Linux find命令汇总大全和举例
一、find命令语法格式:
find [路径] [选项] [操作]
选项参数对照表:
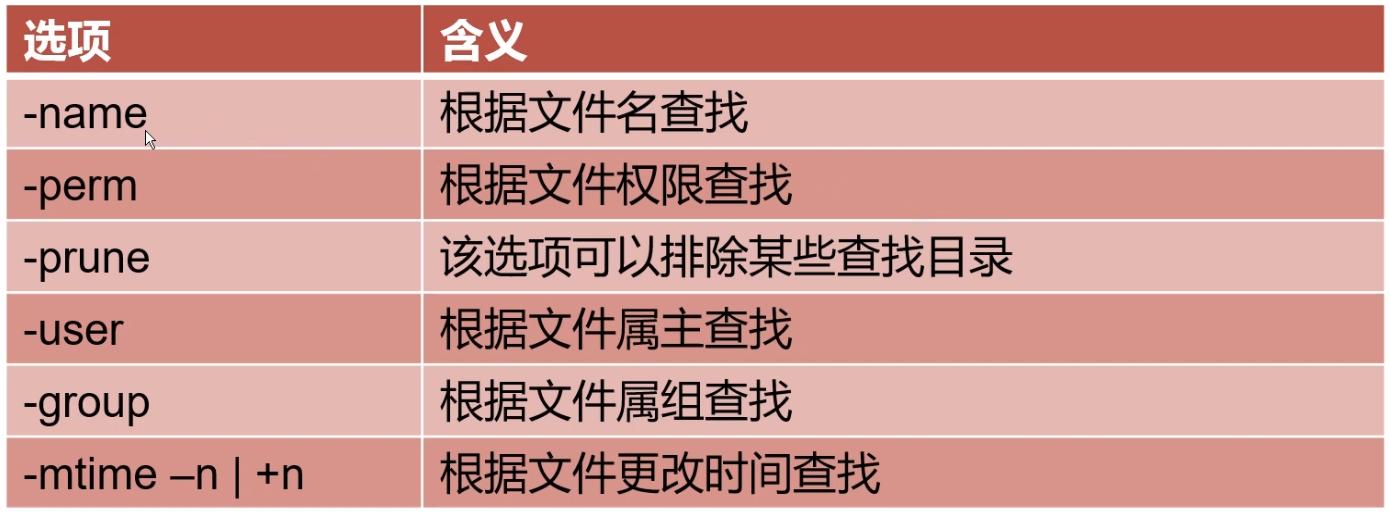
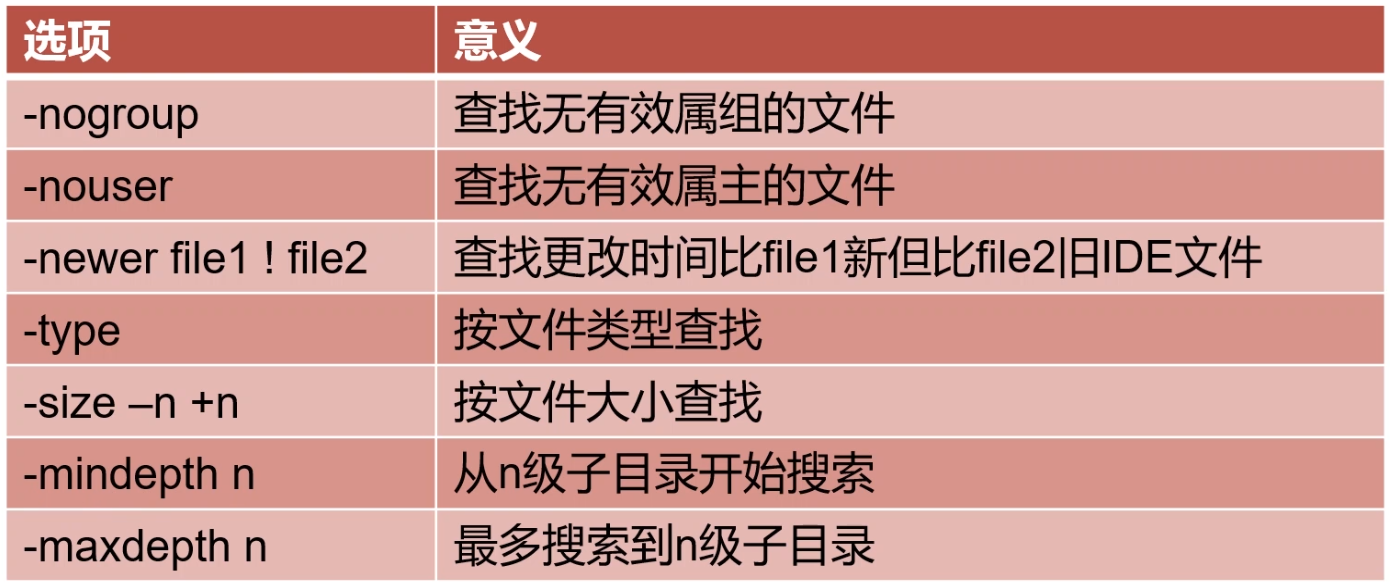
三、常用选项
-name 查找 /etc 目录下以 conf 结尾的文件,文件名区分大小写,例如:find /etc -name '*.conf'
-iname 查找当前目录下所有文件名为 aa 的文件,文件名不区分大小写,例如:find . -name aa
-user 查找文件所属用户为 zhangsan 的所有文件,例如:find . -user zhangsan
-group 查找文件所属组为 dev 的所有文件,例如:find . -group dev
-type 根据类型查找:如下
f 文件 find . -type f
d 目录 find . -type d
c 字符设备文件 find . -type c
b 块设备文件 find . -type b
l 链接文件 find . -type l
p 管道文件 find . -type p
-size 根据文件大小查询
-n 小于 大小为 n 的文件
+n 大于 大小为 n 的文件
举例1:查找 /ect 目录下,小于 10000 字节的文件。 find /etc -size +10000c
举例2:查找 /etc 目录下,大于 1M 的文件。find /etc -size -1M
-mtime
-n n 天以内修改的文件。
+n n 天以外修改的文件。
n 正好 n天 修改的文件
举例1: 查询 /etc 目录下,5天以内修改 且以 conf 结尾的文件。 find /etc -mtime -5 -name '*.conf'
举例2: 查询 /etc 目录下,10天之前修改,且属于 yangyang 的文件。 find /etc -mtime +10 -user yangyang
-mmin
-n n 分钟以内修改过的文件
+n n 分钟之前修改过的文件
举例1: 查询 /etc 目录下 30分钟 之前修改过的文件。 find /etc -mmin +30
举例1: 查询 /etc 目录下 30分钟 之前修改过的目录。 find /etc -mmin -30 -type d
-mindepth n 从第 n 级目录开始搜索
举例:从 /etc 的第三级子目录开始搜索。 find /etc -mindepth 3
-maxdepth n 表示至多搜索到第 n-1 级子目录。
举例1: 在 /etc 中搜索符合条件的文件,但最多搜索到 2级 子目录。 find /etc -maxdepth 3 -name '*.conf'
举例2: find /etc -type f -name '*.conf' -size +10k -maxdepthc 2
四、不常用选项
-nouser 查询没有所属用户的文件
举例:find /etc -type f -nouser
-nogroup 查询没有所属组的文件
举例:find /etc -type f -nogroup
-perm 根据权限查询
举例:find /etc -perm 664
-prune 通常和 -path 一起使用,用于将特定目录排除在搜索条件之外。过滤条件写在其他条件前面。
举例1:查找当前目录下的所有普通文件,但排除 test目录。
find . -path ./test -prune -o -type f
举例2: 查找当前目录下所有普通文件,但排除 test目录 和 opt目录。
find . -path ./test -prune -o -path ./opt -prune -o -type f
举例3: 查找当前目录下所有普通文件,但排除 test目录 和 opt目录,但属主为 yangyang
find . -path ./test -prune -o -path ./opt -prune -o -type f -a -user yangyang
举例4: 查找当前目录下所有普通文件,但排除 test目录 和 opt目录,但属主为 yangyang,且文件大小必须大于 500字节
find . -path ./test -prune -o -path ./opt -prune -o -tyep f -a -user yangyang -a -size +500
-newer file1
举例:查找当前目录下比 a 文件要新的文件。 find . -newer a
五、操作查找到的文件
-print 打印输出。 默认的选项,即打印出找到的结果。
-exec 对搜索到的文件执行特定的操作,固定的格式为:-exec 'commond' {} \; 注意:{} 表示查询的结果。
举例1: 搜索 /etc 目录下的文件(非目录),文件以 conf 结尾,且大于 10k,然后将其删除。
find /etc -type f -name '*.conf' -size +10k -exec rm -f {} \;
举例2: 将 /data/log/ 目录下以 .log 结尾的文件,且更改时间在 7 天以上的删除。
find /data/log -name '*.log' -mtime +7 -exec rm -f \;
举例3: 搜索条件同 例1 一样,但是不删除,只是将其复制到 /root/conf 目录下
find /etc -type f -name '*.conf' -size +10k -exec cp {} /root/conf/ \;
-ok 和 -exec 的功能一样,只是每次操作都会给用户提示。
六、逻辑运算符
-a 与 (默认情况查询条件之间都是 与 的关系)
-o 或
-not | ! 非
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「linjun20」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/linjun20/article/details/119632446


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号