Python案例
音乐播放器
import tkinter as tk import tkinter.filedialog import os from pygame import mixer class MusicPlayer: def __init__(self, root): self.root = root self.root.title("Music Player") self.root.geometry("300x100") # Initialize Pygame mixer mixer.init() # Create a variable to store the current playing status self.playing = False # Create a variable to store the current selected song self.current_song = None # Create the UI elements self.label = tk.Label(root, text="Music Player") self.label.pack() self.play_button = tk.Button(root, text="Play", command=self.play_music) self.play_button.pack() self.stop_button = tk.Button(root, text="Stop", command=self.stop_music) self.stop_button.pack() self.browse_button = tk.Button(root, text="Browse", command=self.browse_music) self.browse_button.pack() def play_music(self): if self.current_song: if not self.playing: mixer.music.load(self.current_song) mixer.music.play() self.play_button.config(text="Pause") self.playing = True else: mixer.music.pause() self.play_button.config(text="Play") self.playing = False def stop_music(self): mixer.music.stop() self.play_button.config(text="Play") self.playing = False def browse_music(self): self.current_song = tk.filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir=os.getcwd(), title="Select Song",filetypes=(("Audio Files", "*.mp3"), ("All Files", "*.*"))) self.label.config(text=os.path.basename(self.current_song)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = tk.Tk() music_player = MusicPlayer(root) root.mainloop()
路径选择案例
from collections import defaultdict import heapq # 定义图 graph = { 'A': {'C': 1, 'B': 3}, 'B': {'A': 3, 'D': 6, 'C': 4}, 'C': {'A': 1, 'B': 4, 'D': 5}, 'D': {'B': 6, 'C': 5} } # 深度优先搜索找所有路径 def dfs(graph, start, end, path=[]): path = path + [start] if start == end: return [path] if start not in graph: return [] paths = [] for node in graph[start]: if node not in path: newpaths = dfs(graph, node, end, path) for newpath in newpaths: paths.append(newpath) return paths # 找A到D的所有路径 all_paths = dfs(graph, 'A', 'D') print(f"从A到D的所有路径个数:{len(all_paths)}") for i, path in enumerate(all_paths, 1): print(f"路径 {i}: {' -> '.join(path)}") # 使用Dijkstra算法找最短路径 def dijkstra(graph, start, end): queue = [(0, start)] visited = set() while queue: (cost, current_node) = heapq.heappop(queue) if current_node not in visited: visited.add(current_node) if current_node == end: return cost for neighbor, weight in graph[current_node].items(): heapq.heappush(queue, (cost + weight, neighbor)) return -1 # 如果没有路径到达end,则返回-1 shortest_path_cost = dijkstra(graph, 'A', 'D') if shortest_path_cost != -1: print(f"A到D的最短路径长度为:{shortest_path_cost}") else: print("A到D之间没有路径")
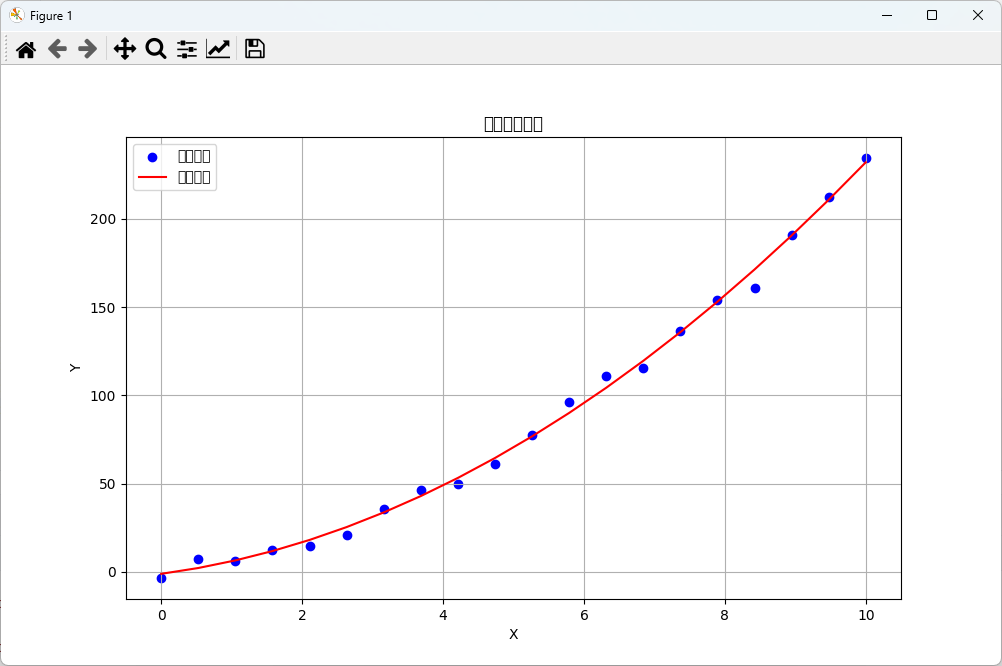
拟合曲线
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 创建一些数据点 x = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) y = 2 * x**2 + 3 * x + 5 + np.random.normal(0, 5, size=x.shape) # 使用numpy的polyfit进行曲线拟合 coefficients = np.polyfit(x, y, 2) # 创建一个多项式对象 polynomial = np.poly1d(coefficients) # 绘制原始数据和拟合曲线 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.scatter(x, y, color='blue', label='原始数据') plt.plot(x, polynomial(x), color='red', label='拟合曲线') plt.title('曲线拟合示例') plt.xlabel('X') plt.ylabel('Y') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.show()
类的方式实现
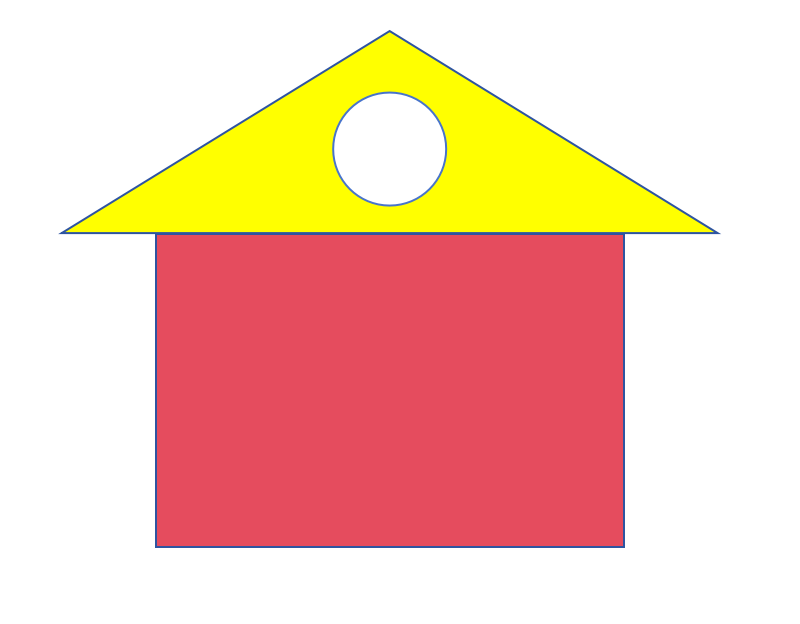
的面积计算
import math class Shape: def __init__(self): pass def get_area(self): raise NotImplementedError("Subclass must implement this method") class Rectangle(Shape): def __init__(self, length, width): self.length = length self.width = width def get_area(self): return self.length * self.width class Triangle(Shape): def __init__(self, base, height): self.base = base self.height = height def get_area(self): return 0.5 * self.base * self.height class Circle(Shape): def __init__(self, diameter): self.diameter = diameter def get_area(self): radius = self.diameter / 2 return math.pi * radius * radius def main(): shapes = [] for i in range(3): shape_type = input(f"请输入第{i+1}个图形的类型(矩形/三角形/圆形):") if shape_type == "矩形": length = float(input(f"请输入第{i+1}个矩形的长度:")) width = float(input(f"请输入第{i+1}个矩形的宽度:")) shapes.append(Rectangle(length, width)) elif shape_type == "三角形": base = float(input(f"请输入第{i+1}个三角形的底边:")) height = float(input(f"请输入第{i+1}个三角形的高:")) shapes.append(Triangle(base, height)) elif shape_type == "圆形": diameter = float(input(f"请输入第{i+1}个圆形的直径:")) shapes.append(Circle(diameter)) else: print("请输入正确的图形名称!") return total_area = sum(shape.get_area() for shape in shapes) print(f"三个图形的总面积为:{total_area}") main()
摄像头瞳距测量
import cv2 import numpy as np # 假设的一些参数 focal_length = 500 # 模拟焦距 baseline = 0.1 # 模拟双目基线 def single_camera_biocular_distance(point1, point2): # 计算像素距离 pixel_distance = np.linalg.norm(point1 - point2) # 根据公式计算距离 distance = (focal_length * baseline) / pixel_distance return distance cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) prev_point = None while True: ret, frame = cap.read() gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) if prev_point is not None: # 这里简单取当前帧中一个随机点作为第二个点进行模拟 current_point = np.array([np.random.randint(0, frame.shape[1]), np.random.randint(0, frame.shape[0])]) distance = single_camera_biocular_distance(prev_point, current_point) print(f"估计的距离: {distance}") # 可以根据需要进行特征提取等操作来获取更有意义的点 prev_point = np.array([np.random.randint(0, frame.shape[1]), np.random.randint(0, frame.shape[0])]) cv2.imshow('Frame', frame) if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
图像描边
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter, ImageDraw def draw_green_contour(image_path): image = Image.open(image_path) # 获取边缘 edge_image = image.filter(ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES) # 创建一个可绘图对象 draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) # 遍历边缘图像的像素 pixels = edge_image.load() for i in range(edge_image.size[0]): for j in range(edge_image.size[1]): if pixels[i, j]!= (0, 0, 0): # 在原始图像上绘制绿色轮廓 draw.line([(i-1, j), (i+1, j), (i, j-1), (i, j+1)], fill=(0, 255, 0)) # 保存图像 image.save("green_contour_image.jpg") # 替换为派大星图片路径 image_path = r"C:\Users\玖\Pictures\微信图片_20240613235807.jpg" draw_green_contour(image_path)
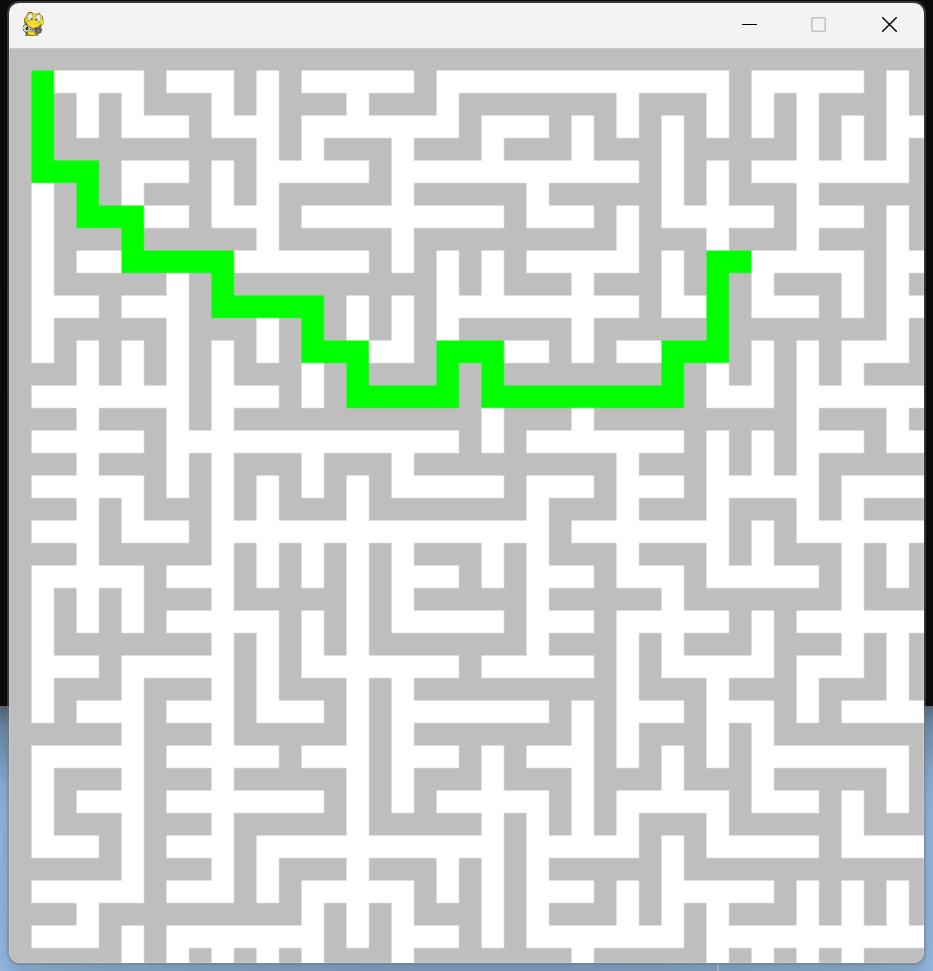
迷宫寻路
import random import sys import pygame to_be_selected=[] random_selectB=[] path_list=[] ROWS=61 COLUMNS=61 x=[0,2,0,-2] y=[2,0,-2,0] px=[0,1,0,-1] py=[1,0,-1,0] isvisit=[[0 for i in range(COLUMNS)] for j in range(ROWS)] isvisit[1][1]=1 def matrix_init(r,c): matrix=[[1 for i in range(c)] for j in range(r)] matrix[1][1]=0 return matrix def put_node_in_to_be_selected(node): for i in range(4): xx=node[0]+x[i] yy=node[1]+y[i] if xx>0 and xx<ROWS and yy>0 and yy<COLUMNS and ([xx,yy] not in to_be_selected) and matrix[xx][yy]==1: to_be_selected.append([xx,yy]) matrix=matrix_init(ROWS,COLUMNS) def random_B(node): random_selectB.clear() for i in range(4): xx = node[0] + x[i] yy = node[1] + y[i] if xx > 0 and xx < ROWS and yy > 0 and yy < COLUMNS and matrix[xx][yy]==0: random_selectB.append([xx,yy]) rand_B=random.randint(0,len(random_selectB)-1) return random_selectB[rand_B] start=[1,1] put_node_in_to_be_selected(start) path_list.append([1,1]) def matrix_generate(): if len(to_be_selected)>0: rand_s=random.randint(0,len(to_be_selected)-1) select_nodeA=to_be_selected[rand_s] selectB=random_B(select_nodeA) matrix[select_nodeA[0]][select_nodeA[1]]=0 mid_x=int((select_nodeA[0]+selectB[0])/2) mid_y=int((select_nodeA[1]+selectB[1])/2) matrix[mid_x][mid_y]=0 put_node_in_to_be_selected(select_nodeA) to_be_selected.remove(select_nodeA) elif len(path_list)>0: matrix[ROWS-2][COLUMNS-2]=3 l=len(path_list)-1 n=path_list[l] if n[0]==ROWS-2 and n[1]==COLUMNS-2: return for i in range(4): xx = n[0]+px[i] yy = n[1]+py[i] if xx > 0 and xx < ROWS-1 and yy > 0 and yy < COLUMNS-1 and (matrix[xx][yy]==0 or matrix[xx][yy]==3) and isvisit[xx][yy]==0: isvisit[xx][yy] = 1 matrix[n[0]][n[1]] =2 tmp = [xx, yy] path_list.append(tmp) break elif i==3: matrix[n[0]][n[1]] = 0 path_list.pop() pygame.init() screen=pygame.display.set_mode((COLUMNS*10,ROWS*10)) pygame.display.set_caption("") def draw_rect(x,y,color): pygame.draw.rect(screen,color,((y * 15, x* 15, 15, 15))) def draw_maze(): for i in range(ROWS): for j in range(COLUMNS): if matrix[i][j]==1: draw_rect(i,j,"grey") if matrix[i][j]==2: draw_rect(i, j, "green") if matrix[i][j] == 3: draw_rect(i, j, "red") while True: for event in pygame.event.get(): if event.type==pygame.QUIT: sys.exit() screen.fill("white") matrix_generate() draw_maze() pygame.display.flip() pygame.time.Clock().tick(60)
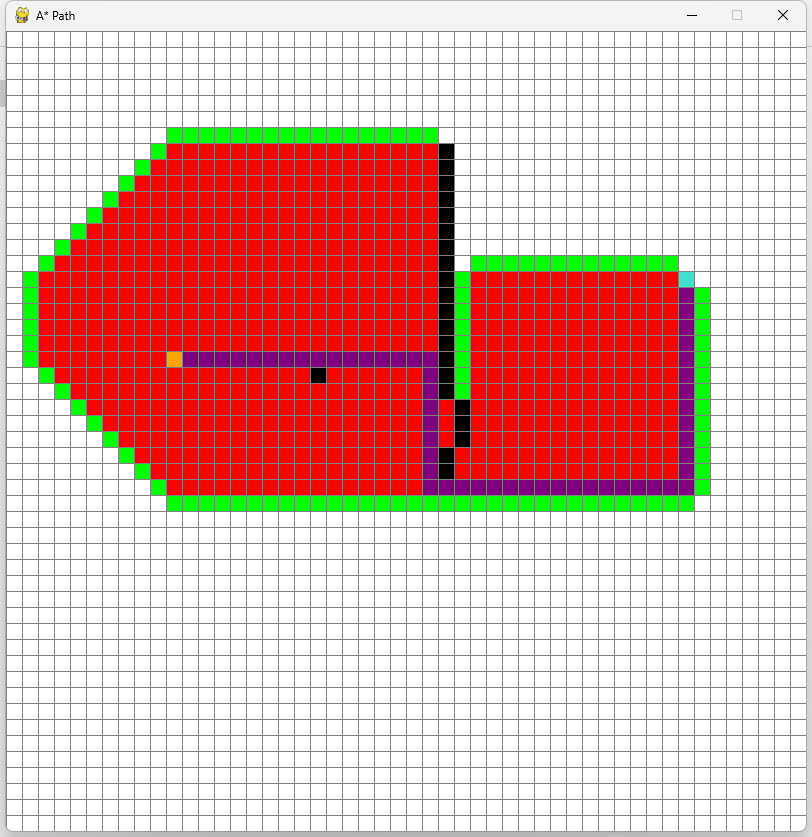
A*寻路
import pygame from queue import PriorityQueue pygame.init() # 设置屏幕大小和标题 WIDTH = 800 WIN = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, WIDTH)) pygame.display.set_caption("A* Path") # 定义颜色 RED = (255, 0, 0) GREEN = (0, 255, 0) BLUE = (0, 0, 255) YELLOW = (255, 255, 0) WHITE = (255, 255, 255) BLACK = (0, 0, 0) PURPLE = (128, 0, 128) ORANGE = (255, 165, 0) GREY = (128, 128, 128) TURQUOISE = (64, 224, 208) # 定义格子类 class Spot: def __init__(self, row, col, width, total_rows): self.row = row self.col = col self.x = row * width self.y = col * width self.color = WHITE self.neighbors = [] self.width = width self.total_rows = total_rows def get_pos(self): # 获取格子坐标 return self.row, self.col def is_closed(self): # 获取格子状态 return self.color == RED # 红色表关闭 def is_open(self): return self.color == GREEN def is_barrier(self): return self.color == BLACK def is_start(self): return self.color == ORANGE def is_end(self): return self.color == TURQUOISE def reset(self): # 重置格子状态(白色) self.color = WHITE def make_closed(self): # 设置为关闭状态 self.color = RED # 设为红色 def make_open(self): self.color = GREEN def make_barrier(self): self.color = BLACK def make_start(self): self.color = ORANGE def make_end(self): self.color = TURQUOISE def make_path(self): self.color = PURPLE def draw(self, win): # 绘制格子 pygame.draw.rect(win, self.color, (self.x, self.y, self.width, self.width)) def update_neighbors(self, grid): # 更新邻居列表 self.neighbors = [] # 初始化邻居列表为空 if self.row < self.total_rows - 1 and not grid[self.row + 1][self.col].is_barrier(): # 不是最底层且下方不是障碍物 self.neighbors.append(grid[self.row + 1][self.col]) # 添加到邻居列表 if self.row > 0 and not grid[self.row - 1][self.col].is_barrier(): self.neighbors.append(grid[self.row - 1][self.col]) if self.col < self.total_rows - 1 and not grid[self.row][self.col + 1].is_barrier(): self.neighbors.append(grid[self.row][self.col + 1]) if self.col > 0 and not grid[self.row][self.col - 1].is_barrier(): self.neighbors.append(grid[self.row][self.col - 1]) def __lt__(self, other): # 小于比较 return False # 始终返回 表示当前格子大于任何格子 # A*算法 def h(p1, p2): # 评估/启发函数 计算最佳路径代价 x1, y1 = p1 x2, y2 = p2 return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2) # 返回两点间曼哈顿距离 def astar(draw, grid, start, end): # 寻找最短路径 count = 0 # 初始化计数器 对优先队列中的节点排序 open_set = PriorityQueue() # 将待探索的点存储到优先队列中 open_set.put((0, count, start)) # 将起点放入优先队列中 初始评估代价为0 依据count排序 came_from = {} # 创建一个空字典 存储路径中每个节点的前一个节点 g_score = {spot: float("inf") for row in grid for spot in row} # 创建一个字典 存储起点到每个节点的实际代价 g_score[start] = 0 # 起点的实际代价设置为0 f_score = {spot: float("inf") for row in grid for spot in row} # 创建一个字典 f_score[start] = h(start.get_pos(), end.get_pos()) # 存储起点经过每个节点到终点的评估代价 open_set_hash = {start} # 创建一个含有起点的集合 存储带探索的节点 while not open_set.empty(): # 循环 只要该集合不为空 for event in pygame.event.get(): # 检测pygame中的事件 if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 检测到关闭事件 pygame.quit() # 退出pygame current = open_set.get()[2] # 从优先队列中获取优先值最高的节点 open_set_hash.remove(current) # 移除current 表示已经探索过该节点 if current == end: # 如果current是终点 reconstruct_path(came_from, end, draw) # 路径重构 end.make_end() # 标记终点颜色 start.make_start() # 标记起点颜色 return True # 重构成功 for neighbor in current.neighbors: # 遍历current的邻居 temp_g_score = g_score[current] + 1 # 计算从起点经过current到邻居的实际代价 if temp_g_score < g_score[neighbor]: # 如果小于最开始计算的实际代价 came_from[neighbor] = current # 当前节点设为邻居的父节点 g_score[neighbor] = temp_g_score # 更换邻居实际代价信息 f_score[neighbor] = temp_g_score + h(neighbor.get_pos(), end.get_pos()) # 计算从起点经过邻居节点到终点的评估总代价 if neighbor not in open_set_hash: # 检测邻居是否在待探索集合 count += 1 # 如果在更新计数器 open_set.put((f_score[neighbor], count, neighbor)) # 如果不在 加入到集合中 open_set_hash.add(neighbor) # 加入哈希集合 快速检测是否存在待探索集合 neighbor.make_open() draw() if current != start: # 不是起点 标记已探索 current.make_closed() return False # 可视化重构路径 def reconstruct_path(came_from, current, draw): while current in came_from: current = came_from[current] # 回溯 current.make_path() draw() # 可视化重构路径 def make_grid(rows, width): grid = [] gap = width // rows for i in range(rows): grid.append([]) for j in range(rows): spot = Spot(i, j, gap, rows) grid[i].append(spot) return grid # 绘制网格线 def draw_grid(win, rows, width): gap = width // rows for i in range(rows): pygame.draw.line(win, GREY, (0, i * gap), (width, i * gap)) # 绘制水平线 for j in range(rows): pygame.draw.line(win, GREY, (j * gap, 0), (j * gap, width)) # 绘制垂直线 # 绘制窗口 def draw(win, grid, rows, width): win.fill(WHITE) # 清空窗口 填充白色 for row in grid: for spot in row: spot.draw(win) draw_grid(win, rows, width) pygame.display.update() # 计算行和列索引 def get_clicked_pos(pos, rows, width): gap = width // rows y, x = pos row = y // gap col = x // gap return row, col # 主函数 def main(win, width): ROWS = 50 grid = make_grid(ROWS, width) start = None end = None run = True while run: draw(win, grid, ROWS, width) # 绘制 for event in pygame.event.get(): if event.type == pygame.QUIT: run = False if pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[0]: # 处理鼠标左键事件 pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos() row, col = get_clicked_pos(pos, ROWS, width) spot = grid[row][col] if not start and spot != end: start = spot start.make_start() elif not end and spot != start: end = spot end.make_end() elif spot != end and spot != start: spot.make_barrier() elif pygame.mouse.get_pressed()[2]: # 处理鼠标右键事件 pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos() row, col = get_clicked_pos(pos, ROWS, width) spot = grid[row][col] spot.reset() if spot == start: start = None elif spot == end: end = None if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN: # 处理键盘事件 if event.key == pygame.K_SPACE and start and end: for row in grid: for spot in row: spot.update_neighbors(grid) astar(lambda: draw(win, grid, ROWS, width), grid, start, end) pygame.quit() if __name__ == "__main__": main(WIN, WIDTH)