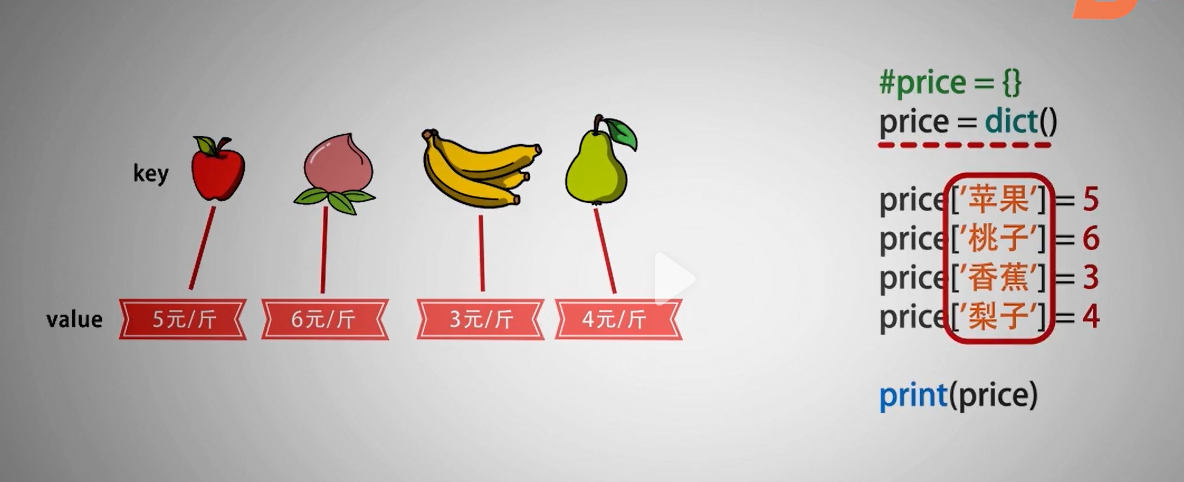
字典案例
# 案例1: # 假设,已知小明、小红、小亮三人的语文、数学、英语三科成绩,将姓名、学科、成绩做对应,并计算谁的总分最高


利用Lambda表达式实现排序功能。 有以下水果价格字典,使用lam
price ={'桃子': 5, '香蕉': 4, '葡萄': 6, '草莓': 7}
#打印今日售卖水果的种类和价格
print("--------今日水果价格--------")
for fruit in price:
print(fruit, price[fruit]) #字典值的访问 字典名[键]
print(" ")
n = int(input("请输入你要购买的水果的种类:"))
sum_price = 0
#for循环遍历求出购买的总金额
for i in range(1, n+1): #for循环区间左闭右开
fruit = input("请输入你要购买的水果的名称:")
num = int(input("请输入你要购买的水果数量:"))
# 判断购买的水果是否有
if fruit in price:
sum_price += price[fruit] * num #求金额
print(f"您购买水果的总金额为:{sum_price}元")
bda表达式,按价格从高到低对字典排序,并输出排序结果。 {'apple': 12.6, 'grape': 21.0, 'orange': 8.8, 'banana': 10.8, 'pear': 6.5}
fruits = {'apple': 12.6, 'grape': 21.0, 'orange': 8.8, 'banana': 10.8, 'pear': 6.5}
sorted_fruits = sorted(fruits.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for fruit in sorted_fruits:
print(fruit[0], fruit[1])
这里使用了 sorted 函数来对字典进行排序,key 参数指定了排序的依据,这里使用了 lambda 表达式来指定以字典的值作为排序依据。reverse=True 表示按从大到小排序。最后遍历排序后的元组列表,输出水果名称和价格。
# 案例2: # 假设,已知小明、小红、小亮三人的语文、数学、英语三科成绩,将姓名、学科、成绩做对应,并计算谁的总分最高
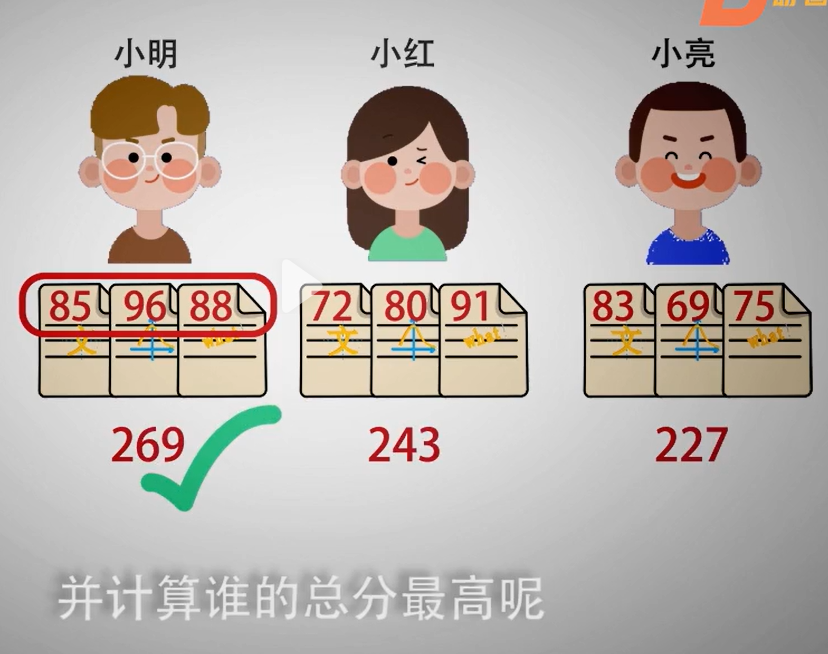
# 创建一个字典,其中包含每个学生的姓名和各科成绩 students = { "小明": {"语": 85, "数": 96, "英": 88}, "小红": {"语": 72, "数": 80, "英": 91}, "小亮": {"语": 83, "数": 69, "英": 75}, } # 初始化用于存储姓名和总分的变量, highest_scorer = "" # 用字符串表示总分最高的考生姓名 highest_score = 0 # 用数字表示总分 # 遍历字典,计算每个学生的总分 for name, scores in students.items(): total_score = sum(scores.values()) print(f"{name}的总分是:{total_score}") # 更新总分最高的学生信息 if total_score > highest_score: highest_score = total_score highest_scorer = name # 输出总分最高的学生信息 print(f"{highest_scorer}的总分最高,为{highest_score}分。")



