laravel的一些高级用法
转载链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000018924969
Laravel 集合是 Laravel 框架中一个十分有用的工具。
Laravel 集合就像是在 PHP 中的数组,但会更好用。
在这篇教程中,我们将会体验一些集合使用时的实用技巧。
集合(Collection)
Illuminate\Support\Collection 类了提供一个便捷的操作数组的封装。
集合 Collection 类实现了部分 PHP 和 Laravel 的接口,例如:
- ArrayAccess - 用于操作数组对象的接口。
- IteratorAggregate - 用于创建外部迭代器的接口。
- JsonSerializable
你可以在这里查看其余已实现的接口。
创建一个新的集合
一个集合可以使用 collect() 帮助函数基于一个数组被创建 或者直接通过 Illuminate\Support\Collection 类实例化。
一个非常简单的使用 collect() 帮助函数的示例:
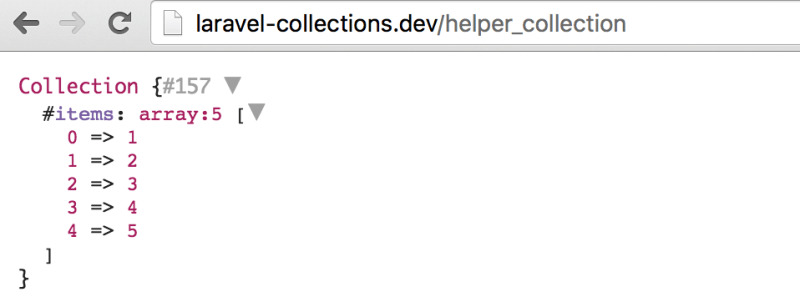
$newCollection = collect([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);一个更复杂的示例:
<?php
namespace app\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Support\Collection;
class TestController extends Controller
{
/**
* Create a new collection using the collect helper method.
*/
public function helperCollection()
{
$newCollection = collect([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
dd($newCollection);
}
/**
* Create a new collection with a Collection class instance.
*/
public function classCollection()
{
$newCollection = new Collection([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
dd($newCollection);
}
}这个帮助函数用起来要简单很多因为你再不需要实例化 Illuminate\Support\Collection 类。
我也有用到 dd() 帮助函数来在浏览器中显示集合。看起来大概会是这样子。
Eloquent ORM 集合
Laravel Eloquent ORM 也以集合的形式返回数据。
Eloquent ORM 的调用会以集合的形式返回数据
为了演示这个效果,我将初始化一个 Sqlite 数据库。
我们将用 Laravel 框架预置的迁移文件来创建一个用户表,然后填充 10 条数据到用户表中。
/**
* 从用户表获取用户列表
*/
public function getUsers()
{
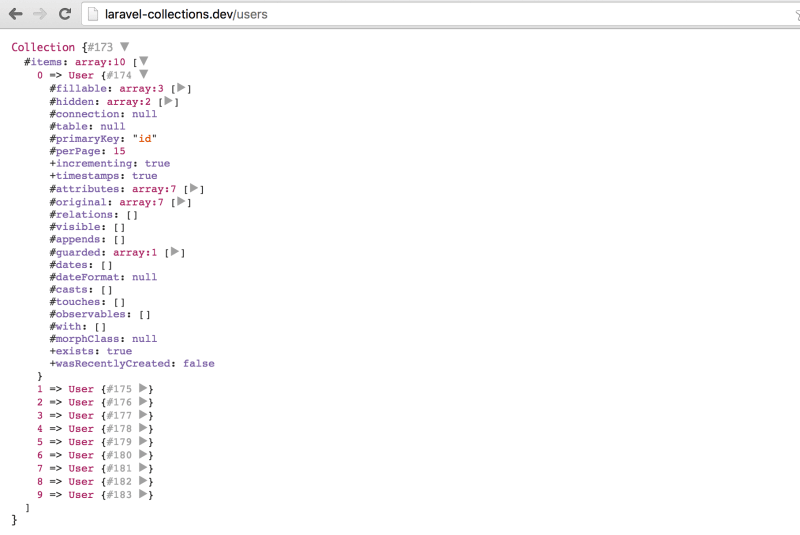
$users = User::all();
dd($users);
}该控制器方法会返回一个如下显示的所有用户的 Laravel 集合。
你可以通过箭头符号便捷的访问集合属性。至于实例,想要获取 $users 集合的第一个用户的名字,我们可以这样做。
/**
* 获取第一个用户的名字
*/
public function firstUser()
{
$user = User::first();
dd($user->name);
}创建我们的示例集合
我们将会使用一些最有用的集合操作技巧,你一定会觉得很好用。
在接下来的几个章节中,我将会用到下面这套用户表的数据以及一些自定义的集合来达到演示的目的。虽然我们这里是手动创建,但使用 Laravel 的模型工厂来创建也是可以的。
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[name] => Chasity Tillman
[email] => qleuschke@example.org
[age] => 51
[created_at] => 2016-06-07 15:50:50
[updated_at] => 2016-06-07 15:50:50
)
...
)查找数据
有多种方法可以在集合中查找数据。
contains
contains() 方法可以传一个单一值,或一组键 / 值对或者一个回调函数,然后它会返回一个布尔值来告知目标内容是否在集合中。
/**
* 判断键 / 值对或回调内容是否存在于集合中
*
*
* @return true or false
*/
public function contains()
{
$users = User::all();
$users->contains('name', 'Chasity Tillman');
//true
$collection = collect(['name' => 'John', 'age' => 23]);
$collection->contains('Jane');
//false
$collection = collect([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
$collection->contains(function ($key, $value) {
return $value <= 5;
//true
});
}where
通过键值对的形式,用 where 方法检索集合.
where () 方法还可以被链式调用。
/**
* 使用 where 方法找到匹配的数据
*
* 通过链式调用来增加匹配条件
*/
public function where()
{
$users = User::all();
$user = $users->where('id', 2);
// 找出 id 为 2 的用户
$user = $users->where('id', 1)
->where('age', '51')
->where('name', 'Chasity Tillman');
// 找出 user 集合中 id 为 1,年龄为 51 岁,名叫 Chasity Tillman 的用户
}还有一些像 where-like 这种用于检索的方法,我就不一一列举的,大家可以通过 Laravel 的官方文档查看。
可以着重看下面几个:
-
whereIn() - 以键值对为参数检索集合,其中值必须是组数。
-
search() - 在一个集合中检索值,如果有值,返回其索引,如果没有,则返回
false。 -
has() - 查看键值对是否存在,返回布尔值。
过滤数据
你可能已经猜到了,用 filter() 方法过滤。
你可能也已经想到了, filter 方法会接收一个回调函数作为参数,在回调函数中做判断的逻辑,对吗?你是这么想的吗?
/**
* 使用 filter 方法,找出所有年龄小于 35 的用户
*/
public function filter()
{
$users = User::all();
$youngsters = $users->filter(function ($value, $key) {
return $value->age < 35;
});
$youngsters->all();
// 所有年龄小于 35 的用户
}filter 方法会接收一个回调函数作为参数,回调函数的参数是键值对,具体筛选的逻辑写在函数里面,并且会返回所有符合条件的值。
这里还用到了 all() 方法,它会返回一个集合里的所有值。
排序 / 排序数据
集合允许我们能够使用两种简单的方法对数据进行排序 :-
sortBy()- 给定数据进行升序排序sortByDesc()- 给定数据降序排序
排序方法接受一个键或回调函数参数用于对集合进行排序。
/**
* 排序方法接受一个键或回调函数参数
* 用于对集合进行排序。
*/
public function sortData()
{
$users = User::all();
$youngestToOldest = $users->sortBy('age');
$youngestToOldest->all();
//列出以年龄升序的所有用户
$movies = collect([
[
'name' => 'Back To The Future',
'releases' => [1985, 1989, 1990]
],
[
'name' => 'Fast and Furious',
'releases' => [2001, 2003, 2006, 2009, 2011, 2013, 2015, 2017]
],
[
'name' => 'Speed',
'releases' => [1994]
]
]);
$mostReleases = $movies->sortByDesc(function ($movie, $key) {
return count($movie['releases']);
});
$mostReleases->toArray();
//列出以上映总数降序排序的电影
dd($mostReleases->values()->toArray());
/*
列出以上映总数降序排序的电影并重置键值
*/
}排序方法维护每个值的键。 虽然这对您的应用程序可能很重要,但您可以通过链式 values() 方法将它们重置为默认的基于零的增量值。
像往常一样,我还使用一个将集合转换为数组的集合方法 toArray() 。
数据 分组
###groupBy
对集合进行分组有助于理解您的数据。 groupBy 方法接受键或回调函数,并根据键值或返回的回调值返回分组集合。
/**
* groupBy 返回基于键或回调函数分组的数据
* 逻辑
*/
public function grouping()
{
$movies = collect([
['name' => 'Back To the Future', 'genre' => 'scifi', 'rating' => 8],
['name' => 'The Matrix', 'genre' => 'fantasy', 'rating' => 9],
['name' => 'The Croods', 'genre' => 'animation', 'rating' => 8],
['name' => 'Zootopia', 'genre' => 'animation', 'rating' => 4],
['name' => 'The Jungle Book', 'genre' => 'fantasy', 'rating' => 5],
]);
$genre = $movies->groupBy('genre');
/*
[
"scifi" => [
["name" => "Back To the Future", "genre" => "scifi", "rating" => 8,],
],
"fantasy" => [
["name" => "The Matrix", "genre" => "fantasy", "rating" => 9,],
["name" => "The Jungle Book", "genre" => "fantasy", "rating" => 5, ],
],
"animation" => [
["name" => "The Croods", "genre" => "animation", "rating" => 8,],
["name" => "Zootopia", "genre" => "animation", "rating" => 4, ],
],
]
*/
$rating = $movies->groupBy(function ($movie, $key) {
return $movie['rating'];
});
/*
[
8 => [
["name" => "Back To the Future", "genre" => "scifi", "rating" => 8,],
["name" => "The Croods", "genre" => "animation", "rating" => 8,],
],
9 => [
["name" => "The Matrix", "genre" => "fantasy", "rating" => 9,],
],
4 => [
["name" => "Zootopia","genre" => "animation", "rating" => 4,],
],
5 => [
["name" => "The Jungle Book","genre" => "fantasy","rating" => 5,],
],
]
*/
}获取数据子集
给定一组数据,然后是一个集合,您可能希望得到它的一部分。 这可能是:
- 前 2 条记录
- 最后 2 条记录
- 除 2 组以外的所有记录。
集合操作帮助我们使用少量的方法完成这些操作。
take
take 方法接受一个整数值并返回指定的项数。给定一个负数,take() 返回集合末尾的指定项数。
/**
* take 方法返回集合中的 n 个项数。
* 给定 -n ,返回最后 n 个项数
*/
public function takeMe()
{
$list = collect([
'Albert', 'Ben', 'Charles', 'Dan', 'Eric', 'Xavier', 'Yuri', 'Zane'
]);
//获取前两个名字
$firstTwo = $list->take(2);
//['Albert', 'Ben']
//获取最后两个名字
$lastTwo = $list->take(-2);
//['Yuri', 'Zane']
}chunk
chunk 方法将集合分割成大小为 n 的较小集合。
/**
* Chunk(n) 返回大小为 n 的较小集合,每个都来自原始集合
*
*/
public function chunkMe()
{
$list = collect([
'Albert', 'Ben', 'Charles', 'Dan', 'Eric', 'Xavier', 'Yuri', 'Zane'
]);
$chunks = $list->chunk(3);
$chunks->toArray();
/*
[
["Albert", "Ben", "Charles",],
[3 => "Dan", 4 => "Eric", 5 => "Xavier",],
[6 => "Yuri", 7 => "Zane",],
]
*/
}这里有很多方法可以达到效果。
当你传递数据到 blade 页面时,你可以将他分块以一次获得 n 行数据,例如,将每 3 个名字装进一行。
@foreach($list->chunk(3) as $names)
<div class="row">
@foreach($names as $name)
{{ $name }}
@endforeach
</div>
@endforeach你也可以使用 collapse() 方法将更新的集合组转成一个大的集合,来反转 chunk 方法,请查看此 here.
遍历数据
map
map 方法会遍历集合,将每个元素传入一个闭包函数,该闭包函数的返回值将替换原来的元素值。
我们创建一个由名字组成的集合,并使用 map 方法返回一个由对应名字长度组成的集合。
/**
* map function iterates a collection through a callback
* function and performs an operation on each value.
*/
public function mapMe()
{
$names = collect([
'Albert', 'Ben', 'Charles', 'Dan', 'Eric', 'Xavier', 'Yuri', 'Zane'
]);
$lengths = $names->map(function ($name, $key) {
return strlen($name);
});
$lengths->toArray();
//[6, 3, 7, 3, 4, 6, 4, 4,]
}transform
虽然 map 方法创建了一个新的集合,但有时候你可能想去修改原始的集合内容。transform 提供了一个回调方法,并对同一个集合进行操作。
因为转换不会产生新的集合,所以你无需把它赋给新的值。
/**
* Transform 操作原始的集合。
*/
public function transformMe()
{
$names = collect([
'Albert', 'Ben', 'Charles', 'Dan', 'Eric', 'Xavier', 'Yuri', 'Zane'
]);
$names->transform(function ($name, $key) {
return strlen($name);
});
$names->toArray();
//[6, 3, 7, 3, 4, 6, 4, 4,]
}reduce
不同于 map 和 transform 方法,reduce 方法返回单个值。他将每次迭代的结果传给下一次迭代。
例如,为了获取一个集合中所有整数的和,reduce 会传递后续数字的总和,并迭代的将结果添加到下一个数字。
/**
* 获取一个集合中所有数字的和
*/
public function reduceMe()
{
$numbers = collect([
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
]);
$sum = $numbers->reduce(function ($sum, $number) {
return $sum + $number;
});
//55
}each
each 方法通过回调函数传递每个数据项。
关于 each 方法最有趣的部分是,你可以简单的在回调函数中返回 false 来跳出循环。
/**
*打印小于等于五的一列数字
*
*/
public function eachMethod()
{
$numbers = collect([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]);
$smallNumbers = $numbers->each(function ($num, $key) {
if ($num > 5) {
return false;
}
echo $num .", ";
});
//1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
}every
every 方法创建一个由集合中每第 n 个元素组成的新集合。
集合论
Laravel 提供了对集合论的支持,这意味着我们可以对两个不同集合取交集、并集等操作。
union
union 方法将给定的数组添加到集合。如果给定的数组含有与原集合一样的键,则原集合的值不会被改变:
/**
* add array values to a collection using union
*/
public function union()
{
$coolPeople = collect([
1 => 'John', 2 => 'James', 3 => 'Jack'
]);
$allCoolPeople = $coolPeople->union([
4 => 'Sarah', 1 => 'Susan', 5 =>'Seyi'
]);
$allCoolPeople->all();
/*
[
1 => "John", 2 => "James", 3 => "Jack", 4 => "Sarah", 5 => "Seyi",
]
*/
}intersect
intersect () 方法接收一个数组或集合作为参数,该方法会将集合中那些不包含在传入参数的元素移除。
/**
* Return a list of very cool people in collection that
* are in the given array
*/
public function intersect()
{
$coolPeople = collect([
1 => 'John', 2 => 'James', 3 => 'Jack'
]);
$veryCoolPeople = $coolPeople->intersect(['Sarah', 'John', 'James']);
$veryCoolPeople->toArray();
//[1 => "John" 2 => "James"]
}可以发现, intersect 方法的返回值保留了原有的键。
结论
我试图涵盖你可能找到你能自己找到所需的集合方法,但这仍然有太多需要学的。
最值得注意的,我留下以下内容
在 Laravel 文档 和 Laravel API 文档 上还有你可以用于操作集合的更多方法,或许你想查看一下。
要跟进本教程代码,查看 gtihub 仓库 here。随意贡献你的代码。
posted on 2021-03-04 00:01 shenzen_小白 阅读(974) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报