PostgreSQL-建表-查询-自定义函数--(一)
学习初期,有目标学习有效果,同事给了几个题,这样有目标的去练习学习;
题目如下:
使用 PostgreSQL 数据库
使用语句创建表和字段
1. 新增订单表 和 物流表
订单表:订单号、订单数量、商品名称、商品型号、售价、订单生成时间
物流表:物流号、省、市、区、地址、收货人、手机号
2.订单表和物流表使用用订单号进行关联
3.查询所销售商品的金额总和
4.按订单时间倒序排列所有订单
5.查询消费金额最多的省
6.创建一个自定义函数返回物流表中的所有省数据,并调用自定义函数查询所有省数据;
以上的内容,涉及到了建表,建字段,插入数据,查询,自定义函数的使用;
练习后结果如下:
1. 新增订单表 和 物流表
订单表:订单号、订单数量、商品名称、商品型号、单价、订单生成时间
物流表:物流号、省、市、区、地址、收货人、手机号
2.订单表和物流表使用用订单号进行关联
1和2,用以下语句实现;注意字段语句后面都带有逗号;‘,’
create table order_master( // 建订单表:表名为 order_master
id int primary key not null unique, // 订单号:表中第一个字段名为:id;primary key 代表设置字段 id为主键; not null 代表 字段不可为空,unique 代表 字段唯一不可重复;
number int not null, // 订单数量:表中第二个字段名为:number; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
goodsname text not null, // 商品数量:表中第三个字段名为:goodsname; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
goodstype text not null, // 商品型号:表中第四个字段名为:goodstype; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
goodsprice money not null, // 单价:表中第五个字段名为:goodsprice; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
loaddate date not null // 订单生成时间:表中第六个字段名为:loaddate; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
)
create table logistics ( // 建物流表:表名为 logistics
Logistics varchar not null, // 物流号:表中第一个字段名为:Logistics ;varchar 字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
province text not null, // 省:表中第二个字段名为:province ;text字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
city text not null, // 市:表中第三个字段名为:city;text字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
area text not null, // 区:表中第四个字段名为:area;text字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
address text not null, // 地址:表中第五个字段名为:address ;text字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
consignee text not null, // 收货人:表中第六个字段名为:consignee ;text字段类型; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
phonenumber char(11) not null, // 电话:表中第七个字段名为:phonenumber ;char(11)字段类型,且11位; not null 代表 字段不可为空;
id_d INT references ORDER_MASTER(ID) // 表中 id_d字段,int类型,与 ORDER_MASTER表中的字段(ID)为外键
)


3.查询所销售商品的金额总和
金额总和=订单数量*售价,再求所有订单号的结果总和
select sum(number*goodsprice) from order_master;

4.按订单时间倒序排列所有订单
语法例子:SELECT column-list FROM table_name [WHERE condition] [ORDER BY column1, column2, .. columnN] [ASC | DESC];
用 DESC 表示按倒序排序(即:从大到小排序) ---降序排列
用 ACS 表示按正序排序(即:从小到大排序)---升序排列
最终语句:
select * from order_master order by loaddate DESC; //order by 按照xxx排序;按照时间倒序排列;

5.查询消费金额最多的省
首先,两个表用left join,合并成一个表来展示内容;
select * from order_master left join logistics on order_master.id= logistics.id_d;
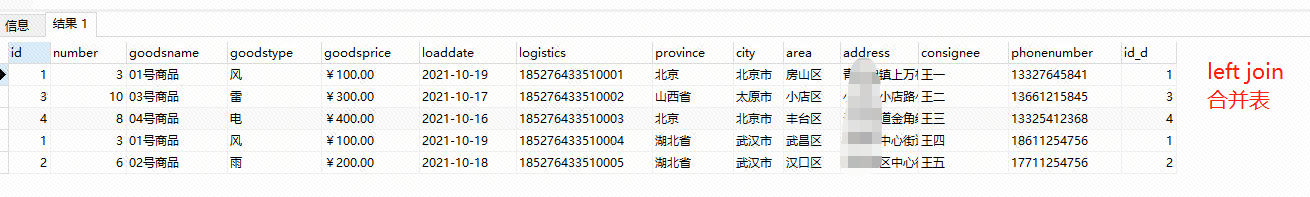
合并之后,我们来计算消费金额,消费金额=number*goodsprice
因为每个订单,至是单省的销售情况,所以这里要消费金额最多的省,
首先,相同省份的消费金额,要加起来展示,所以这里是:sum(number*goodsprice)
第二步:消费金额最多的省,也就是要按照金额进行倒序排列;这里有两个关键词,一个是按照省份来分组,一个是按照金额多少来排序;
所以用到 group by province; order by 消费金额;
第三步:经过第二步扩展后,语句如下 ,这里用到了一个别名的概念,详细见下面的说明部分;
select sum(number*goodsprice) as je from order_master t left join logistics a on id = a.id_d group by province order by je desc;
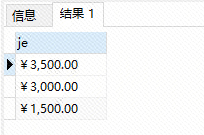 这里金额是按照排序显示出来了,但是没有省份数据,现在加上省份的数据
这里金额是按照排序显示出来了,但是没有省份数据,现在加上省份的数据
第四步:增加省份数据;
这个还在尝试中,后面成功了补上来;
select concat (concat(province),concat(sum(number*goodsprice)) ) as je from order_master t left join logistics a on id = a.id_d group by province order by je desc;
用到了concat
结果:
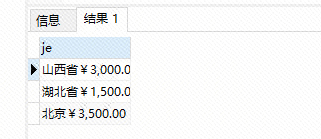
跟预期有点差别,最好是分成两个字段展示,继续研究,回头补上;
说明:
这里用到了别名这个概念; 这里je是金额的别名=sum(number*goodsprice)
order_master 别名:t; logistics 别名: a;
说明:这里首先把两个表合并一下,利用order_master表的id=logistics表的id_d;其中 id 是order_master的主键,id_d 是logistics表的外键;且他两对应;
首先合并使用的是left join
left join 使用方法如下:select * from order_master left join logistics on order_master.id= logistics.id_d;
这里注意:把order_master表也就是左表,返回加入(join)到logistics表中;依据是两个表的主外键;
注意点2:在id和id_d这里,表名.id=表名.id_d,表名和字段名中间,有个点儿;
语法:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
6.创建一个自定义函数返回物流表中的所有省数据,并调用自定义函数查询所有省数据;
说明:
create or replace function ss() // 建一个名字为ss的自定义函数
returns varchar as // returns 理解为返回一个xxxx类型的结果;xxxx是返回的字段的类型,我这里是varchar的;
$$ // 理解为固定写法
select province from logistics; // 从logistics表里获取省份数据;
$$ LANGUAGE SQL; // 理解为固定写法
---------------------------以上,就是完成了一个自定义函数设定;设定了一个名字是ss的自定义函数,这个函数的返回值是varchar型的,返回的内容就是 从logistics表里获取省份数据;
select * from ss(); // 调用自定义函数,查询所有的省数据;
执行结果:
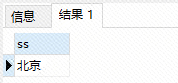
这里有个说明:
关于 SETOF ,这个加到returns后面,如下;如果不加SETOF,则返回查询结果的第一条数据,加上之后,返回所有数据;
关于多次执行:因为执行一次之后,就已经建立了ss的自定义函数,所以这里如果继续执行这段内容,就会提示已经有了ss的自定义函数了,这里就改个名字,然后执行就可以了;
create or replace function ss1()
returns setof varchar as
$$
select province from logistics;
$$ LANGUAGE SQL;
select * from ss1();
执行结果:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号