tensorboard 可视化的训练
1. 使用 with tf.name_scope('layer') 加标签
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): with tf.name_scope('layer'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): Weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W') # 初始权重随机 with tf.name_scope('biases'): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b') # biases推荐不为0,所以需要加上0.1 with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weight), biases) # 激活前 if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs
2. pycharm terminal 中进入project目录
输入 tensorboard --logdir=logs
将得到的网址 http://DESKTOP-V7I30OQ:6006 输入浏览器,即可得到
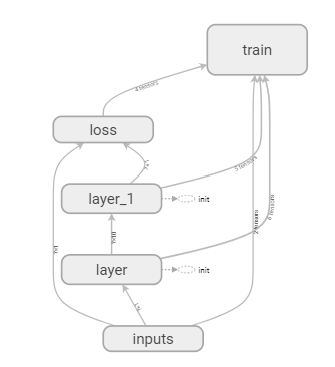
3. 查看weight、biases、loss
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+'/weights', Weight) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) merged = tf.summary.merge_all() # 打包 result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) writer.add_summary(result, i) # 每i步画一个点
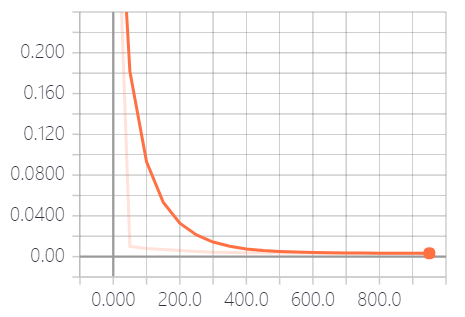
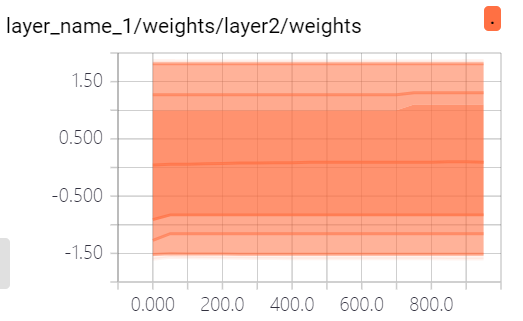
4. 参考代码
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, n_layer, activation_function=None): layer_name = 'layer%s' % n_layer with tf.name_scope('layer_name'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): Weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W') # 初始权重随机 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+'/weights', Weight) with tf.name_scope('biases'): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b') # biases推荐不为0,所以需要加上0.1 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weight), biases) # 激活前 if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs) return outputs # 数据准备 x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis] # 生成[-1,1]之间的300个数,组成300行的一个数组 noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) # mean = 0;std = 0.05; 格式:x_data y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise # y = x^2 - 0.5 with tf.name_scope('inputs'): xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_input') # None表示sample数量任意 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_input') # 搭建神经网络 # 由于输入一维,输出一维,所以我们定义的神经网络为输入层一个神经元,输出层一个神经元,中间隐藏层10个神经元 l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, n_layer=1, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) # 隐藏层 prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, n_layer=2, activation_function=None) # 输出层 # 计算损失函数 with tf.name_scope('loss'): loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # 距离平方求和求平均,reduction_indices表示数据处理的维度 tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) # 训练 with tf.name_scope('train'): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) # learning rate = 0.1 # 初始化 init = tf.initialize_all_variables() # 初始化所有变量 sess = tf.Session() merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph) sess.run(init) # 可视化输出 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1) ax.scatter(x_data, y_data) plt.ion() # 保证连续输出 for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: # 每50个数据输出一次 try: # 为了避免第一次remove时报错 ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) except Exception: pass prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5) plt.pause(0.1) # 暂停0.1秒 result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) writer.add_summary(result, i) # 每i步画一个点



