java实现简易计算器
Java简易计算器
用java语言写的一个简易计算器,实现了最基本的+、-、*、/ 运算。
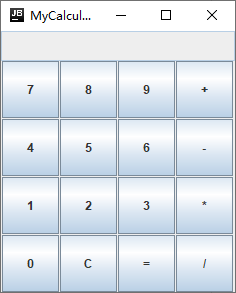
先来看下效果:
界面简述:
整个面板的由一个JTextFiled组件+16个JButton组件构成,外加一个JPanel组件存放16个按钮,其布局为4x4的网格布局(GridLayout)。
显示框与按钮面板放在了整个面板容器中,布局为BorderLayout,显示框放容器北部,整个按钮面板放容器中部。
功能实现简述:
由匿名内部类实现ActionListener接口,按钮注册进行监听,并捕获按钮事件。
由于该计算器只能计算中缀表达式,即数字与运算符交替出现的表达式,获取输入的运算表达式,并将其存与一个字符串中。
这里需要借助栈来完成表达式的计算,首先将字符串分割成字符串数组,由中缀的定义知数组奇数位为运算符(从第0位开始),偶数位为操作数,因此可将偶数为操作数进栈,遇见+(-)运算符,则将下一个数以正(负)的形式压人栈中,遇见*或/运算符,则将栈顶元素出栈与数组后一元素进行计算,并将其结果重新压入栈中,直至遍历至数组最后一个元素。
最后将栈中的元素进行求和。
代码实现:
//package com.cal; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.Stack; import javax.swing.*; class MyException extends Exception{ public MyException() { super(); } public MyException(String message) { super(message); } } class SwingConsole{ public static void run(final JFrame f,final int width,final int height){ SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable(){ public void run(){ f.setTitle(f.getClass().getSimpleName()); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setSize(width,height); f.setVisible(true); } }); } } public class MyCalculator extends JFrame{ /* * */ private JTextField textField; //输入文本框 private String input; //结果 private String operator; //操作符 public MyCalculator() { input = ""; operator = ""; Container container = this.getContentPane(); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); textField = new JTextField(30); textField.setEditable(false); //文本框禁止编辑 textField.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.LEFT); //textField.setBounds(100, 100, 20, 20); //在容器布局为空情况下生效 textField.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,30)); container.add(textField, BorderLayout.NORTH); String[] name= {"7","8","9","+","4","5","6","-","1","2","3","*","0","C","=","/"}; panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,1,1)); for(int i=0;i<name.length;i++) { JButton button = new JButton(name[i]); button.addActionListener(new MyActionListener()); panel.add(button); } container.add(panel,BorderLayout.CENTER); } class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{ //内部类实现按钮响应 @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { int cnt=0; String actionCommand = e.getActionCommand(); //获取按钮上的字符串 if(actionCommand.equals("+") || actionCommand.equals("-") || actionCommand.equals("*") || actionCommand.equals("/")) { input += " " + actionCommand + " "; } else if(actionCommand.equals("C")) { //清除输入 input = ""; } else if(actionCommand.equals("=")) { //按下等号 try { input+= "="+calculate(input); } catch (MyException e1) { if(e1.getMessage().equals("Infinity")) input+= "=" + e1.getMessage(); else input = e1.getMessage(); } textField.setText(input); input=""; cnt = 1; } else input += actionCommand; //按下数字 if(cnt == 0) textField.setText(input); } } private String calculate(String input) throws MyException{ //计算函数 String[] comput = input.split(" "); Stack<Double> stack = new Stack<>(); Double m = Double.parseDouble(comput[0]); stack.push(m); //第一个操作数入栈 for(int i = 1; i < comput.length; i++) { if(i%2==1) { if(comput[i].equals("+")) stack.push(Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1])); if(comput[i].equals("-")) stack.push(-Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1])); if(comput[i].equals("*")) { //将前一个数出栈做乘法再入栈 Double d = stack.peek(); //取栈顶元素 stack.pop(); stack.push(d*Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1])); } if(comput[i].equals("/")) { //将前一个数出栈做乘法再入栈 double help = Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1]); if(help == 0) throw new MyException("Infinity"); //不会继续执行该函数 double d = stack.peek(); stack.pop(); stack.push(d/help); } } } double d = 0d; while(!stack.isEmpty()) { //求和 d += stack.peek(); stack.pop(); } String result = String.valueOf(d); return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new MyCalculator(), 250, 300); } }
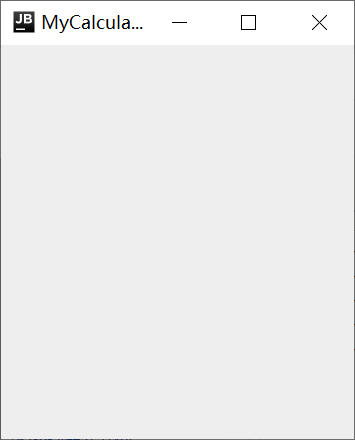
一、先实现窗口
package 菜鸟教程.NumberMath; //package com.cal; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.Stack; import javax.swing.*; class SwingConsole{ public static void run(final JFrame f,final int width,final int height){ SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable(){//线程里修改swing组件的外观 public void run(){ f.setTitle(f.getClass().getSimpleName()); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setSize(width,height); f.setVisible(true); } }); } } public class MyCalculator extends JFrame{ public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new MyCalculator(), 250, 300); } }
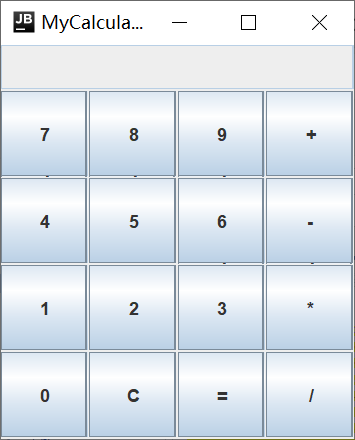
二、实现其他按钮和输入框等
package 菜鸟教程.NumberMath; //package com.cal; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.Stack; import javax.swing.*; class SwingConsole{ public static void run(final JFrame f,final int width,final int height){ SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable(){//线程里修改swing组件的外观 public void run(){ f.setTitle(f.getClass().getSimpleName()); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setSize(width,height); f.setVisible(true); } }); } } public class MyCalculator extends JFrame{ private JTextField textField; //输入文本框 private String input; //结果 private String operator; //操作符 public MyCalculator() { input = ""; operator = ""; Container container = this.getContentPane(); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); textField = new JTextField(30); textField.setEditable(false); //文本框禁止编辑 textField.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.LEFT); //textField.setBounds(100, 100, 20, 20); //在容器布局为空情况下生效 textField.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,30)); container.add(textField, BorderLayout.NORTH); String[] name= {"7","8","9","+","4","5","6","-","1","2","3","*","0","C","=","/"}; panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,1,1)); for(int i=0;i<name.length;i++) { JButton button = new JButton(name[i]); // button.addActionListener(new MyActionListener()); panel.add(button); } container.add(panel,BorderLayout.CENTER); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new MyCalculator(), 250, 300); } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律