【Spring】Spring和SpringMVC项目父子容器下Spring事务不生效问题 & SSM框架中,事务无法回滚的原因和解决
Spring + Spring MVC +Mybatis架构下,事务无法回滚的原因和解决
1.首先原理图
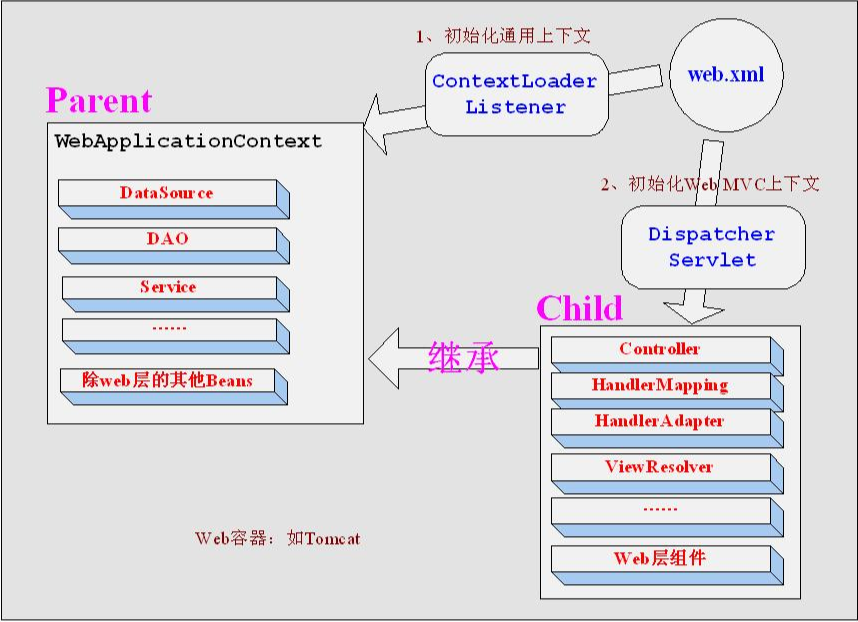
2. 父子容器下为什么事务不生效
①第一阶段 -- 容器初始化 一个项目中既有Spring,又有Spring MVC的情况下,默认web.xml配置如下。 Web容器(一般是Tomcate)启动,加载web.xml,就会开始上下文的加载。 1>先加载applicationContext.xml,完成Spring容器的初始化。 2>后加载springMVC-servlet.xml,完成Spring MVC容器的初始化。 3>由于一般情况下,两个xml文件中都会配置<context-conpent-scan>,即会开启注解的扫描。 4>因此,Spring容器和Spring MVC容器就都会扫描到 以@Conpent、@Controller、@Service、@Repository等作用在类上生效的注解管理的Bean ②第二阶段 -- 父子容器调用关系 再来理解父子容器的关系: 用一句话来理解,儿子可以继承并使用老子的资产,但儿子的财产一般不给老子用。 父子容器关系如此,Spring MVC作为子容器,是可以用到Spring父容器的Bean,反之父容器的Bean无法调用子容器的Bean. 5>Spring容器,父容器。 一般声明式事务的开启是在Spring容器中, 因此Spring容器里面扫描到的@Service声明的Bean,才有了底层AOP动态代理的支持,它就有事务的增强。 而Spring MVC子容器也有注解扫描能力,也扫描到了@Service标注的Bean,但是这个Bean只是一个原始的Bean,并没有事务增强的能力。 6>Spring MVC容器,子容器。 由于DispacherServlet作为前端控制器的存在,因此默认由它接收到来自前端的HTTP请求,并通过@RequestMapping等定位到url地址,进入由Spring MVC子容器扫描到的@Controller中。 ③第三阶段 -- 那怎么会出现事务不生效呢? 7>Spring MVC容器的@Controller Bean,通过@Autowired或@Resource注解注入了@Service, 但它默认注入的,是Spring MVC容器扫描到的没有 事务增强能力的 普通Bean. 8>因此,这种情况下,就出现了事务不生效的问题。
<!-- 加载spring容器 --> <!-- 初始化加载application.xml的各种配置文件 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/application-*.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 配置springmvc前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>taotao-manager</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- contextConfigLocation不是必须的, 如果不配置contextConfigLocation, springmvc的配置文件默认在:WEB-INF/servlet的name+"-servlet.xml" --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet>
3. 怎么解决父子容器下事务不生效
解决方案1:
1.在主容器中(applicationContext.xml),将Controller的注解排除掉:
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
</context:component-scan>
2.而在springMVC配置文件中将Service注解给去掉:
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service" />
</context:component-scan>
3. 最终达到效果,就是@Controller Bean只在Spring MVC容器,@Service Bean只在Spring父容器
如此。通过@Controller Bean调用 @Service的Bean
就只能找到Spring父容器中的Bean,也就只能找到那个 被事务增强了的 @Service。
事务就可以生效了。
解决方案2:
取消 @Service 注解标注 Bean的方式,
使用XML配置的方式去 完成 Service类的Bean的配置
这样做,就导致SpringMVC子容器无法扫描到Service管理的Bean,只能将Service类的Bean交给Spring容器ServletContextListener去管理了。
这样,同样保证了 Service类的Bean只在Spring容器中,有了事务增强。
以下参考文章转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiesir/p/11058541.html
另参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34126557/article/details/92250009
=========================================================
原因:
由ServletContextListener加载spring配置文件产生的是父容器,springMVC产生的是子容器,子容器对Controller进行扫描装配时装配了@Service注解的实例,而该实例理应由父容器进行初始化以保证事务的增强处理。所以此时得到的将是原样的Service(没有经过事务加强处理),故而没有事务处理能力。
第一种解决办法:
1.在主容器中(applicationContext.xml),将Controller的注解排除掉:
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
</context:component-scan>
2.而在springMVC配置文件中将Service注解给去掉:
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service" />
</context:component-scan>
第二种解决办法:
将service层改用xml配置,其实这样做也是变相的让springmvc无法扫描service,而只能依赖父窗口也就是ServletContextListener来进行初始化,这样同样被赋予了事务性。
Spring和SpringMVC的父子容器关系
1.讲问题之前要先明白一个关系
一般来说,我们在整合spring和SpringMVC这两个框架中,web.xml会这样写到:
1 <!-- 加载spring容器 --> 2 <!-- 初始化加载application.xml的各种配置文件 --> 3 <context-param> 4 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 5 <param-value>classpath:spring/application-*.xml</param-value> 6 </context-param> 7 <listener> 8 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 9 </listener> 10 11 <!-- 配置springmvc前端控制器 --> 12 <servlet> 13 <servlet-name>taotao-manager</servlet-name> 14 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 15 <!-- contextConfigLocation不是必须的, 如果不配置contextConfigLocation, 16 springmvc的配置文件默认在:WEB-INF/servlet的name+"-servlet.xml" --> 17 <init-param> 18 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 19 <param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value> 20 </init-param> 21 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 22 </servlet>
首先配置的是Spring容器的初始化加载的application文件,然后是SpringMVC的前端控制器(DispatchServlet),当配置完DispatchServlet后会在Spring容器中创建一个新的容器。其实这是两个容器,Spring作为父容器,SpringMVC作为子容器。
让我们用图来看一下这个父子关系的原理:

平时我们在项目中注入关系是这样的顺序(结合图来说):在Service中注入Dao(初始化自动注入,利用@Autowired),接着在Controller里注入Service(初始化自动注入,利用@Autowired),看图,这就意味这作为SpringMVC的子容器是可以访问父容器Spring对象的。
那么问大家一个问题。要是反过来呢,你把Controller注入到Service中能行么?
肯定是不行的啊!(如图,这也说明了父容器是不能调用子容器对象的)
如果Dao,Serive,Controller要是都在Spring容器中,无疑上边的问题是肯定的,因为都是在一个bean里,一个容器中。
2.如果只用Spring容器,直接把所有层放入Spring容器中可不可以?
例如:一个项目中我总项目的名字叫com.shop,我们在配置applicationContext-service.xml中,包扫描代码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 ...../ 此处省略> 5 6 <!-- 扫描包Service实现类 --> 7 <context:component-scan base-package="com.shop.service"></context:component-scan> 8 </beans>
上面所配置的是一个局部扫描,而不是全局扫描。接下来说原因:
这里就和上面讲到的父子容器有关系,假设我们做了全局扫描那么代码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 ...../ 此处省略> 5 6 <!-- 扫描包Service实现类 --> 7 <context:component-scan base-package="com.shop"></context:component-scan> 8 </beans>
此时的Spring容器中就会扫描到@Controller,@Service,@Reposity,@Component,此时的图如下:
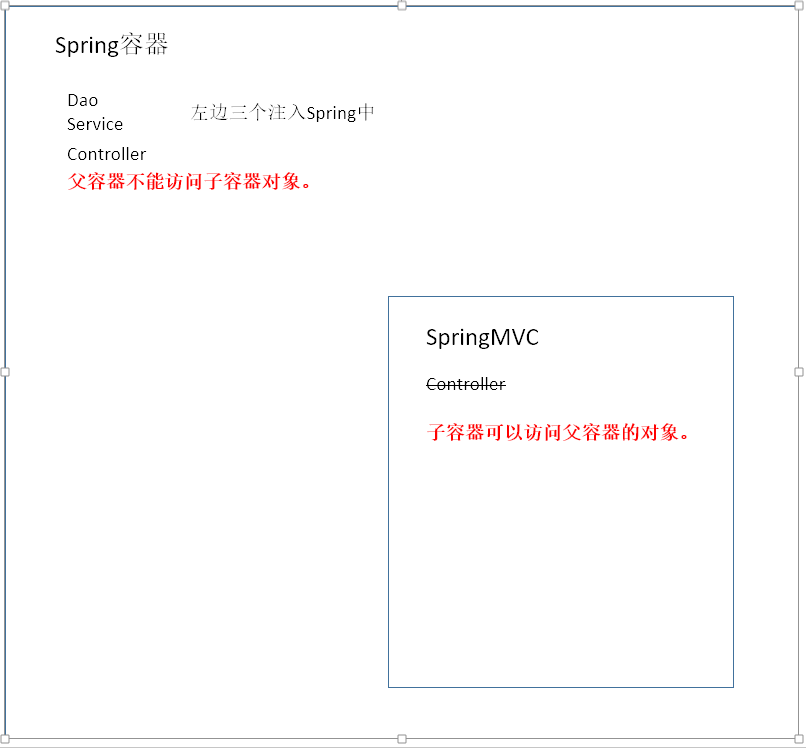
结合图去看,相当于他们都会放到大的容器中,而这时的SpringMVC容器中没有对象,没有对象就没有Controller,所以加载处理器,适配器的时候就会找不到映射对象,映射关系,因此在页面上就会出现404的错误。
3.如果不用Spring容器,直接把所有层放入SpringMVC容器中可不可以?
当然可以,如果没有Spring容器,我们是可以把所有层放入SpringMVC的。单独使用这个容器是完全可以的,而且是轻量级的。就是直接把所有的层次关系都放到了SpringMVC中,并没有用到Spring容器。
4.那么为什么我们在项目中还要联合用到Spring容器和SpringMVC容器?
答案是:Spring的扩展性,如果要是项目需要加入Struts等可以整合进来,便于扩展框架。如果要是为了快,为了方便开发,完全可以用SpringMVC框架。
疑问一: 单例的bean在父子容器中存在一个实例还是两个实例?
答:初始化两次,Spring 容器先初始化bean,MVC容器再初始化bean,所以应该是两个bean。
疑问二:为啥不把所有bean 都在子容器中扫描?
答: 网上很多文章说子容器不支持AOP,其实这是不对的。因为正常会有AOP的相关配置都在Spring容器中配置,如果都迁移到MVC配置文件,则所有bean都在子容器中,相当于只有一个容器了,所以也就实现了AOP。缺点是不利于扩展。
5.以上是传统型SSM(spring+springmvc+mybatis)配置时,父类容器负责扫描装配service层和dao层,子类容器负责扫描装配controller层,但是在轻量化的javaEE开发中,我们可以不用spring框架,只是利用spinrgmvc+mybatis即可
具体操作:不使用listener监听器来加载spring的配置文件,只使用DispatcherServlet来加载spring的配置,不要父子上下文,只使用一个DispatcherServlet。将原本应该放在父容器中的数据源、服务层、DAO层、事务的Bean、以及子容器controller的Bean都放在子上下文容器中,这样也可以实现事务。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
2019-01-02 【elasticsearch】关于elasticSearch的基础概念了解【转载】