二叉树
一.概念
二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。
一棵深度为k,且有2^k-1个结点的二叉树,称为满二叉树。这种树的特点是每一层上的结点数都是最大结点数。而在一棵二叉树中,除最后一层外,若其余层都是满的,并且或者最后一层是满的,或者是在右边缺少连续若干结点,则此二叉树为完全二叉树。具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为floor(log2n)+1。深度为k的完全二叉树,至少有2k-1个叶子结点,至多有2k-1个结点。
定义
树(tree)是包含n(n>=0)个结点的有穷集,其中:
(1)每个元素称为结点(node);
(2)有一个特定的结点被称为根结点或树根(root)。
(3)除根结点之外的其余数据元素被分为m(m≥0)个互不相交的集合T1,T2,……Tm-1,其中每一个集合Ti(1<=i<=m)本身也是一棵树,被称作原树的子树(subtree)。
树也可以这样定义:树是由根结点和若干颗子树构成的。树是由一个集合以及在该集合上定义的一种关系构成的。集合中的元素称为树的结点,所定义的关系称为父子关系。父子关系在树的结点之间建立了一个层次结构。在这种层次结构中有一个结点具有特殊的地位,这个结点称为该树的根结点,或称为树根。
我们可以形式地给出树的递归定义如下:
单个结点是一棵树,树根就是该结点本身。
设T1,T2,..,Tk是树,它们的根结点分别为n1,n2,..,nk。用一个新结点n作为n1,n2,..,nk的父亲,则得到一棵新树,结点n就是新树的根。我们称n1,n2,..,nk为一组兄弟结点,它们都是结点n的子结点。我们还称T1,T2,..,Tk为结点n的子树。
空集合也是树,称为空树。空树中没有结点。
结点的度:一个结点含有的子结点的个数称为该结点的度;
叶结点或终端结点:度为0的结点称为叶结点;
非终端结点或分支结点:度不为0的结点;
双亲结点或父结点:若一个结点含有子结点,则这个结点称为其子结点的父结点;
孩子结点或子结点:一个结点含有的子树的根结点称为该结点的子结点;
兄弟结点:具有相同父结点的结点互称为兄弟结点;
树的度:一棵树中,最大的结点的度称为树的度;
结点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子结点为第2层,以此类推;
树的高度或深度:树中结点的最大层次;
堂兄弟结点:双亲在同一层的结点互为堂兄弟;
结点的祖先:从根到该结点所经分支上的所有结点;
子孙:以某结点为根的子树中任一结点都称为该结点的子孙。
森林:由m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
种类
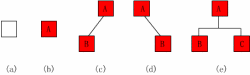
(1)空二叉树——如图(a);
(3)只有左子树——如图(c);
(4)只有右子树——如图(d);
(5)完全二叉树——如图(e)。
注意:尽管二叉树与树有许多相似之处,但二叉树不是树的特殊情形。
类型
(2)满二叉树——除了叶结点外每一个结点都有左右子叶且叶子结点都处在最底层的二叉树。
二.代码实现
1.设计数的结点
(1)包括前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、删除节点
public class Hero { int no; String name; Hero left;//null Hero right;//null public Hero(int no, String name) { this.no = no; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Hero{" + "no=" + no + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } /*前序遍历的方法*/ public void preOrder(){ System.out.println(this);//输出父节点 if (this.left!=null){//如果左节点不为空,进行左递归前序遍历 this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){//如果右节点不为空,进行右递归前序遍历 this.right.preOrder(); } } /*中序遍历的方法*/ public void infixOrder(){ if (this.left!=null){//如果左节点不为空,进行左递归中序遍历 this.left.infixOrder(); } System.out.println(this);//输出父节点 if (this.right!=null){//如果右节点不为空,进行右递归中序遍历 this.right.infixOrder(); } } /*后序遍历的方法*/ public void postOrder(){ if (this.left!=null){//如果左节点不为空,进行左递后序遍历 this.left.postOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){//如果右节点不为空,进行右递归后序遍历 this.right.postOrder(); } System.out.println(this);//输出父节点 } /*前序遍历查找*/ public Hero preOrderSearch(int no){ System.out.println("进入前序"); //比较当前节点 if (this.no==no){ return this; } Hero resNode = null; if (this.left!=null){//左节点是否为空,进行递归前序查找 resNode =this.left.preOrderSearch(no); } if (resNode!=null){//左子树找到 return resNode; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no); } return resNode; } /*中序遍历查找*/ public Hero infixOrderSearch(int no){ Hero resNode = null; if (this.left!=null){//左节点是否为空,进行递归前序查找 resNode =this.left.infixOrderSearch(no); } if (resNode!=null){//左子树找到 return resNode; } //比较当前节点 if (this.no==no){ return this; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no); } return resNode; } /*后序遍历查找*/ public Hero postOrderSearch(int no){ Hero resNode = null; if (this.left!=null){//左节点是否为空,进行递归前序查找 resNode =this.left.infixOrderSearch(no); } if (resNode!=null){//左子树找到 return resNode; } if (this.right!=null){ resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no); } if (resNode!=null){//左子树找到 return resNode; } /*左右子树都没有找到*/ //比较当前节点 if (this.no==no){ return this; } return resNode; } /*删除节点 * 1.如果是父节点删除子树 * 2.否:直接删除*/ public void delNode(int no){ if (this.left!=null && this.left.no==no){ this.left=null; return; } //判断删除右子树 if (this.right!=null&& this.right.no==no){ this.right= null; return; } //递归向左子树查找 if (this.left!=null){ this.left.delNode(no); } //递归右子树 if (this.right!=null){ this.right.delNode(no); } } }
2.创建二叉树
public class BinaryTree { /* 1.创建二叉树 * 2.前序遍历 * 2.1先输出父节点(初始为root) * 2.2如果左节点不为空,进行左递归前序遍历 * 2.3如果右节点不为空,进行右递归前序遍历 * 3.中序遍历 * 3.1当前左节点不为空,进行左递归中序遍历 * 3.2输出当前节点 * 3.3如果右节点不为空,进行右递归中序遍历 * 4.后序遍历 * 4.1当前左节点不为空,进行左递归中序遍历 * 4.2如果右节点不为空,进行右递归中序遍历 * 4.3输出当前节点*/ private Hero root; public void setRoot(Hero root){ this.root=root; } /*前序遍历的方法*/ public void preOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.preOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空无法遍历"); } } /*中序遍历的方法*/ public void infixOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.infixOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空无法遍历"); } } /*后序遍历的方法*/ public void postOrder(){ if (this.root!=null){ this.root.postOrder(); }else { System.out.println("二叉树为空无法遍历"); } } /*查找思路 * 1.先判断当前节点的no是否=要查找的 * 2.如果相等,返回当前节点 * 3.不相等 * 3.1左节点是否为空,进行递归前序查找 * * 3.2右节点是否为空,进行递归前序查找 * */ /*前序遍历查找*/ public Hero preOrderSearch(int no){ if (root!=null){ return root.preOrderSearch(no); }else { return null; } } /*中序遍历查找*/ public Hero infixOrderSearch(int no){ if (root!=null){ return root.infixOrderSearch(no); }else { return null; } } /*后序遍历查找*/ public Hero postOrderSearch(int no){ if (root!=null){ return root.postOrderSearch(no); }else { return null; } } /*删除节点*/ public void delNode(int no){ if (root!=null){ //如果恰好为root节点清空二叉树 if (root.no ==no){ root = null; }else { root.delNode(no); } } } }
3.进行测试
public class BinaryTreeDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); Hero root = new Hero(1,"宋江"); Hero hero2 = new Hero(2,"吴用"); Hero hero3 = new Hero(3,"卢俊义"); Hero hero4 = new Hero(4,"林冲"); Hero hero5 = new Hero(5,"关胜"); /*手动创建二叉树 和递归方式创建二叉树*/ root.left=hero2; root.right=hero3; hero3.right=hero4; hero3.left=hero5; binaryTree.setRoot(root); /* *//*前序遍历*//* System.out.println("前序遍历:");//1.2.3.5.4 binaryTree.preOrder(); *//*中序遍历*//* System.out.println("中序遍历");//2.1.5.3.4 binaryTree.infixOrder(); *//*后序遍历*//* System.out.println("后序遍历:");//2.5.4.3.1 binaryTree.postOrder();*/ /*前序查找*/ /*System.out.println("前序查找:"); Hero res = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5); if (res!=null){ System.out.printf("找到了,信息为no= %d name=%s\n",res.no,res.name); }else { System.out.println("没有找到"); } //中序查找 System.out.println("中序查找:"); Hero res1 = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(5); if (res1!=null){ System.out.printf("找到了,信息为no= %d name=%s\n",res1.no,res1.name); }else { System.out.println("没有找到"); } //后序查找 System.out.println("后序查找:"); Hero res2 = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(5); if (res2!=null){ System.out.printf("找到了,信息为no= %d name=%s\n",res2.no,res2.name); }else { System.out.println("没有找到"); }*/ //删除节点 binaryTree.delNode(3); binaryTree.preOrder(); }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构