SSM-springMVC
springMVC完成表现层的开发

servlet能做的事情,springMVC都能做。servlet用来接收请求参数,参数响应结果,springMVC也可以做到这些


springMVC简介

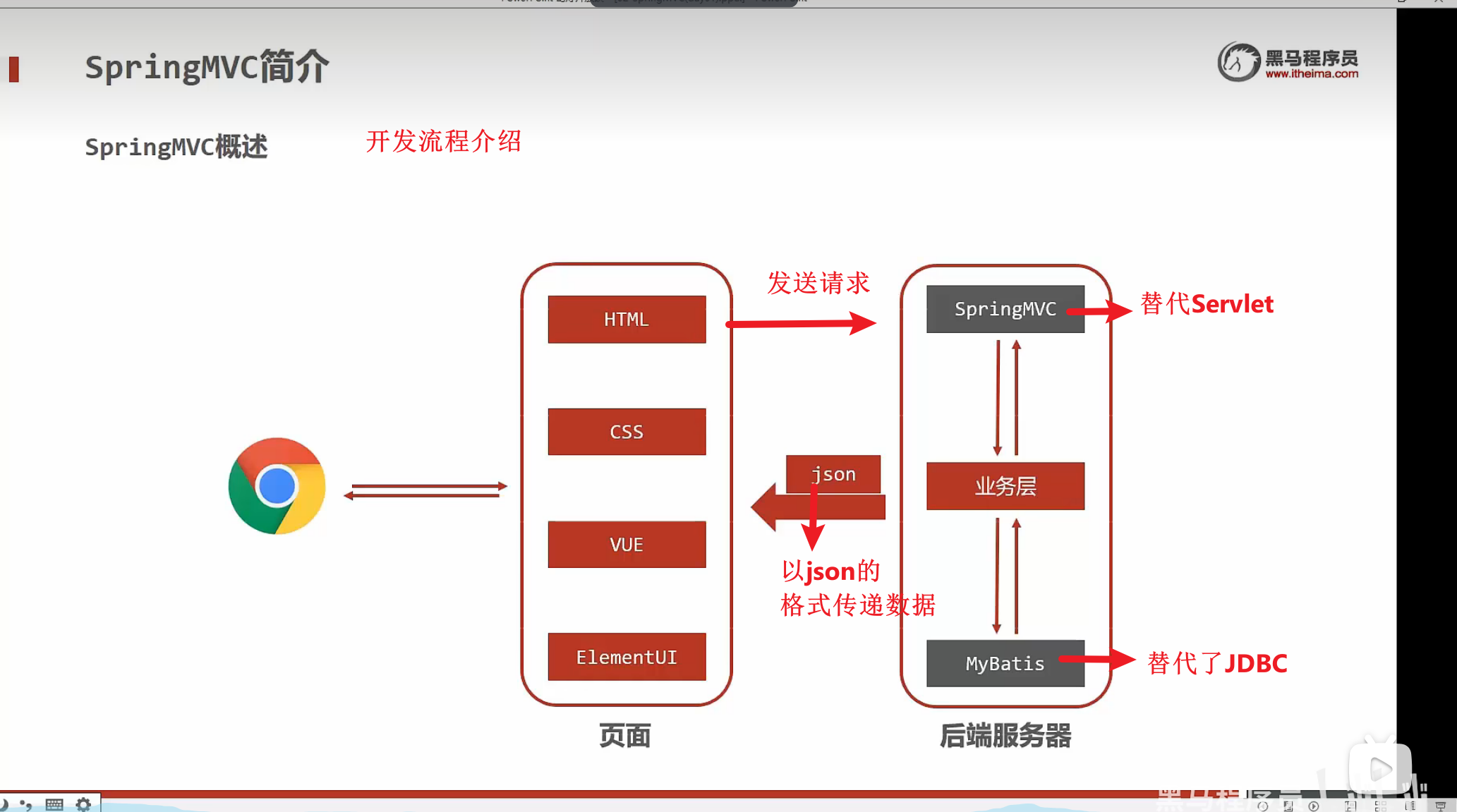
- MVC模型
![]()


springMVC入门案例

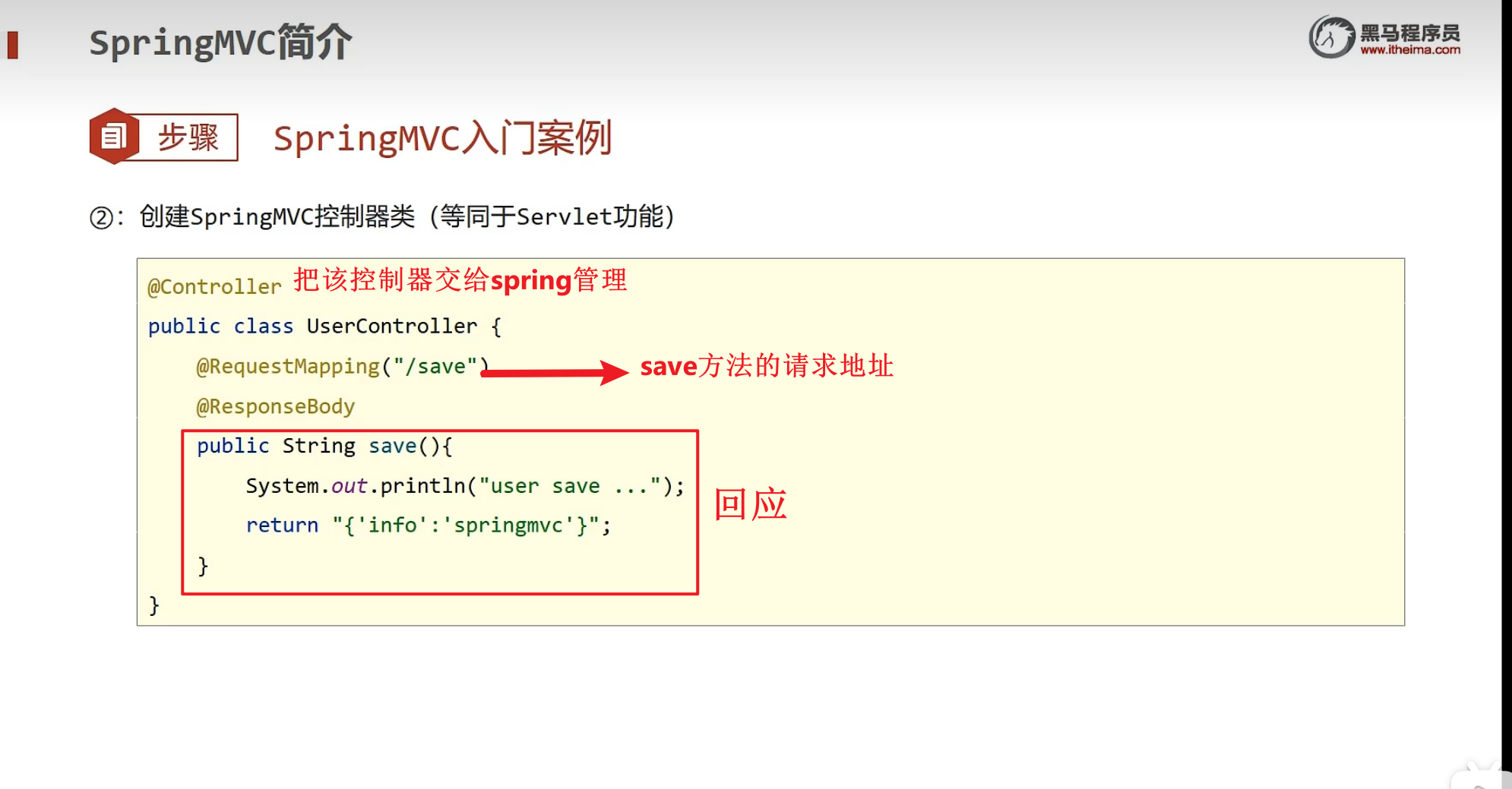


按照上面说的步骤来构建项目
-
1.导入依赖
![]()
-
2.制作控制器
-
4.创建sevlet容器的配置类,由tomcat负责加载并创建servlet容器(替代web.xml)
-
注意
![]()
-
第一步
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_01_quickstart</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!--第一步导入依赖-->
<!--springmvc底层使用的是servlet-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope><!--避免和tomcat冲突-->
</dependency>
<!--里面已经集成了spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--Tomcat7-maven-plugin这个插件可以快速配置并部署和启动web工程(这里没有使用,没有学习过)-->
<!--<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>-->
</project>
- 第二部
package com.itheima.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
//第二步:定义controller
@Controller//2.1 将控制器将给spring管理
public class UserController {
//2.2设置当前方法的访问路径
@RequestMapping("/save")
//2.3设置当前操作的返回值(以save方法的返回值作为返回值)
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save....");
return "{'module':'springmvc'}";//以joson的形式返回数据
}
}
- 第三步
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
//springmvc的配置类(其实就是spring的配置类)
//第三步:创建springMvc的配置文件,并加载对应的bean
@Configuration//配置类
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")//组件扫描
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
- 第四步,让tomcat加载springmvc配置文件,创建出servlet容器(替代web.xml)
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer;
//第四步:一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring配置(替代web.xml文件)
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
//加载springmvc容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
//设置哪些请求归属springmvc处理
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };//所有请求都交给springmvc处理
}
//加载spring容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
return null;
}
}
当我们访问时将返回下面的结果

- 总结
![]()
入门案例工作流程


bean加载控制


对应的方案

- 具体方案
![]()
- 注意
![]()
- 2种方案
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
@Configuration
//@ComponentScan({"com.itheima.dao", "com.itheima.service"})//精确扫描
@ComponentScan(value = "com.itheima",excludeFilters =@ComponentScan.Filter//使用不包含过滤器
(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,//按照注解进行过滤
classes = Configuration.class))//带有Configuration注解的类将不进行扫描
public class SpringConfig {
}
此时我们在仅仅加载spring的配置文件时,在获得controller的bean的时候将会报错(因为他的类并没有被加载)


此时我们就可以在tomcat启动的时候同时加载springconfig和springmvc了
- 此时服务器加载的配置类就是:
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer;
//第四步:一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring配置(替代web.xml文件)
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
//加载springmvc容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
//设置哪些请求归属springmvc处理
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };//所有请求都交给springmvc处理
}
//加载spring容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
}


- 我们只需要传入各自的配置文件就可以了,不需要自己创建容器了
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer;
//第四步:一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring配置(替代web.xml文件)
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}
postMan工具介绍

- 需要先创建一个工作空间
![]()
![]()
![]()
总结来说postman可以模拟浏览器向我的服务器发送请求,使用这个工具我们可以在很大程度上忽略前端的必要性,可以加速我们后端的开发
第二部分:请求与响应
设置请求映射路径
问题1:不同模块相同的请求路径冲突问题
- 下面有2个模块:user和book
//第二步:定义controller
@Controller//2.1 将控制器将给spring管理
public class UserController {
//2.2设置当前方法的访问路径
@RequestMapping("/save")
//2.3设置当前操作的返回值(以save方法的返回值作为返回值)
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save....");
return "{'UserController':'springmvc'}";//以joson的形式返回数据
}
@Controller
public class BookController {
//配置请求路径
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
System.out.println("user save....");
return "{'BookController':'springmvc'}";
}
他们都有save方法,并且他们的请求路径都是/save

- 解决冲突的方式
![]()

这样我们的路径冲突就解决了
问题2:同一个模块中请求路径冗长问题


一个小注意点:在postman中使用ctrl+ 加号和ctrl+减号可以调整页面的大小
get和post请求发送普通参数
1.get请求发送参数



对于我们controller中的方法是不区分get请求还是post请求的,他都能进行处理。不需要写doget和dopost方法了(在之前web中需要使用dopost调用doget以达到,方法对于get和post请求都能处理)。现在简化了这个过程
1.post请求发送参数
我们的post请求的参数不是放在url中发送的,而是放在了请求体中进行发送的(也就是为什么我们在地址栏中看不到post请求的参数了),我们的post请求目前我知道的只能在from表单中进行发送(method=post)



我们的get请求一般不会发送中文的参数,下面解决post请求参数中文乱码问题
解决post请求中文乱码问题
- 过去的处理方式
![]()
在springmvc中我们在servlet容器的启动配置类中设置过滤器可以同样达到这个效果 - 增加一个过滤器可以解决乱码
//第四步:一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring配置(替代web.xml文件)
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[0];
}
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
//设置请求体的字符集过滤器
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}

注意我们这个仅仅可以解决post请求体中文乱码问题,对于get请求体的中文乱码问题并不能解决

5种类型参数传递

在前面的我们必须在服务器端设置和发送的参数相同名称的方法形参,才能接收到这个传递过来的参数。我们怎样可以实现不这样做也可以接收到参数呢?
设置请求参数和controller中方法参数的映射(解决上面的问题)


在一般情况下我们使用默认的映射就可以了,不需要写这个映射关系
但是在大多数情况下我们都是收集一些数据封装成一个domain,所以下面将演示传递一个domain作为参数
- POJO数据类型
package com.itheima.domain;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "User{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
- 控制器
@RequestMapping("/pojoParam")
@ResponseBody
public String pojoParam(User user){
System.out.println("接收到的参数:"+user);
return "{'BookController':'pojo'}";
}


只要我们的请求参数名和我们的domain的属性名相同,将会被自动封装成domain对象
- 嵌套POJO类型参数(pojo对象里面还有引用类型的属性)
- User类(里面包含引用类型的属性Address)
package com.itheima.domain;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Address address;
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public User() {
}
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}
- Address
package com.itheima.domain;
public class Address {
private String province;
private String city;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String province, String city) {
this.province = province;
this.city = city;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return province
*/
public String getProvince() {
return province;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param province
*/
public void setProvince(String province) {
this.province = province;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return city
*/
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param city
*/
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String toString() {
return "Address{province = " + province + ", city = " + city + "}";
}
}


- 数组类型参数


- 集合类型参数
![]()
![]()
因为他对于引用类型的处理方案是:创建出这个类型的对象,然后将请求参数setter进去。(作为属性)。但是我们现在是想让请求参数作为集合的
值而不是属性,而且list是接口也没有构造方法
![]()
![]()
对于传递参数总的来说,名称可以对应上的直接传递就可以了,名称对应不上 是使用@RequestParam绑定一下就可以了
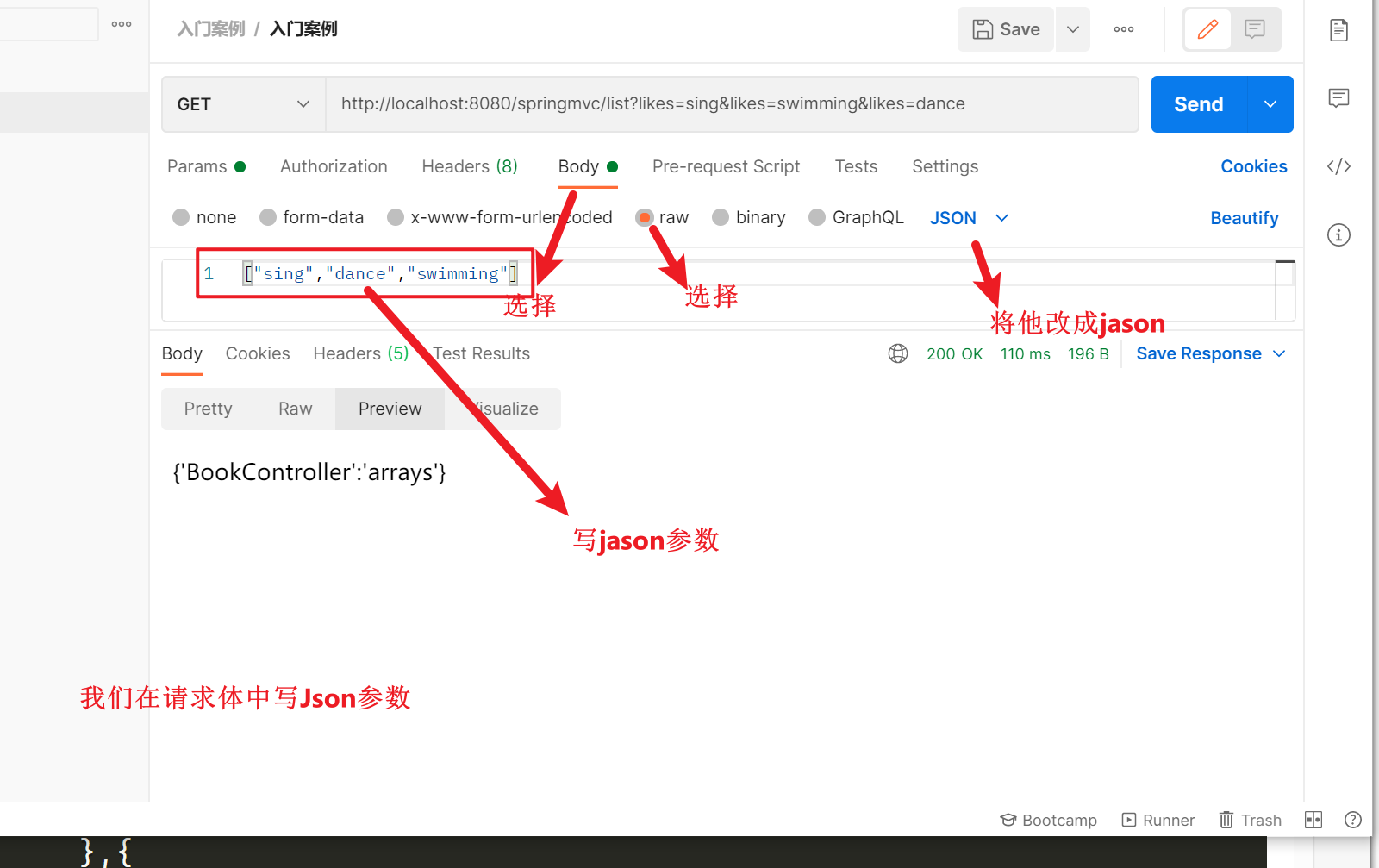
jason数据传递参数(在开发中大概率使用的是这种方式)

我们的jason参数是放在请求体里面发送的
- 集合类型
![]()
- 1.添加jason依赖
<!--jason依赖,实现将jason数据转化成java对象-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
-
2.在postman中编写jason参数
![]()
但是此时我们springmvc还不知道传递过来的jason数据,我们必须开启一个功能键让spingmvc帮我们转化jason数据 -
3.开启转化jason数据
![]()
-
4.设置参数映射
![]()
此时我们的jason数据就成功封装到我们的domain中了 -
pojo类型
![]()
![]()
![]()
好像我们的address的值没有,因为我们并没有传递address属性的值 -
传递address的值
![]()
![]()
-
JSON对象数组
![]()
![]()
![]()
-
注意点
![]()
![]()
从目前实验来看好像发送jason类型的数据,在接收端的参数中都必须加上RequestBody注解才行。对于非jason参数,
只有list集合才需要加上RequestParam注解(因为是将他作为值,不符合默认的)
使用tomcat7-maven-plugin插件简化tomcat启动
- 在pom.xml中添加toncat插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<!--tomcat插件-->
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port><!--设置项目使用的端口号(80为http协议默认端口号)将不需要写端口号了-->
<path>/</path><!--默认访问路径-->
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
- 可以使用下面的步骤快速启动tomcat服务器
![]()
当我们将端口号设置成http协议默认端口号80,我们可以省略工程名和端口号的书写
![]()
日期型参数传递

1.对于默认格式可以直接转化为Date


2.对于不是默认格式的日期(指定日期格式即可)



响应

1.响应页面

但是不知道为什么我的方法可以被访问到,但是页面一直无法被显示
响应页面问题的解决

补充配置maven-tomcat插件的快速启动(不是添加模板,是添加新配置)


2.响应文本
我们前面的测试返回的都不是jason对象,都是返回的字符串(只是是jason格式的字符串)
@ResponseBody注解表示响应的是数据


pojo对象


对象数组




第三部分内容--REST风格
REST风格简介


- 存在问题
![]()
![]()
![]()
对于请求方式有很多种,但是常用的也就是上面提到的4种
RESTFU入门案例


package com.itheima.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
//rext风格
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.POST)//表明是保存行为(请求不是post将报错)
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
return "'module':'user save' ";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)//表明是删除行为(请求不是delete将报错)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable int id){
System.out.println("参数是"+id);
return "'module':'user delete' ";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.PUT)//表明是更新行为(请求不是post将报错)
@ResponseBody
public String update(){
return "'module':'user update' ";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)//表明是查询行为(请求不是delete将报错)
@ResponseBody
public String selectById(@PathVariable int id){
System.out.println("参数是"+id);
return "'module':'user select' ";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.GET)//表明是查询行为(请求不是delete将报错)
@ResponseBody
public String select(){
return "'module':'user select' ";
}
}

RESTFUL快速开发

@RestController //@Controller + ReponseBody
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book save..." + book);
return "{'module':'book save'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book delete..." + id);
return "{'module':'book delete'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
/* 名称 @RestController
类型 类注解
位置 基于SpringMVC的RESTful开发控制器类定义上方
作用 设置当前控制器类为RESTful风格,
等同于@Controller与@ResponseBody两个注解组合功能
对于刚才的问题,我们都有对应的解决方案:
问题1:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都定义了访问路径/books,重复性太高。
问题2:每个方法的@RequestMapping注解中都要使用method属性定义请求方式,重复性太高。
问题3:每个方法响应json都需要加上@ResponseBody注解,重复性太高。
知识点1:@RestController
知识点2:@GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping*/
@PutMapping
public String update(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println("book update..." + book);
return "{'module':'book update'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("book getById..." + id);
return "{'module':'book getById'}";
}
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping
public String getAll(){
System.out.println("book getAll...");
return "{'module':'book getAll'}";
}
}
总结来说是使用了下面新的注解

案例:基于RESTFUL页面数据交互(后台接口的开发)
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
//保存图书
@PostMapping
//RequestBody注解表明参数从请求体重获取
public String save(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("book-->" + book);
return "'book':'book' ";
}
//查询所有图书
@GetMapping
public List<Book>getAll(){
List<Book> list = new ArrayList<Book>();
Book book1 = new Book();
book1.setName("红楼梦");
book1.setType("小说");
book1.setDescription("一本好书");
list.add(book1);
Book book2 = new Book();
book2.setName("西游记");
book2.setType("小说");
book2.setDescription("一本好书");
list.add(book2);
return list;
}
}


案例:基于RESTFUL页面数据交互(页面访问处理)
1.放行非springmvc的请求
当我们直接访问静态页面的时候将无法封装:

因为我们没有在controller中给页面配置请求地址

解决方案
- springMVC需要将静态资源进行放行。
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
//设置静态资源访问过滤,当前类需要设置为配置类,并被扫描加载
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//当访问/pages/????时候,从/pages目录下查找内容
registry.addResourceHandler("/pages/**").addResourceLocations("/pages/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/js/**").addResourceLocations("/js/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/css/**").addResourceLocations("/css/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/plugins/**").addResourceLocations("/plugins/")
;
}
}
- 可以正常访问了
![]()
ajax请求可以实现异步发送请求,局部更新页面
下面以ajax请求举例,前端发送ajax请求,后台返回jason对象,然后前台使用返回的数据进行页面的局部更新
前端不熟悉,故不展开
第四部分-SSM整合
ssm-整合配置



在配置方面好像就是spring将mybatis的配置放在自己配置里面一起加载。springmvc则自己加载。把这2方面放在servletconfig中各自加载
ssm-功能模块开发
1.创建表并插入数据
CREATE DATABASE ssm
USE ssm
CREATE TABLE tbl_book(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
TYPE VARCHAR(20),
NAME VARCHAR(50),
description VARCHAR(255)
)
INSERT INTO tbl_book(id,type,name,description) VALUES (1,'计算机理
论','Spring实战 第五版','Spring入门经典教程,深入理解Spring原理技术内幕'),(2,'计算机理
论','Spring 5核心原理与30个类手写实践','十年沉淀之作,手写Spring精华思想'),(3,'计算机理
论','Spring 5设计模式','深入Spring源码刨析Spring源码中蕴含的10大设计模式'),(4,'计算机
理论','Spring MVC+Mybatis开发从入门到项目实战','全方位解析面向Web应用的轻量级框架,带你
成为Spring MVC开发高手'),(5,'计算机理论','轻量级Java Web企业应用实战','源码级刨析
Spring框架,适合已掌握Java基础的读者'),(6,'计算机理论','Java核心技术 卷Ⅰ 基础知识(原书
第11版)','Core Java第11版,Jolt大奖获奖作品,针对Java SE9、10、11全面更新'),(7,'计算
机理论','深入理解Java虚拟机','5个纬度全面刨析JVM,大厂面试知识点全覆盖'),(8,'计算机理
论','Java编程思想(第4版)','Java学习必读经典,殿堂级著作!赢得了全球程序员的广泛赞誉'),
(9,'计算机理论','零基础学Java(全彩版)','零基础自学编程的入门图书,由浅入深,详解Java语言
的编程思想和核心技术'),(10,'市场营销','直播就这么做:主播高效沟通实战指南','李子柒、李佳
奇、薇娅成长为网红的秘密都在书中'),(11,'市场营销','直播销讲实战一本通','和秋叶一起学系列网
络营销书籍'),(12,'市场营销','直播带货:淘宝、天猫直播从新手到高手','一本教你如何玩转直播的
书,10堂课轻松实现带货月入3W+');
SELECT * FROM tbl_book

ssm整合--接口测试
在开发中有2个环节需要停下来做测试:1.当持业务层(即sevice和dao都写完的时候)开发完成时需要使用junit做业务层接口的测试2.当表现层测试完成需要使用postman做表现层接口的测试
注意正规的junit测试还需要做断言和匹配
- 1.测试业务层
- 2.测试表现层
![]()
- 3.配置事务
传播行为等书写,先不要配置看具体需求 - ssm整合全套代码
建表语句看前面 - config
- jdbcconfig
package com.itheima.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
return dataSource;
}
//配置事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);//配置数据源
return transactionManager;
}
}
- mybatisconfig
package com.itheima.config;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class MyBatisConfig {
//将sqlSessionFactory交给spring
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);//设置数据源
factoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain");//设置别名
return factoryBean;
}
//映射器
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao");//将dao包的路径作为映射路径
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
- servletconfig
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
//web容器配置类
public class ServletConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};//将该路径的请求都交给springmvc
}
}
- springconfig
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.service")//组件扫描
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")//导入配置文件
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启事务管理
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class})//导入其他配置类
public class SpringConfig {
}
- springmvcconfig
package com.itheima.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")
@EnableWebMvc//开启web相关的功能
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
- bookcontroller
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import com.itheima.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@PostMapping
public boolean save(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("保存的图书信息:"+book);
return bookService.save(book);
}
@PutMapping
public boolean update(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.update(book);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public boolean delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.delete(id);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Book getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.getById(id);
}
@GetMapping
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookService.getAll();
}
}
- bookdao
package com.itheima.dao;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import java.util.List;
public interface BookDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_book values(null,#{type},#{name},#{description})")
public void save(Book book);
@Update("update tbl_book set type=#{type},name=#{name},description=#{description} where id=#{id}")
public void update(Book book);
@Delete("delete from tbl_book where id=#{id}")
public void delete(Integer id);
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id=#{id}")
public Book getById(Integer id);
@Select("select * from tbl_book")
public List<Book> getAll();
}
- book
package com.itheima.domain;
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
public Book() {
}
public Book(Integer id, String type, String name, String description) {
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return id
*/
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param id
*/
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return type
*/
public String getType() {
return type;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param type
*/
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return description
*/
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param description
*/
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String toString() {
return "Book{id = " + id + ", type = " + type + ", name = " + name + ", description = " + description + "}";
}
}
- bookservice
package com.itheima.service;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
/*
1.一般业务层方法名和持久层不同(需要一眼就知道是什么业务
2.业务层删除修改保存方法一般返回boolean)
* */
@Transactional//给所有的业务方法加上事务
public interface BookService {
public boolean save(Book book);
public boolean update(Book book);
public boolean delete(Integer id);
public Book getById(Integer id);
public List<Book> getAll();
}
- bookserviceimpl
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.BookDao;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import com.itheima.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public boolean save(Book book) {
bookDao.save(book);
return true;
}
public boolean update(Book book) {
bookDao.update(book);
return true;
}
public boolean delete(Integer id) {
bookDao.delete(id);
return true;
}
public Book getById(Integer id) {
return bookDao.getById(id);
}
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookDao.getAll();
}
}
表现层与前端数据传输协议的定义

前端将无法区分哪个是直接可以使用的数据


- 但是可能还是存在下面问题
![]()
![]()
- 最终的骨架
![]()
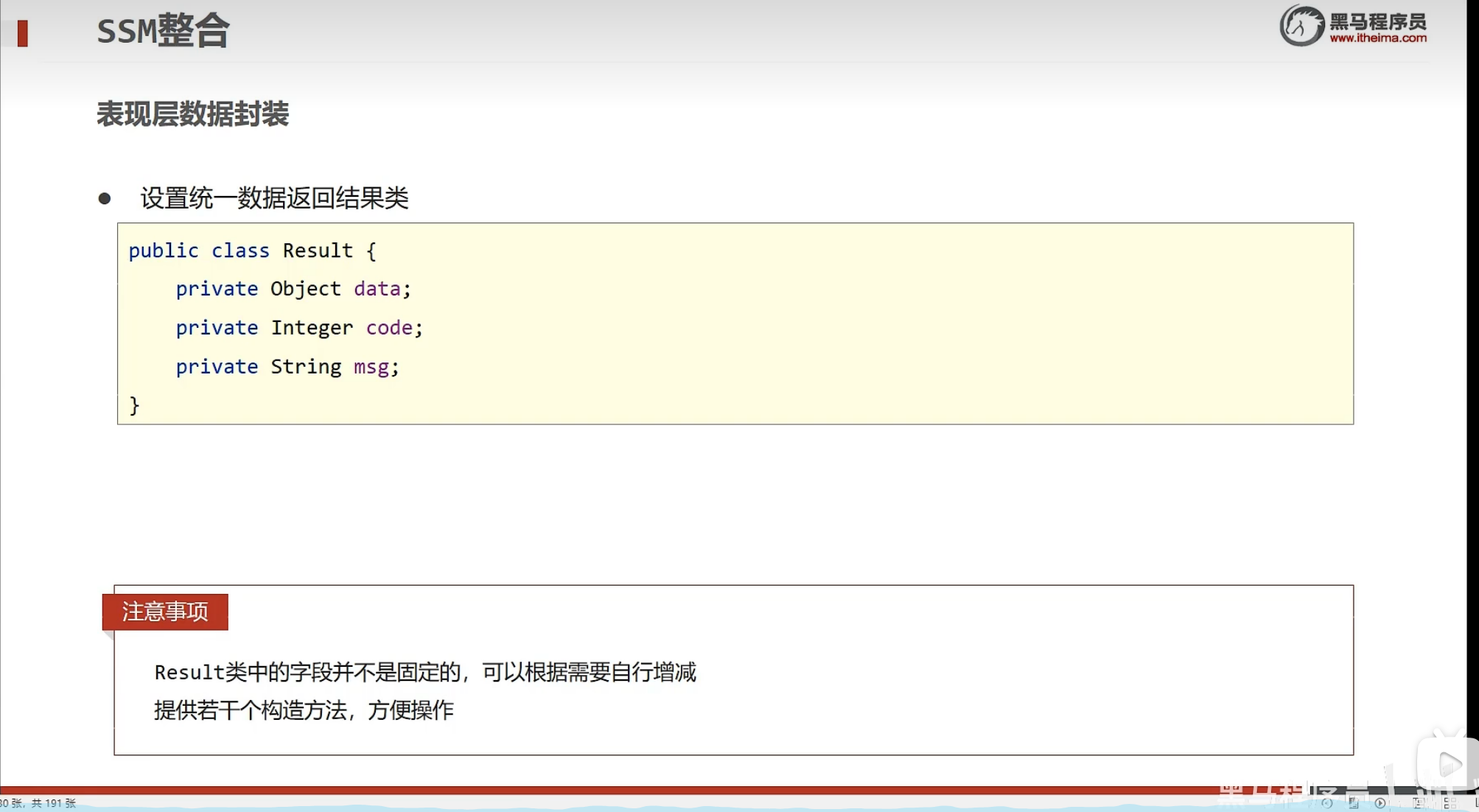
- 封装模型如下
![]()
表现层与前端数据传输协议的实现
我们需要定义的数据结果模型应该是给表现层使用的,所以我们一般把result类放在controller包中
在这个实现中,我们在查询中我们将返回null设置为查询失败,将返回非null设置为查询成功(并不是表示代码异常错误的失败)
其实就是和前端通信的协议
- 数据结果封装类
package com.itheima.controller;
//数据结构封装模型
public class Result {
private Object data;//数据
private Integer code;//状态码
private String msg;//特殊信息
//提供多种形式的构造方法以方便我们使用
public Result() {
}
public Result( Integer code,Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.code = code;
}
public Result(Integer code,Object data, String msg) {
this.data = data;
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return data
*/
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param data
*/
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return code
*/
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param code
*/
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return msg
*/
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param msg
*/
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public String toString() {
return "Result{data = " + data + ", code = " + code + ", msg = " + msg + "}";
}
}
package com.itheima.controller;
//状态码类
public class Code {
public static final Integer SAVE_OK=20011;
public static final Integer DELETE_OK=20021;
public static final Integer UPDATE_OK=20031;
public static final Integer GET_OK=20041;
public static final Integer SAVE_ERR=20010;
public static final Integer DELETE_ERR=20020;
public static final Integer UPDATE_ERR=20030;
public static final Integer GET_ERR=20040;
}
- 修改后的控制器类
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.domain.Book;
import com.itheima.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody Book book) {
final boolean flag = bookService.save(book);
return new Result(flag?Code.SAVE_OK:Code.SAVE_ERR,flag);
}
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Book book) {
final boolean flag = bookService.update(book);
return new Result(flag?Code.UPDATE_OK:Code.UPDATE_ERR,flag);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public Result delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
final boolean flag = bookService.delete(id);
return new Result(flag?Code.DELETE_OK:Code.DELETE_ERR,flag); }
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
final Book book = bookService.getById(id);
Integer code = book!=null?Code.GET_OK:Code.GET_ERR;
String msg = book!=null?"":"查询失败";//对于查询成功的msg可以随便写,前端不会去使用
return new Result(code,book,msg);
}
@GetMapping
public Result getAll() {
final List<Book> bookList = bookService.getAll();
Integer code = bookList!=null?Code.GET_OK:Code.GET_ERR;
String msg = bookList!=null?"":"查询失败";//对于查询成功的msg可以随便写,前端不会去使用
return new Result(code,bookList,msg);
}
}
ssm整合-异常处理器
- 当我们程序出现异常时-返回的前端的是什么呢?
![]()


- 分析异常
![]()
![]()
![]()
总结异常处理 - 1.异常需要分类处理
- 2.异常需要放在表现层处理
- 3.异常需要使用AOP的思想处理
我们不需要自己写AOP,spring给我们提供了建议方法--异常处理器
![]()
- 该节代码基于前面的代码
我们的异常处理器是集中处理controller中的异常的,所以写在contaroller包中比较好 - 异常处理器类
package com.itheima.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
//异常处理器
@RestControllerAdvice//用于处理rest风格开发的controller
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)//定义该方法用来处理哪一种异常
public Result doException(Exception e){
//此时还没有设置异常的相关状态码(仅仅示意)
return new Result(666,null);//将异常包装成结果返回给前端
}
}

- 总结


这时候我们正常情况和异常情况下都可以返回给前端统一的数据,有利协调了前后的开发
ssm整合--项目异常处理
- 我们在项目中的异常处理
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 完成处理方案的代码编写
- 1.定义异常编码
![]()
2.我们需要自定义系统异常和业务异常
package com.itheima.exception;
public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException{
private Integer code;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public BusinessException(Integer code, String message ) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(Integer code, String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
}
}
package com.itheima.exception;
public class SystemException extends RuntimeException{
private Integer code;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public SystemException(Integer code, String message ) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public SystemException( Integer code,String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
}
}
- 3.在controller中模拟出业务异常和系统异常
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
//模拟业务异常
if(id!=1){
throw new BusinessException(Code.BUSINESS_ERR,"请不要使用你的技术挑战我们的耐性");
}
final Book book = bookService.getById(id);
//模拟系统异常
try {
int a=2/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
//将出现的异常封装成系统异常
throw new SystemException(Code.SYSTEM_ERR,"服务区超时,请重试",e);
}
Integer code = book!=null?Code.GET_OK:Code.GET_ERR;
String msg = book!=null?"":"查询失败";//对于查询成功的msg可以随便写,前端不会去使用
return new Result(code,book,msg);
}
- 4.编写不同种类的异常处理器
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.exception.BusinessException;
import com.itheima.exception.SystemException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
//异常处理器
@RestControllerAdvice//用于处理rest风格开发的controller
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
//处理系统异常
@ExceptionHandler(SystemException.class)//定义处理系统异常
public Result doSystemException(SystemException e){
//1.记录日志
// 2.发送消息给运维
//3.发送邮件给开发人员(将e这个对象发送给开发人员)
//code和massage通过异常对象传递过来了
return new Result(e.getCode(),null,e.getMessage());//将异常包装成结果返回给前端
}
//处理业务异常
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)//定义处理系统异常
public Result doBusinessSystemException(BusinessException e){
//code和massage通过异常对象传递过来了
return new Result(e.getCode(),null,e.getMessage());//将异常包装成结果返回给前端
}
//处理其他异常
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Result doException(Exception e){
//1.记录日志
// 2.发送消息给运维
//3.发送邮件给开发人员(将e这个对象发送给开发人员)
//code和massage通过异常对象传递过来了
return new Result(Code.SYSTEM_UNKNOW_ERR,null,"系统繁忙,请稍后再试");//将异常包装成结果返回给前端
}
}
- 注意
![]()
对于异常的封装我们可以使用AOP来完成
前后端协议联调--列表查询功能
1.给直接访问页面的请求放行

- 前端页面发送
![]()
前后端协议联调(添加功能)
- 1.弹出添加窗口
![]()
![]()
![]()
前后端协议联调(添加功能状态处理)

在已有的代码中,我们的程序只可能是添加成功的

修改:我们可以根据dao层中函数的返回值(收到影响的行数)来判断是否执行成功,进而通过这个决定servcie层的返回值


- 我们现在实验添加失败的情况
![]()
但是我们点击后,并没有出现添加失败的提示框 - 我们在控制台中删除后台返回的数据:
![]()
![]()
- 这里我们就把这个异常当成是其他异常处理把
![]()
- 一个小问题
![]()
![]()
前后端协议联调(修改功能)
1.在修改编辑框中显示修改前的元数据

2.执行更新操作

前后端协议联调(删除功能)

ssm整合标准总结


第五部分:拦截器

拦截器简介




拦截器入门案例

建议将拦截器类下载controller中,因为拦截器都是给表现层用的





我们修改一下拦截器的配置,让他可以拦截更多的东西

- 注意
![]()
拦截器配置的简化

我们可以将support类中的拦截器配置和静态资源访问放行的配置都放在springmvcconfig中配置,以后就不用写support类了。
但是感觉会造成springmvc类冗余,个人不建议这么做
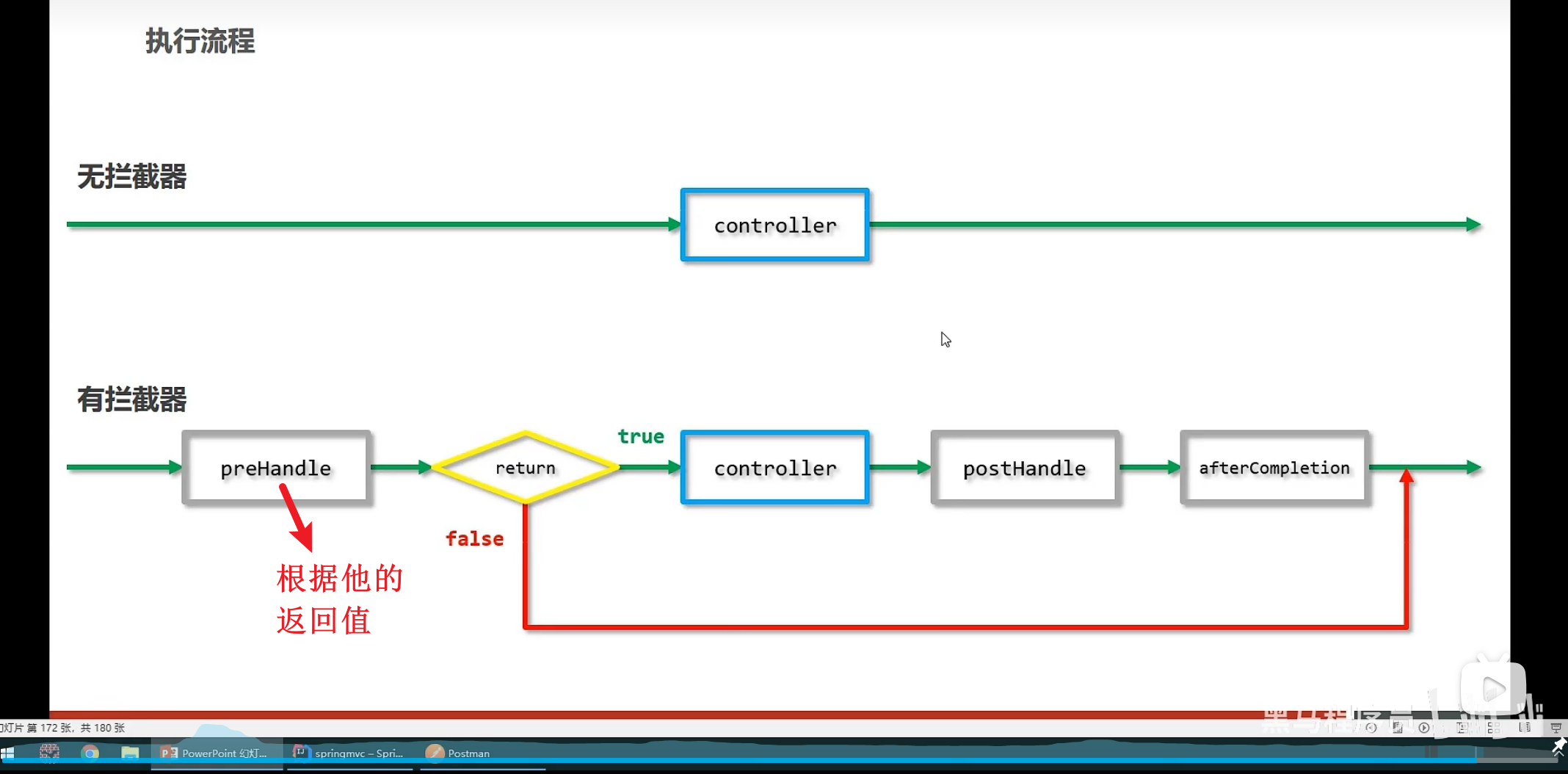
- 2种方式(有无使用拦截器)执行流程在分析
![]()

拦截器参数
应用的比较多是preHandle中的参数
public class ProjectInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//原始方法调用前执行的内容
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response, Object handler) throws Exception {
final String header = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
System.out.println("header:"+header);
System.out.println("preHandle...");//1.获取请求相关的信息
//handler(真实类型:HandlerMethod)对象封装了我们正在执行的方法
HandlerMethod hm = (HandlerMethod) handler;//强转成真实类型
final Method method = hm.getMethod();//2.此时可以得到我们需求执行的方法
System.out.println(method);
//可以在该方法中做校验,以确定该方法是返回true还是false
return true;
}
//原始方法调用后执行的内容
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("postHandle...");
//ModelAndView类封装了进行页面跳转的一些数据
}
//原始方法调用完成后执行的内容
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception
{
//ex中可以拿到原始程序执行过程中抛出的异常
System.out.println("afterCompletion...");
}
handle对象是对原始执行方法的封装,如果得到了handle对象,就可以对原始方法进行操作了
拦截器链配置



- 我们将第一个拦截器的pre返回值改为fasle
![]()
![]()
但是在实际开发中,拦截器配置一个就可以了。配置拦截器链的情况还是很少的
![]()
































































 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号