大数据自动化安装部署方案(一) - 集群系统环境设置
1.前期准备
1.1系统和yum源镜像准备
需要的条件:
① 至少三台刚装上Centos7.0系统的物理机或者虚拟机;
② CentOS-7.0-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso镜像,用于制作本地yum源;
注意:本文三台物理机或虚拟机的操作系统镜像是CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1804.iso。
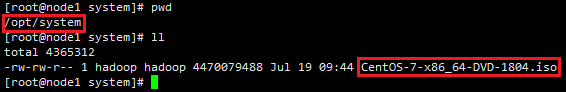
用于制作本地yum源的CentOS-7.0-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso镜像默认存放于第一节点node1的/opt/system下
1.2 配置文件host_ip.txt和frames.tx准备
host_ip.txt文件为集群ip、hostname、root账号密码配置;而frames.txt为所需要安装的软件配置说明,其中false为不安装,true为安装
host_ip.txt内容为:
192.168.187.201 node1 root hadoop 192.168.187.202 node2 root hadoop 192.168.187.203 node3 root hadoop
frames.txt内容为:
jdk-8u181-linux-x64.tar.gz true scala-2.11.0.tgz true hadoop-2.7.6.tar.gz true hbase-2.0.1-bin.tar.gz true apache-hive-2.3.3-bin.tar.gz true zookeeper-3.4.13.tar.gz true spark-2.3.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz true kafka_2.11-1.1.1.tgz true
1.3 安装软件准备
需要在官网上下载frames.txt所列的软件安装包,可以自行下载。
这里默认所有的软件安装包放在第一节点node1的/opt/frames目录下,下面涉及软件部分的shell操作都会根据/opt/frames/目录下是否有该软件再进行自动安装。

1.4 shell命令文本准备
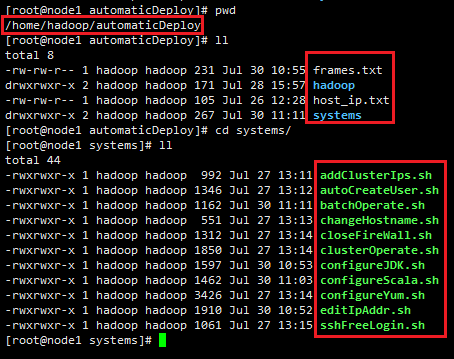
以下shell文本文件,以及host_ip.txt和frames.txt文件,都默认放置在第一节点node1的/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy目录下,如图:
2.模块化自动安装部署
注意:以下所有shell命令的执行,都需要以root用户执行
模块化自动安装部署包括IP地址设置、机器名hostname修改、host配置文件修改、关闭防火墙/SELINUX、添加bigdata用户名、配置yum源、配置SSH无密码登录、配置JDK环境、配置Scala环境共9个模块。
2.1 集群中每台机器IP地址的设置
集群中每台机器首先需要设置IP地址,保证机器与机器之间可以直接通过ip地址访问。
IP地址设置shell命令文件editIpAddr.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash ################ #针对Centos-7.0 ################ #处理涉及到IP地址设置的网络文件,备份并创建新的 function doWithNetworkFile() { #1.查找/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/目录下是否存在ifcfg-ens33文件,存在则重命名为.bak结尾的 fileResult=`find /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ -name "ifcfg-ens33"` if [[ $fileResult != "" ]] then #2.创建一个ifcfg-ens33文件用于配置网络设置 result=`find /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts -wholename $fileResult.bak` if [[ -z $result ]] then mv $fileResult $fileResult.bak fi cp $fileResult.bak $fileResult else touch /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 fi } #配置ip地址 function configureIpAddr() { ip=$1 gateway=$2 fileUrl=/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 #1.把ifcfg-ens33文件非#开头的行注释掉 sed -i 's/^[^#]/#&/' $fileUrl UUID=`grep "^#UUID=*" $fileUrl | head -1` #2.配置内网IP地址 #连接类型 echo "TYPE=Ethernet" >> $fileUrl #静态IP echo "BOOTPROTO=static" >> $fileUrl echo "DEFROUTE=yes" >> $fileUrl echo "IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no" >> $fileUrl #IPV6关闭 echo "IPV6INIT=no" >> $fileUrl #配置名字 echo "NAME=ens33" >> $fileUrl #唯一标识 echo "${UUID:1}" >> $fileUrl #网卡名称 echo "DEVICE=ens33" >> $fileUrl #开机即启动网络 echo "ONBOOT=yes" >> $fileUrl #IP地址 echo "IPADDR=$ip" >> $fileUrl echo "PREFIX=24" >> $fileUrl #网络掩码 echo "NETMASK=255.255.255.0" >> $fileUrl #网关 echo "GATEWAY=$gateway" >> $fileUrl } function editIpAddr() { ip=$1 gateway=$2 #处理涉及到IP地址设置的网络文件,备份并创建新的 doWithNetworkFile #在/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33上设置IP地址 configureIpAddr $ip $gateway #重启网络服务 service network restart } ip=$1 gateway=$2 editIpAddr $ip $gateway
分别在三台机器上以root用户执行如下命令:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/editIpAddr.sh 192.168.187.*** 192.168.187.2
注意:
①网关192.168.187.2需要通过 route -n 命令(CentOS7以上使用)查看,如图:
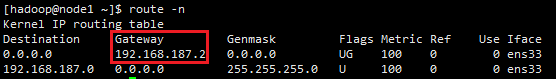
②不同机器的ip地址是不一样的,这里指IP地址的前三个数值是一样,前三个数值与网关的前三个数值是一致的;只有最后一个***是根据需求设置,一般在0~255之间。这里我假定三个节点node1、node2、node3的IP分别为192.168.187.201,192.168.187.202,192.168.187.203。
2.2 修改机器名hostname
changeHostname.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash #修改机器名hostname function changeHostname() { hostname=$1 #echo "change the hostname $1" egrep "^HOSTNAME=" /etc/sysconfig/network >& /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ] then #存在则删除旧的hostname sed -i "/^HOSTNAME=/d" /etc/sysconfig/network fi #添加新的hostname echo "HOSTNAME=$hostname" >> /etc/sysconfig/network #echo "change the hostname $1 successfully" } #获取参数 node=$1 if [ -z $node ] then echo "参数为空,请输入参数node1,node2,node3..." else changeHostname $node fi
以root用户执行如下命令,$hostname为参数传值,设为node1、node2、node3....
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/changeHostname.sh $hostname
2.3 host配置文件修改
addClusterIps.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash #添加Ip、hostname到/etc/hosts文件里面 function addIpToHostFile() { ip=$1 hostname=$2 #查询$ip是否存在于/etc/hosts里面 egrep "^$ip" /etc/hosts >& /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ] then #$?是上一个程序执行是否成功的标志,如果执行成功则$?为0,否则不为0,存在则先把就的ip设置删除掉 sed -i "/^$ip/d" /etc/hosts fi #把ip、hostname添加到/etc/hosts中 echo "$ip $hostname" >> /etc/hosts } #执行ssh免密登录之前,hosts文件里面需要存储每台机器的ip地址 function editHostFile() { #echo "edit the host file" #1./home/hadoop/host_ip.txt文件中读取ip和hostname while read line do #提取文件中的ip ip=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f1` #提取文件中的用户名 hostname=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f2` addIpToHostFile $ip $hostname done < /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/host_ip.txt #读取存储ip的文件 #echo "edit the host file successfully" } editHostFile
以root用户执行命令:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/addClusterIps.sh
2.4 关闭防火墙、SELINUX
closeFirewall.sh命令如下:
#! /bin/bash function closeFirewallAndGetenforce() { #1.关闭防火墙 firewallStatus=`firewall-cmd --state` if [[ $firewallStatus = "running" ]] then systemctl stop firewalld.service &&systemctl disable firewalld.service fi #2.关闭getenforce getenforceStatus=`getenforce` egrep "^SELINUX=enforcing" /etc/selinux/config >& /dev/null if [[ $getenforceStatus = "Enforcing" || $? -eq 0 ]] then sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config fi #3.重启,使设置生效 #reboot } function startFirewallAndGetenforce() { #1.开启防火墙 firewallStatus=`firewall-cmd --state` if [[ $firewallStatus != "running" ]] then systemctl enable firewalld.service && systemctl start firewalld.service fi #2.开启getenforce getenforceStatus=`getenforce` egrep "^SELINUX=disabled" /etc/selinux/config >& /dev/null if [[ $getenforceStatus = "Disabled" || $? -eq 0 ]] then sed -i 's/^SELINUX=disabled/SELINUX=enforcing/' /etc/selinux/config fi #3.重启,使设置生效 #reboot } operate=$1 if [ -z $operate ] then echo "参数为空,请输入参数close或start" else if [[ $operate = "close" ]] then closeFirewallAndGetenforce fi if [[ $operate = "start" ]] then startFirewallAndGetenforce fi fi
这里提供开启和关闭防火墙两种功能,方便操作。以root用户执行该shell命令时,需要输入参数close或start:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/closeFirewall.sh close
2.5 添加系统bigdata用户
autoCreateUser.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash #创建bigdata用户组,创建bigdata用户并设置密码 function createUserAndGroup() { echo "start to create user 'bigdata'!" user=$1 group=$2 #create group if not exists #在/etc/group中查找用户组是否存在,并把错误输出输到/dev/null中 egrep "^$group" /etc/group >& /dev/null # 判断上一命令是否等于0,不等于则创建用户组 if [ $? -ne 0 ] then groupadd $group fi #create user if not exists egrep "^$user" /etc/passwd >& /dev/null if [ $? -ne 0 ] then useradd -g $group $user fi #在shell中使用expect实现自动输入密码,通常需要与'expect <<EOF EOF'、spawn、子expect一起使用 expect << EOF spawn passwd $user expect "New password:" send "${user}\r" expect "Retype new password:" send "${user}\r" expect eof; EOF } #删除bigdata用户,删除bigdata用户组 function deleteUserAndGroup() { user=$1 group=$2 echo "delete the user:" $user " and the userGroup:" $group userdel -r $user if [ $user != $group ] then groupdel $group fi } operate=$1 if [ -z $operate ] then echo "参数为空,请输入参数create或delete" else if [[ $operate = "create" ]] then createUserAndGroup bigdata bigdata fi if [[ $operate = "delete" ]] then deleteUserAndGroup bigdata bigdata fi fi
这里提供创建、删除用户两种操作,以root用户执行该命令需要输入参数create或者delete:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/autoCreateUser.sh create
2.6 配置yum源
由于大数据平台一般是在内网环境下搭建的,所以需要配置本地yum源,用以解决一些依赖包缺少的问题,这里以node1节点作为本地yum源所在的服务器,以CentOS-7.0-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso作为yum源的source。
configureYum.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash #配置yum源 function configureYumSource() { yumUrl=$1 yumFile=$2 #1.把CentOS-Media.repo文件非#开头的行注释掉 sed -i 's/^[^#]/#&/' $yumFile #2.配置本地源 echo "[base]" >> $yumFile echo "name=CentOS-Local" >> $yumFile echo "baseurl=$yumUrl" >> $yumFile echo "gpgcheck=0" >> $yumFile echo "enabled=1" >> $yumFile echo "gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7" >> $yumFile #3.清除YUM缓存 yum clean all > /dev/null 2>&1 #4.列出可用的YUM源 yum repolist > /dev/null 2>&1 } #处理并保证只有一个CentOS-Media.repo文件存在 function doWithRepoFile() { #1.进入到yum.repos.d目录 cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ #2.查找/etc/yum.repos.d/目录下是否存在.repo结尾的文件,存在则重命名为.repo.bak结尾的 fileResult=`find /etc/yum.repos.d/ -name "*.repo"` for file in $fileResult do onlyFile=`find /etc/yum.repos.d -wholename $file.bak` if [[ -z $onlyFile ]] then mv $file $file.bak fi done #3.只创建一个.repo文件用于配置本地yum源 result=`find /etc/yum.repos.d/ -name CentOS-Media.repo.bak` if [[ -z $result ]] then touch CentOS-Media.repo else cp CentOS-Media.repo.bak CentOS-Media.repo fi } ############################################################################# #同一函数及其调用的子函数,父函数与子函数均有一样的变量名,而内容不一样会报错 ############################################################################# #配置本地源 function localYumSource() { systemUrl=$1 ip=$2 yumFile=/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Media.repo #1.不存在则创建mount的目录 if [ ! -d /var/iso ] then mkdir /var/iso fi #挂载系统,已挂载则不再次挂载 if [ ! -d /var/iso/CentOS_BuildTag ] then mount -o loop $systemUrl /var/iso fi #2.处理并保证只有一个CentOS-Media.repo的文件用于配置本地yum源 doWithRepoFile #3.配置yum源 configureYumSource file:///var/iso $yumFile #4.安装相应的软件 httpdIsExists=`rpm -qa | grep http` if [[ -z $httpdIsExists ]] then yum install -y httpd fi #5.开启httpd使用浏览器访问 #service httpd start httpdStatus=`systemctl status httpd.service` result=$(echo $httpdStatus | grep "Active: active (running)") if [[ $result = "" ]] then systemctl start httpd.service fi #6.将YUM源配置到httpd中,其他的服务器可通过网络访问这个内网中的YUM源 httpUrl=/var/www/html/CentOS-7.0 if [ ! -e $httpUrl/lock ] then cp -r /var/iso $httpUrl echo "lock" >> $httpUrl/lock fi #7.取消先前挂载的镜像 强制取消,哈哈哈哈 umount -fl /var/iso #8.修改yum源指向的地址 sed -i 's/^baseurl\=file:\/\/\/var\/iso/baseurl\=http:\/\/'$ip'\/CentOS-7.0/' $yumFile #9.清除YUM缓存 yum clean all > /dev/null 2>&1 #10.列出可用的YUM源 yum repolist > /dev/null 2>&1 #echo "create the local yum source successfully" } #配置远程yum源 function remoteYumSource() { ip=$1 yumUrl=http://$ip/CentOS-7.0 yumFile=/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Media.repo #1.处理并保证只有一个CentOS-Media.repo的文件用于配置yum源 doWithRepoFile #2.配置yum源 configureYumSource $yumUrl $yumFile } hostname=$1 if [[ $hostname = "node1" ]] then localYumSource /opt/system/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1804.iso 192.168.187.201 else remoteYumSource 192.168.187.201 fi
以root用户执行代码如下,参数$hostname一般为node1、node2、node3:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureYum.sh $hostname
2.7 配置SSH无密码登录
sshFreeLogin代码如下:
#! /bin/bash function sshFreeLogin() { #1.检测expect服务是否存在,不存在则使用yum安装expect expectIsExists=`rpm -qa | grep expect` if [ -z $expectIsExists ] then yum -y install expect fi #2.密钥对不存在则创建密钥 [ ! -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub ] && ssh-keygen -t rsa -P "" -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa while read line;do #提取文件中的ip hostname=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f2` #提取文件中的用户名 user_name=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f3` #提取文件中的密码 pass_word=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f4` expect <<EOF #复制公钥到目标主机 spawn ssh-copy-id $hostname expect { #expect实现自动输入密码 "yes/no" { send "yes\n";exp_continue } "password" { send "$pass_word\n";exp_continue } eof } EOF # 读取存储ip的文件 done < /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/host_ip.txt } sshFreeLogin
以root用户执行代码如下:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/sshFreeLogin.sh
2.8 配置JDK环境
configureJDK.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash function configureJDK() { #1.在frames.txt中查看是否需要安装java javaInfo=`egrep "^jdk" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/frames.txt` java=`echo $javaInfo | cut -d " " -f1` isInstall=`echo $javaInfo | cut -d " " -f2` #是否安装 if [[ $isInstall = "true" ]];then #2.查看/opt/frames目录下是否有java安装包 javaIsExists=`find /opt/frames -name $java` if [[ ${#javaIsExists} -ne 0 ]];then if [ -d /usr/lib/java ];then rm -rf /usr/lib/java fi mkdir /usr/lib/java && chmod -R 777 /usr/lib/java #2.解压到指定文件夹/usr/lib/java中 echo "开启解压jdk安装包" tar -zxvf $javaIsExists -C /usr/lib/java >& /dev/null echo "jdk安装包解压完毕" java_home=`find /usr/lib/java -maxdepth 1 -name "jdk*"` #3.在/etc/profile配置JAVA_HOME profile=/etc/profile sed -i "/^export JAVA_HOME/d" $profile echo "export JAVA_HOME=$java_home" >> $profile #4.在/etc/profile配置PATH sed -i "/^export PATH=\$PATH:\$JAVA_HOME\/bin/d" $profile echo "export PATH=\$PATH:\$JAVA_HOME/bin" >> $profile sed -i "/^export CLASSPATH=.:\$JAVA_HOME/d" $profile echo "export CLASSPATH=.:\$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:\$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar" >> $profile #5.更新/etc/profile文件 source /etc/profile && source /etc/profile else echo "/opt/frames目录下没有jdk安装包" fi else echo "/opt/frames目录下没有jdk安装包" fi } configureJDK
以root用户执行代码如下:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureJDK.sh
2.9 配置Scala环境
configureScala.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash function configureScala() { #1.在frames.txt中查看是否需要安装scala scalaInfo=`egrep "^scala" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/frames.txt` scala=`echo $scalaInfo | cut -d " " -f1` isInstall=`echo $scalaInfo | cut -d " " -f2` #是否安装 if [[ $isInstall = "true" ]];then #1.查找/opt/frames目录下是否有Scala安装包 scalaIsExists=`find /opt/frames -name $scala` if [[ ${#scalaIsExists} -ne 0 ]];then if [ -d /usr/lib/scala ];then rm -rf /usr/lib/scala fi mkdir /usr/lib/scala && chmod -R 777 /usr/lib/scala #2.解压到指定文件夹/usr/lib/scala中 echo "开始解压scala安装包" tar -zxvf $scalaIsExists -C /usr/lib/scala >& /dev/null echo "scala安装包解压完毕" scala_home=`find /usr/lib/scala -maxdepth 1 -name "scala-*"` #3.在/etc/profile配置SCALA_HOME profile=/etc/profile sed -i "/^export SCALA_HOME/d" $profile echo "export SCALA_HOME=$scala_home" >> $profile #4.在/etc/profile配置PATH sed -i "/^export PATH=\$PATH:\$SCALA_HOME\/bin/d" $profile echo "export PATH=\$PATH:\$SCALA_HOME/bin" >> $profile #5.更新/etc/profile文件 source /etc/profile && source /etc/profile else echo "/opt/frames目录下没有scala安装包1" fi else echo "/opt/frames目录下没有scala安装包2" fi } configureScala
以root用户执行代码如下:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureScala.sh
3.0 集群模块整合自动化部署安装
3.1 单机上整合第2点的9个模块自动化批量执行
batchOperate.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash hostname=$1 #1.ip地址修改,目前只能每台机器独自修改ip地址 echo "1.ip地址修改暂无" #2.修改机器名hostname echo "2.修改hostname为node1" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/changeHostname.sh $hostname #3.host配置文件修改 echo "3.把集群ip及其映射的hostname添加到/etc/hosts中" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/addClusterIps.sh #4.关闭防火墙、SELINUX ,需要输入参数close或start echo "4.关闭防火墙、SELINUX" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/closeFirewall.sh close #5.添加bigdata用户名 ,需要输入参数create或delete echo "5.添加bigdata用户名" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/autoCreateUser.sh create #6.配置yum源 echo "6.配置yum源" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureYum.sh $hostname #7.配置SSH无密码登录 echo "7.集群各节点之间配置SSH无密码登录" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/sshFreeLogin.sh #8.配置JDK环境 echo "8.配置jdk环境" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureJDK.sh #9.配置SCALA环境 echo "9.配置scala环境" /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/configureScala.sh echo ""
以root用户执行代码如下,参数$hostname一般为node1、node2、node3::
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/batchOperate.sh $hostname
在一台机器上执行以上命令,可以迅速设置该台机器的系统环境。但是如果集群机器过多,则需要每台机器都要执行batchOperate.sh,所以需要3.2点在集群上一次性部署整个集群上机器的系统环境,而不需要每台机器都重复部署。
3.2 集群上自动化部署安装
这里以node1为基点,集群上的所有操作触发点都在node1上,操作原理为:在clusterOperate.sh代码里,node1上本地执行batchOperate.sh设置本地机器的系统环境,而利用ssh远程执行batchOperate.sh设置远程机器的系统环境。
clusterOperate.sh代码如下:
#! /bin/bash function clusterOperate() { #1.远程复制文件 while read line; do hostname=`echo $line | cut -d " " -f2` echo "目前正在设置$hostname节点的系统环境" #默认node1为本地主机 if [[ $hostname = "node1" ]] then #2.本地主机操作 /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/batchOperate.sh $hostname else #3.远程主机操作 if ssh -n $hostname test -e /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy then #3.1 存在则先删除旧的 ssh -n $hostname "rm -rf /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy" fi #3.2 把本地的automaticDeploy里面的脚本文件复制到远程主机上 scp -r /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/ $hostname:/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy #3.3 把本地的/opt/frames里的软件安装包复制到远程主机的/opt/frames上 #判断远程主机上/opt/frames是否存在,不存在则创建 if ssh -n $hostname test -e /opt/frames/;then echo "存在" > /dev/null else ssh -n $hostname "mkdir /opt/frames" fi #遍历需要安装的软件 while read lineString; do software=`echo $lineString | cut -d " " -f1` isInstall=`echo $lineString | cut -d " " -f2` if [[ $isInstall = "true" ]];then if ssh -n $hostname test -e /opt/frames/$software;then echo "存在" > /dev/null else scp /opt/frames/$software $hostname:/opt/frames/$software fi fi done < /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/frames.txt #4.远程执行文件 ssh -n $hostname /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/batchOperate.sh $hostname fi done < /home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/host_ip.txt } clusterOperate
在node1节点上,以root用户执行clusterOperate.sh,一次性部署集群三个节点的系统环境:
/home/hadoop/automaticDeploy/systems/clusterOperate.sh
到此,集群中每台机器的环境自动化设置完成,下一篇介绍如何自动化部署大数据组件hadoop、spark、hbase、hive、kafka等等。
所有shell文件代码存放在github上,代码可能写得不是很完美,欢迎指出错误。
github地址为:https://github.com/SwordfallYeung/BigData_AutomaticDeploy
参考资料:
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/502381951517702724.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34685846/article/details/72825587
https://www.cnblogs.com/cute/archive/2011/08/26/2154137.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/mark-zhou/p/5976222.html
https://blog.csdn.net/kinger0/article/details/52251847
https://blog.csdn.net/wyl9527/article/details/72831567
https://blog.csdn.net/hello_hwc/article/details/40118129
http://www.codebelief.com/article/2017/02/26-examples-of-find-command-on-linux/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号