
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//e
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//报错
五.字符串比较
1.equals(Object o)方法

String string1="abcDa";
String string2="abcda";
boolean result1=string1.equals(string2);
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//false
2.equalsIgnoreCase(Object o)方法

String string1="abcDa";
String string2="abcda";
boolean result2=string1.equalsIgnoreCase(string2);
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//true
3.compareTo(String str)方法

String string1="a";
String string2="A";
String string3="bb";
String string4="a";
int result1=string1.compareTo(string2);
int result2=string1.compareTo(string4);
int result3=string1.compareTo(string3);
Log.d("TAG","result1----:"+result1);//32
Log.d("TAG","result2----:"+result2);//0
Log.d("TAG","result3----:"+result3);//-1
4.compareToIgnoreCase(String str)方法

String string1="a";
String string2="A";
String string3="bb";
String string4="a";
int result4=string1.compareToIgnoreCase(string2);
int result5=string1.compareToIgnoreCase(string4);
int result6=string1.compareToIgnoreCase(string3);
Log.d("TAG","result4----:"+result4);//0
Log.d("TAG","result5----:"+result5);//0
Log.d("TAG","result6----:"+result6);//-1
在compareTo上会返回的数据类型为int型,而对于int型有如下三种的返回
大于:>0
小于:<0
等于:=0
compareTo对于大小的比较就是字母编码的比较

参看链接:https://gitcode.csdn.net/65e935e11a836825ed78d5f7.html
2、使用
2.1、String类型转成int类型
在将String类型转换成int类型时:
int n = Interger.parseInt(Stringnum);
如果报错,可以改成:
int n = Interger.parseInt(Stringnum.trim());
trim()函数的作用是去掉字符串左右两边的空格。
2.2、判断String类型里是否包含指定字符
String lineText = "cz8108_1接口业务参数:{\"EInvoiceNumber\":\"0003656276\",\"EInvoiceCode\":\"41060221\",\"AgencyCode\":\"0000510000025760\",\"RandomNumber\":\"126501\"}";
方式一
大小写敏感(区分大小写);存在,返回第一次出现的下标索引数;不存在,返回-1;通常与截取字符串结合使用。 System.out.println(lineText.indexOf("cz8108_1接口业务参数:"));// 0 System.out.println(lineText.indexOf("cz8108接口业务参数:"));// -1
方式二:contains()
大小写敏感(区分大小写);存在,返回true;不存在,返回false; System.out.println(lineText.contains("cz8108_1接口业务参数:"));// true System.out.println(lineText.contains("cz8108接口业务参数:"));// false 点击contains()方法,我们可以查看源码,会发现:它的使用方法和方式一,一模一样
方式三:正则表达式
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("cz8108_1接口业务参数:"); System.out.println(p.matcher(lineText).find());// true p = Pattern.compile("cz8108接口业务参数:"); System.out.println(p.matcher(lineText).find());// false
方式四:由apache的commons-lang3.jar包提供
System.out.println(StringUtils.contains(lineText, "cz8108_1接口业务参数:"));// true System.out.println(StringUtils.contains(lineText, "cz8108接口业务参数:"));// false 有个使用的功能是,它提供了不区分大小的方法: System.out.println(StringUtils.containsIgnoreCase(lineText, "einvoicenumber"));// true System.out.println(StringUtils.containsIgnoreCase(lineText, "EINVOICENUMBER"));// true
2.3、字符串截取
1、含头不含尾:
zrjoutstandingtreaty.getTreatyid().substring(0,2)
2、截取最后一位:
"Q".equals(treatyLists.getAccperiod().substring(treatyLists.getAccperiod().length()-1))
2.4、获得指定长度的随机字符串
public static String getRandString(int maxLength){
String source ="abcdefghijklmnopqrskuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
Random rand = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<maxLength;i++){
sb.append(source.charAt(rand.nextInt(source.length())));
}
return sb.toString();
}
2.5String.format()的详细用法
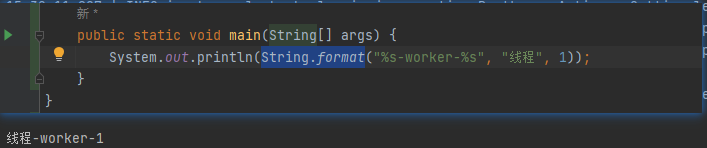
参看链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45606067/article/details/127449245
在所有的矛盾中,要优先解决主要矛盾,其他矛盾也就迎刃而解。
不要做个笨蛋,为失去的郁郁寡欢,聪明的人,已经找到了解决问题的办法,或正在寻找。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通