实验2 多线程
创建一个线程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
void* threadFunc(void* arg)
{
printf("In NEW threaad\n");
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
//create thread function
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,threadFunc,NULL);
//wait result
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
printf("IN main thread\n");
return 0;
}
在linux中运行多线程需要实验 gcc helloprocess.c -o helloprocess.h -pthread的命令
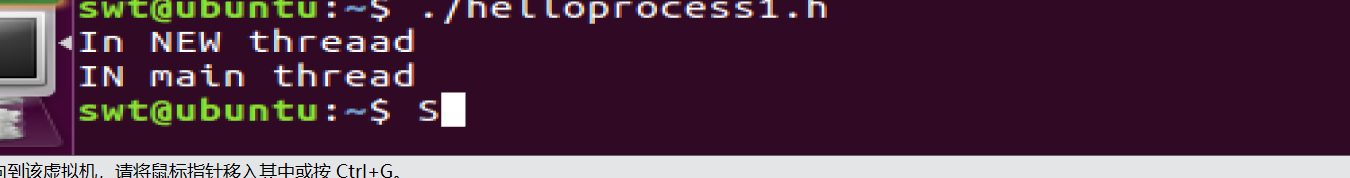
当我们把等待语句注释了
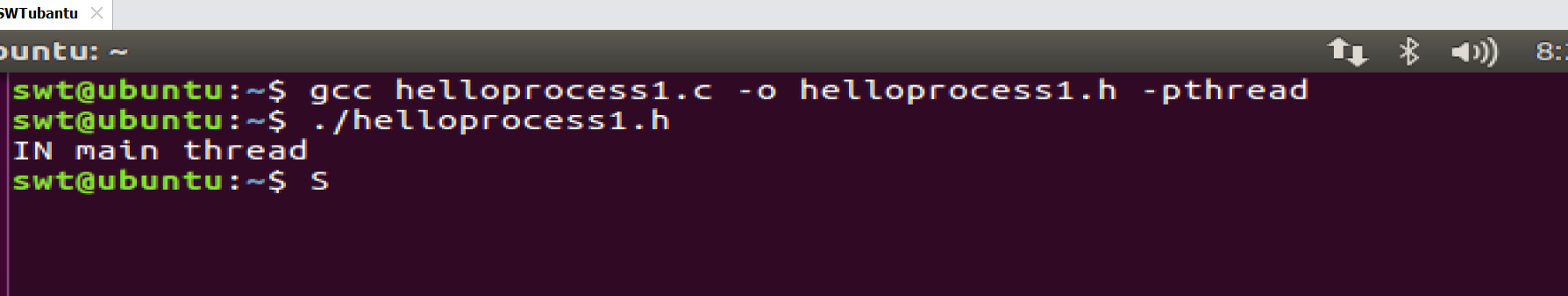
此时我们的main线程没有等待新创建的线程,直接执行了return ,此时程序已经结束了,新创建的线程的执行语句还没有执行
这里记住:一定要在主线程中等待其他线程先执行完毕,要不然return 时其他的线程将自动截至(这和实验一中的孤儿进程很像)

共享数据段
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void* hello(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 30000; i++){
printf("hello(%d)\n", rand()%100);
sleep(1);
}
}
void* world(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 30000; i++){
printf("world(%d)\n", rand()%100);
sleep(2);
}
}
int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_t tid,tid2;
// 线程创建函数
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, hello, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, world, NULL);
// 等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("In Main Thread\n");
return 0;
}
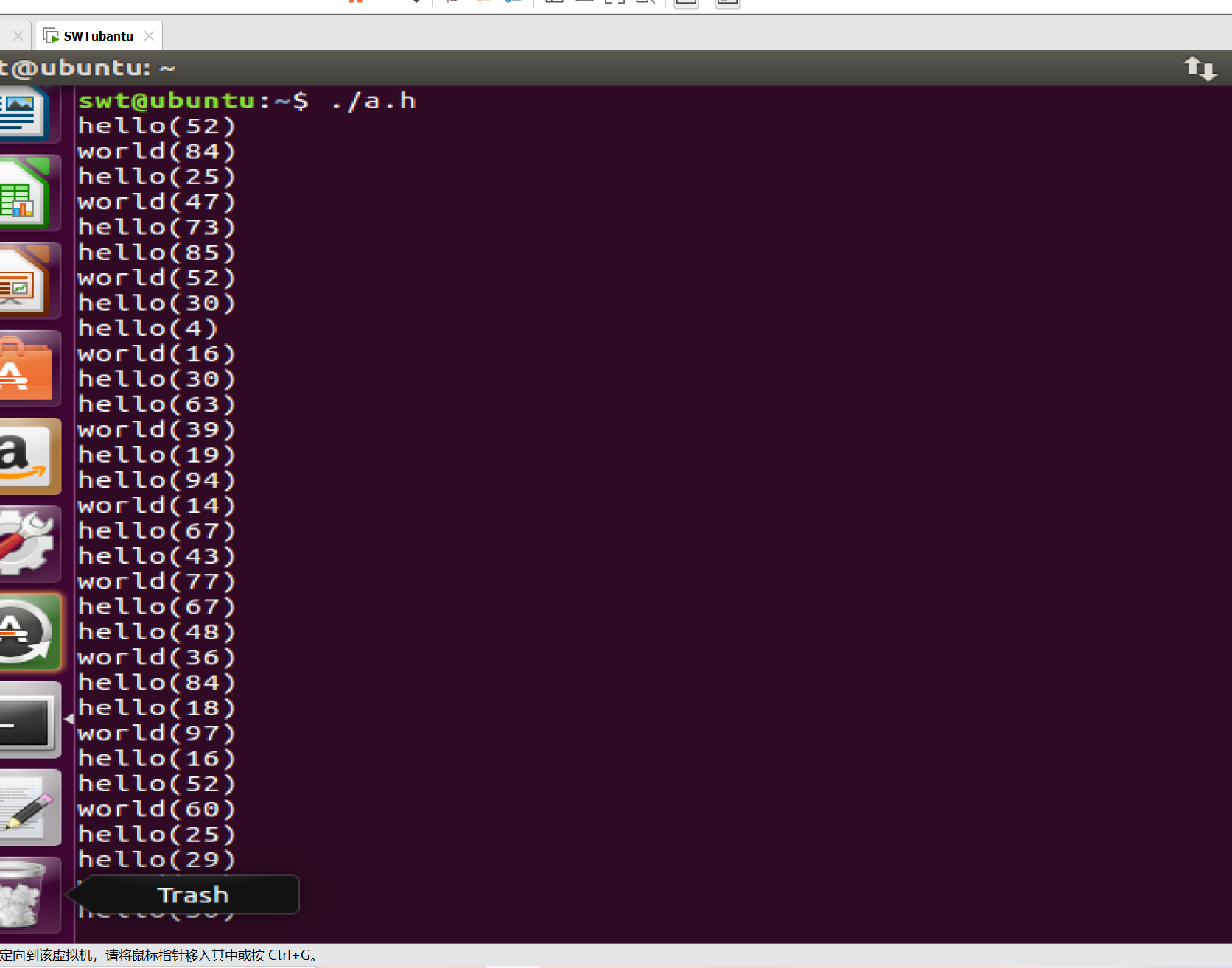
我们可以看出我们创建的2个线程是并发执行的
接着我们创建⼀个全局变量,我们观察⼀下两个线程是否可以操作同⼀份全局变量
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int value=100;
void* hello(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("hello(%d)\n",value++);
sleep(1);
}
}
void* world(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("world(%d)\n", value++);
sleep(2);
}
}
int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_t tid,tid2;
// 线程创建函数
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, hello, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, world, NULL);
// 等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("In Main Thread(%d)\n",value);
return 0;
}
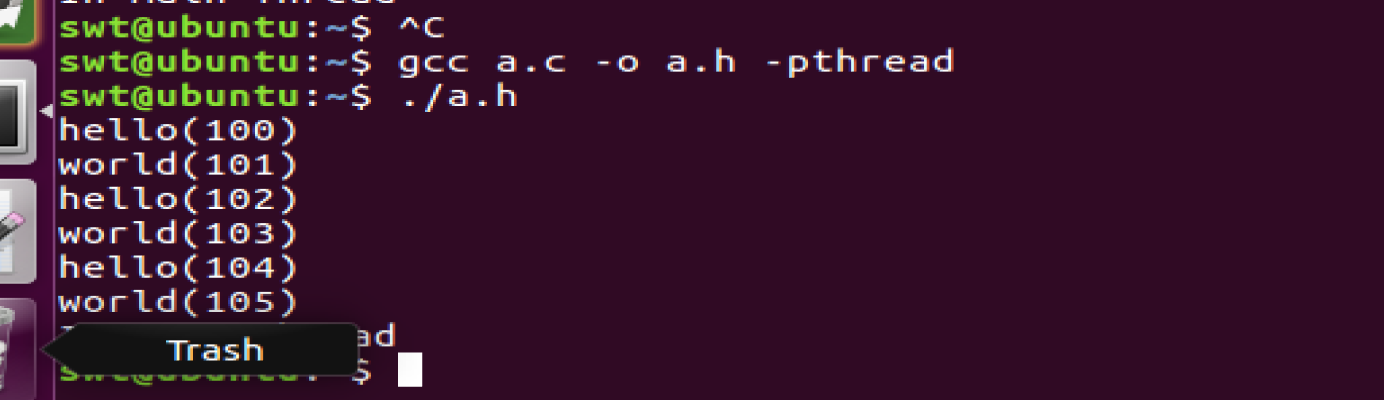
这表明多线程共享data段。data来自进程s
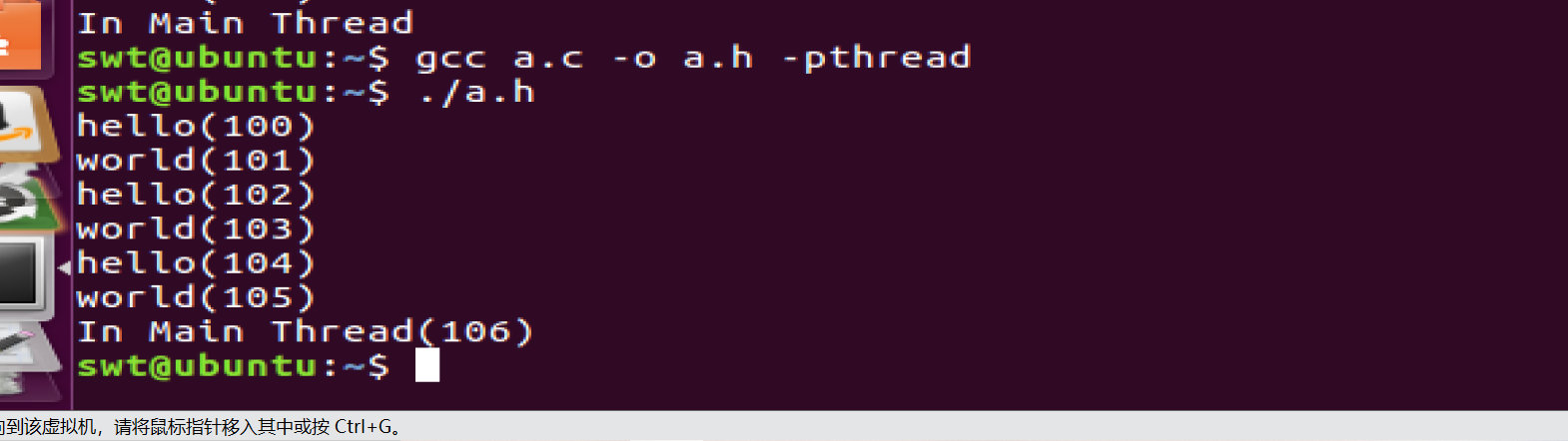
上面:我们创建的2个线程和主线程一起共享全局变量
蒙特卡洛模拟(演示多线程的效率更高)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void calculate_pi(int intervals){
unsigned int seed = time(NULL);
int circle_points = 0;
int square_points = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < intervals * intervals; ++i)
{
double rand_x = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
double rand_y = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
if ((rand_x * rand_x) + (rand_y * rand_y) <= 1){
circle_points++;
}
square_points++;
}
double pi = (double)(4.0*circle_points)/square_points;
printf("The estimated PI is %lf in %d times\n", pi, intervals * intervals);
}
int main(){
clock_t start,deleta;
double time_used;
double pi;
start = clock();
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(10)
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
calculate_pi(1000*(i+1));
}
deleta = clock() - start;
printf("The time taken in total: %lf seconds\n", (double)deleta/CLOCKS_PER_SE
return 0;
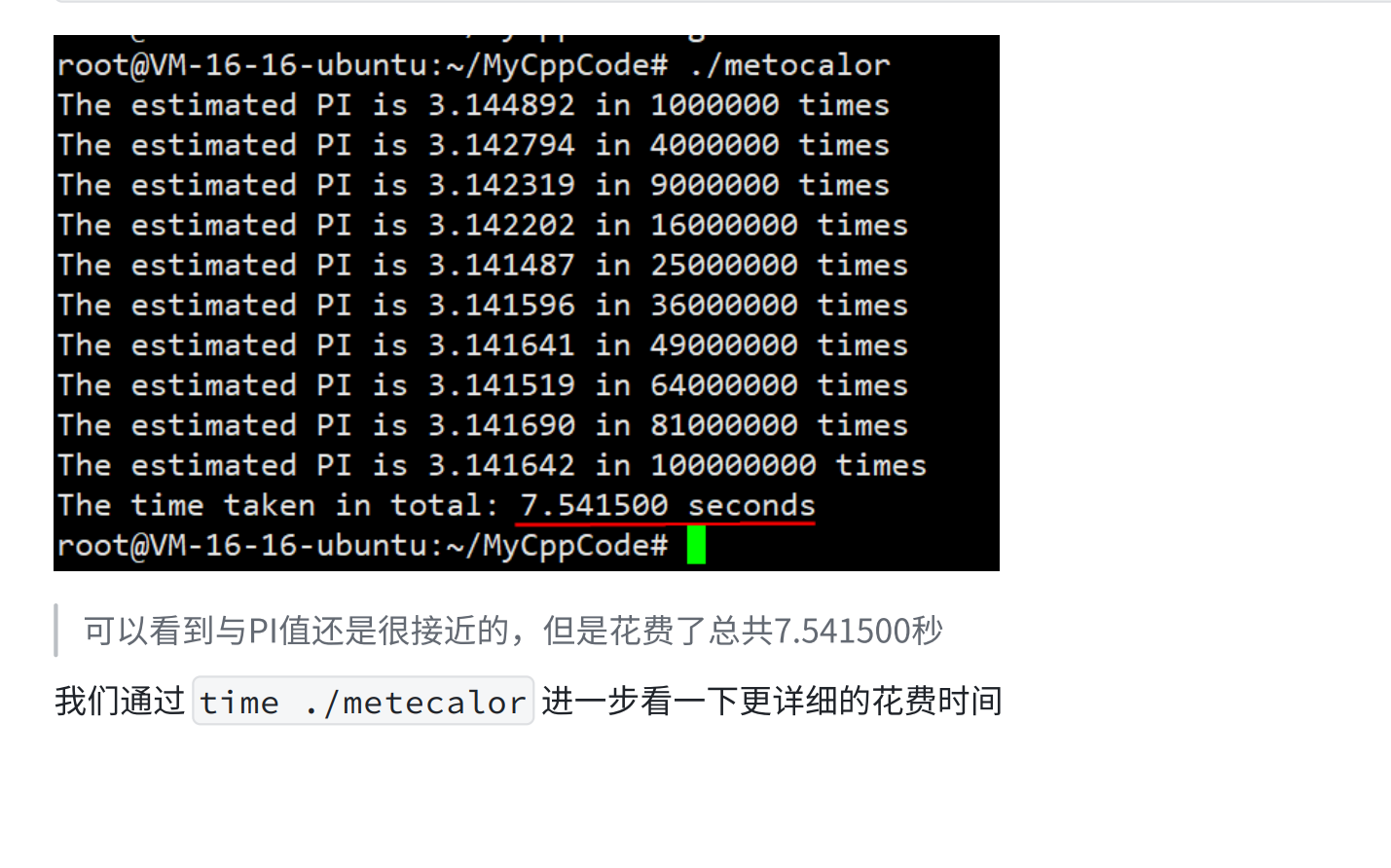
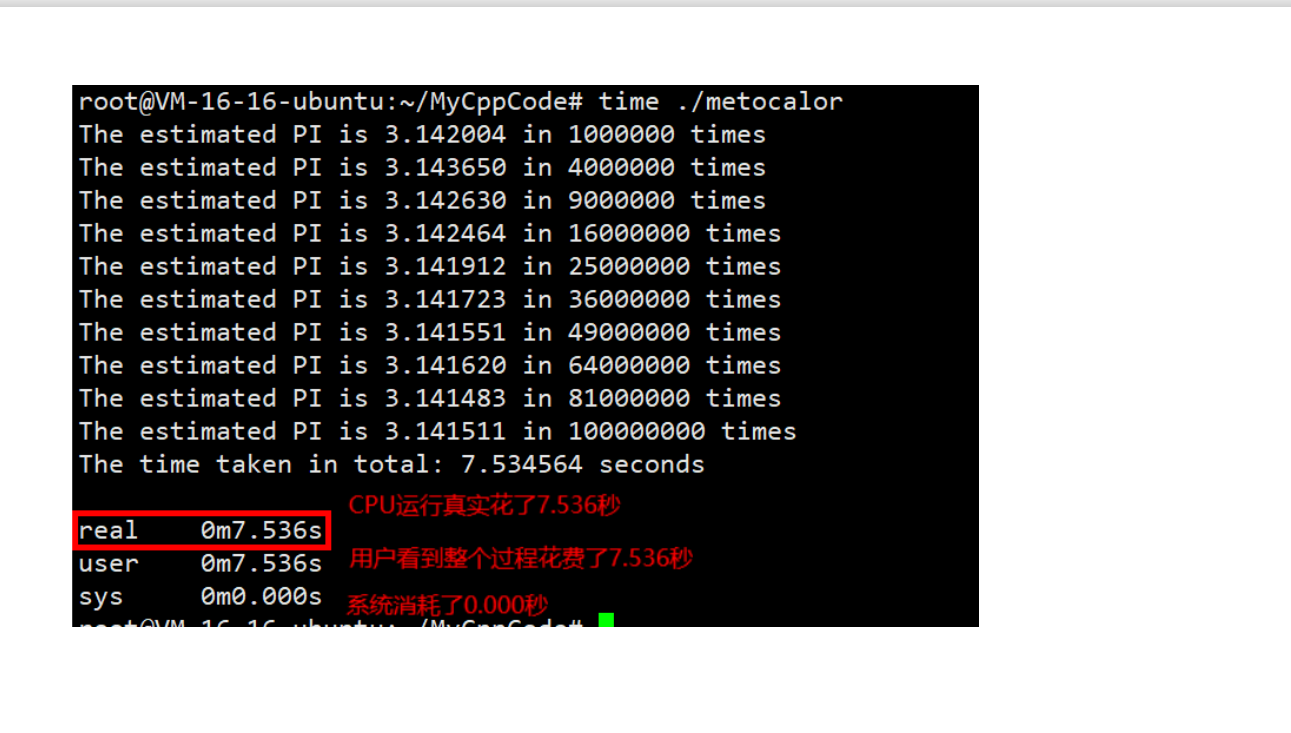
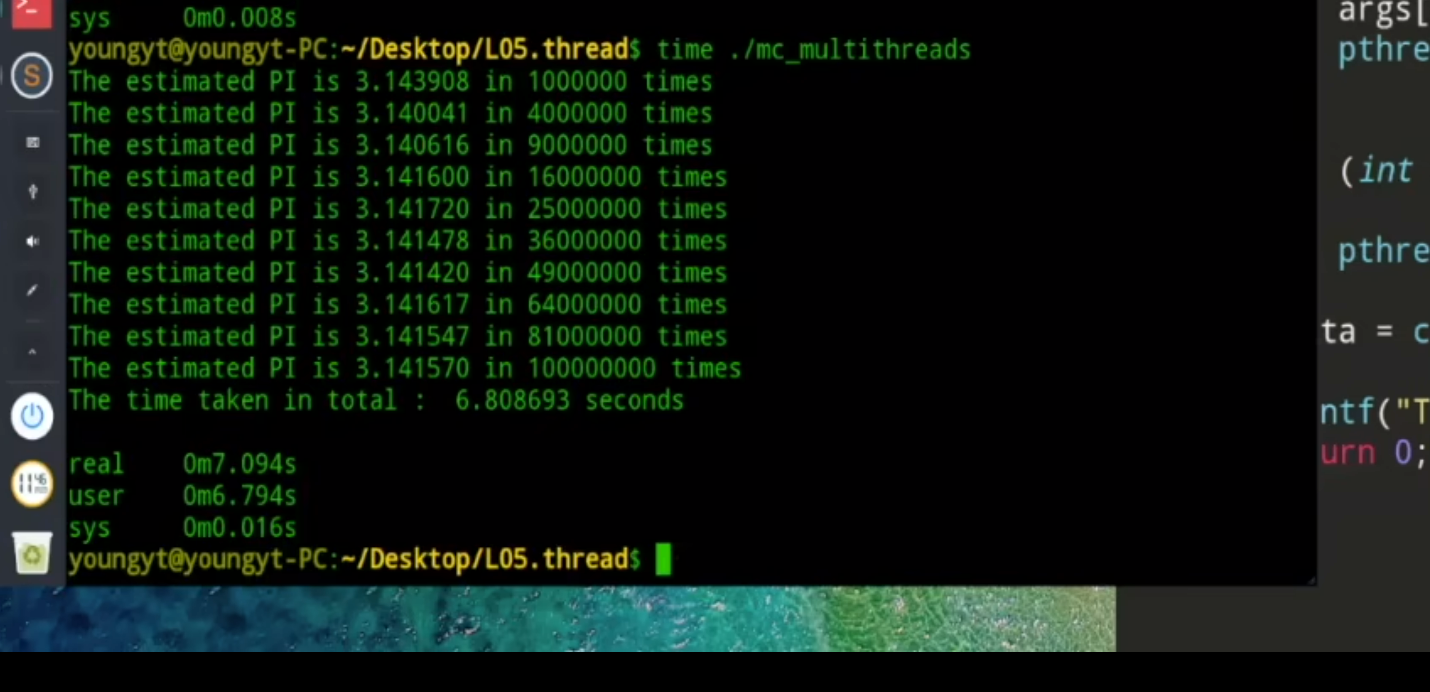
接下来我们来看⼀下开启多线程花费的时间
我们使用10条线程并发执行来代替前面的10次顺序执行
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void* calculate_pi(void* args){
unsigned int seed = time(NULL);
int circle_points = 0;
int square_points = 0;
int intervals = *((int*)args);
for (int i = 0; i < intervals * intervals; ++i)
{
double rand_x = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
double rand_y = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
if ((rand_x * rand_x) + (rand_y * rand_y) <= 1){
circle_points++;
}
square_points++;
}
double pi = (double)(4.0*circle_points)/square_points;
printf("The estimated PI is %lf in %d times\n", pi, intervals * intervals);
pthread_exit(0);
}
int main(){
clock_t start,deleta;
double time_used;
start = clock();
pthread_t calculate_pi_threads[10];
int args[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){
args[i] = 1000*(i+1);
pthread_create(calculate_pi_threads+i,NULL,calculate_pi,args+i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){
pthread_join(calculate_pi_threads[i],NULL);
}
deleta = clock() - start;
printf("The time taken in total: %lf seconds\n", (double)deleta/CLOCKS_PER_SE
return 0;
}
- 当多线程程序执行在单核cpu上面
![]()
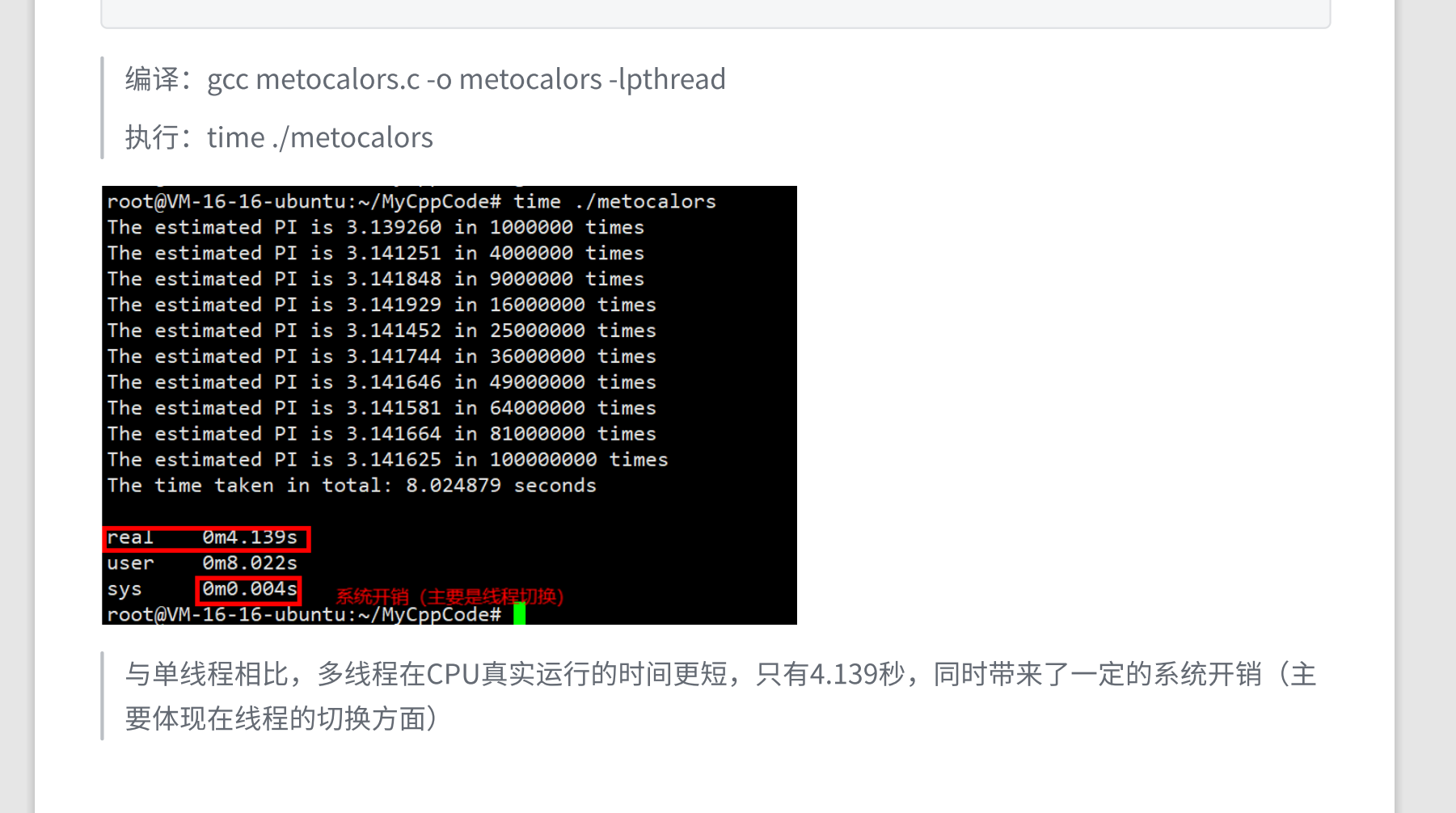
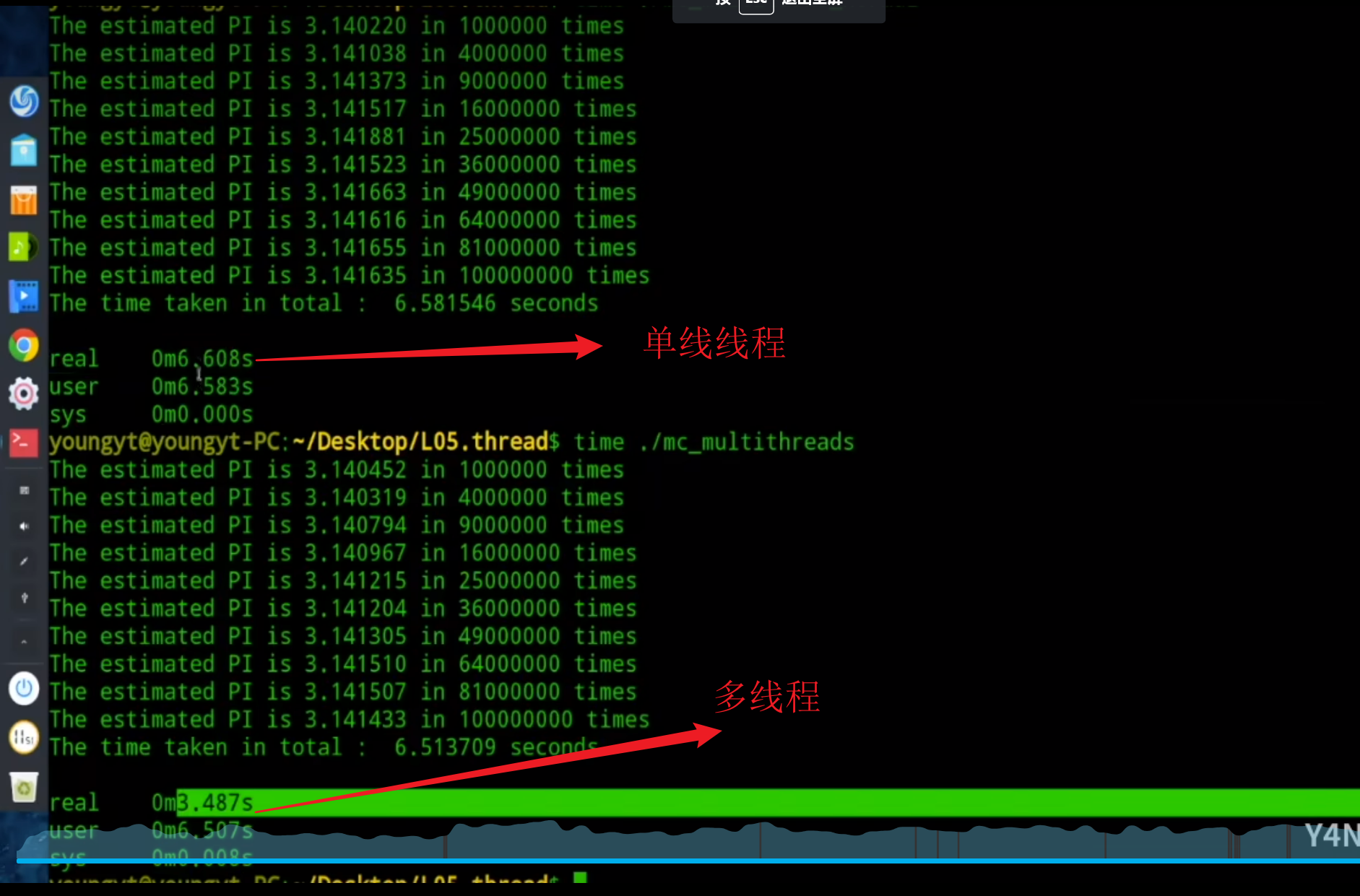
我们在用户态下进行计算,程序在用户态执行的时间即总共花费的时间不会改变,10个苹果1个人吃和10个人吃,总共耗费的时间一样。但是实际耗时会减少。还有我们是sys时间会增加,因为使用多线程线程切换会耗能
上面的这种情况我们将cpu内核数量换成2个,多线程可以并发执行,单线程还是将会顺序执行


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号